Intravenous Chemotherapy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
IV chemo is medicine used to shrink a tumor or kill cancer cells. IV chemo is injected into your blood through an IV. Chemo can help cure cancer, prevent cancer from spreading, and relieve symptoms caused by cancer. You may be given 1 or more types of chemo. You may get chemo at home, in your healthcare provider's office, in a clinic, or in a hospital.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have chest pain, shortness of breath, or trouble breathing.
- Your throat feels swollen and you have trouble swallowing or breathing.
- You cough up blood.
- You have arm or leg weakness, trouble walking, or trouble seeing.
- You have blood in your urine or bowel movement.
- You vomit blood.
Seek care immediately if:
- You feel confused or have a severe headache that does not go away.
- You have pain where your IV was or at your catheter site.
- Your arm or leg feels warm, painful, or looks bigger than usual.
- You urinate a lot less than usual or stop urinating.
- You feel weak, dizzy, or faint.
- Your heart is beating faster than usual.
Call your doctor or oncologist if:
- You have a fever of 100.5°F (38°C) or higher or chills.
- You have bleeding from your gums.
- You have white spots or sores in your mouth.
- You have bruises on your body that are not caused by an injury or fall.
- You feel depressed.
- You have a cough that lasts more than a few days.
- You have diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting that lasts more than 2 days.
- You have frequent, painful urination.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Side effects of chemo:
Chemo can damage healthy cells in your digestive system, bone marrow, and mouth. Chemo may also attack your hair follicles. This attack or damage is what causes side effects. You may or may not have side effects from chemo. Your healthcare provider may give you medicine to prevent certain side effects. Side effects may depend on the type of chemo that you are given. Common side effects of chemo include the following:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Hair loss, including loss of eyelashes, eyebrows, and body hair
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation
- Poor appetite or changes in taste
- Neuropathy (numbness, tingling, or pain) in your hands or feet that may go away between doses or worsens as treatment continues
- Problems with memory or concentration
- Dry skin, changes in skin color, or easy bruising
- Weight loss or gain
Medicines
Show your healthcare provider a list of everything that you currently take. Ask him or her if it is safe for you to take your regular medicines, vitamins, or supplements during chemo. Certain medicines or vitamins may prevent chemo from working correctly. You may also need any of the following:
- Medicines may be given to help manage side effects of chemotherapy. This may include medicines to decrease nausea and vomiting, or to manage pain.
- Antivirals may be given to prevent a hepatitis B infection, or to prevent an infection from becoming active again.
- An antidepressant may be given to treat peripheral neuropathy (a nerve disorder) caused by chemo.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Rest as needed. You may feel tired for a few days after getting chemo. Return to activities slowly. Do more as you feel stronger.
- Eat healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Several small meals a day may be easier to eat than a few large meals.

- Drink plenty of liquids. Liquids will help prevent dehydration from vomiting or diarrhea. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
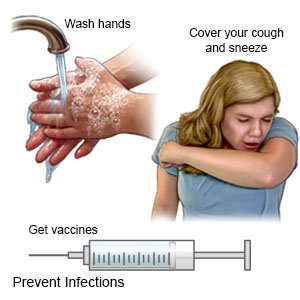
- Prevent infection. Stay away from people who are sick. Wash your hands frequently and ask visitors to wash their hands. Ask family and friends not to visit if they are sick. Do not spend time in crowded places such as movie theaters, malls, or elevators. Ask your healthcare provider if you need vaccines.
- Manage hair loss. Use mild shampoos if your hair begins to thin or fall out. Use a soft bristled brush to comb your hair. If you lose your hair, wash your scalp with moisturizing shampoos or conditioners. Apply lotion and massage your scalp after a shower. Use sunscreen, a hat, a scarf, or a wig to protect your scalp from the sun. Ask your healthcare provider where you can purchase a wig or hair piece.
- Work with your healthcare provider to manage side effects. Always tell your healthcare provider if you have side effects. Take medicines that manage side effects as directed. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on how to manage certain side effects.
Follow up with your doctor or oncologist as directed:
You will need to see your oncologist for ongoing tests and treatment. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
For more information and support:
It may be difficult for you and your family to go through cancer and cancer treatments. Join a support group or talk with others who have gone through treatment.
- American Cancer Society
250 Williams Street
Atlanta , GA 30303
Phone: 1- 800 - 227-2345
Web Address: http://www.cancer.org
- National Cancer Institute
6116 Executive Boulevard, Suite 300
Bethesda , MD 20892-8322
Phone: 1- 800 - 422-6237
Web Address: http://www.cancer.gov
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
