Male Infertility
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
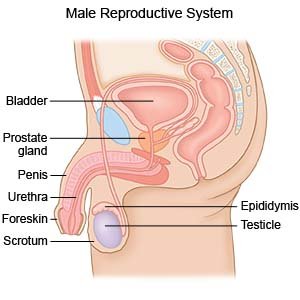
What is male infertility?
Male infertility means your female partner is not pregnant after 1 year of unprotected sex. You may not be physically able to get your partner pregnant. Subfertility means you are physically able, but your partner has not yet become pregnant. Pregnancy may still happen, but it is less likely without medical help.
 |
How is the causes of male infertility diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may ask about your health history. Tell your provider if you fathered any children or if you and your partner have tried assisted reproductive therapy. Also tell your provider if your partner has lost any pregnancies. Your provider will also do a physical exam. You may also need any of the following:
- Blood tests are used to check your hormone levels.
- Semen may be checked for problems that can affect sperm movement and function. Your urine may be checked for sperm. Sperm in your urine may mean you have a blockage or other problem.
- X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI pictures may show a problem or infection with your reproductive organs. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. The MRI machine uses a powerful magnet. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet.
How is male infertility treated?
The treatment depends on the cause:
- Medicine may be given to treat an infection of the reproductive system. Testosterone may be given if your level is too low. Steroids may be used to treat infertility caused by a problem in the immune system.
- Percutaneous embolization is a procedure to treat a varicocele. The blood flow in the enlarged veins is blocked to stop the flow of blood.
- Sperm extraction is a procedure to remove sperm from the testicles or epididymis if you have a blockage. The collected sperm may be saved or used to fertilize your partner's egg.
- Assisted reproductive technology (ART) can be done in several ways. An unfertilized egg may be placed into your partner's fallopian tube along with sperm. This allows fertilization to happen inside your partner's body. Eggs may be removed and fertilized by sperm outside your partner's body. Then the fertilized eggs (embryos) are put back into the uterus or fallopian tubes.
- Surgery may be done to repair a blockage in the sperm duct or remove a tumor.
What can I do to increase my fertility?
- Create a healthy lifestyle. Talk to your healthcare provider about a healthy weight for you. Extra body weight increases your risk for infertility. Healthcare providers can help you create healthy meal and exercise plans, if needed. Do not drink alcohol, smoke cigarettes, or use illegal drugs. Any of these can cause infertility. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you need help quitting.
- Ask about ways to manage stress. Stress can make infertility problems worse. Stress can become worse the longer infertility continues. Try to find ways to help yourself relax. A regular sleep schedule can also help lower stress. Talk to your provider if you continue to have problems managing stress.
- Do not let your testicles get too warm. Warmth can kill sperm. Hot tubs and tight underwear are common causes of overheating. Tight underwear pulls your testicles up where they are affected by body heat. You may need to use a different kind of underwear, such as boxers. Do not sit in hot tubs while you and your partner are trying to conceive.
Where can I find support and more information?
- American Academy of Family Physicians
11400 Tomahawk Creek Parkway
Leawood , KS 66211-2680
Phone: 1- 913 - 906-6000
Phone: 1- 800 - 274-2237
Web Address: http://www.aafp.org
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine
1209 Montgomery Highway
Birmingham , AL 35216-2809
Phone: 1- 205 - 978-5000
Web Address: http://www.asrm.org
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
