Intrauterine Device
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is an intrauterine device (IUD)?
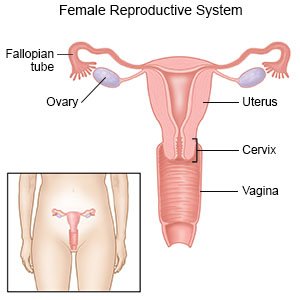
An IUD is a type of birth control that is inserted into your uterus. It is a small, flexible piece of plastic with a string on the end. It is inserted and removed by your healthcare provider. IUDs prevent sperm from reaching or fertilizing an egg. IUDs also prevent a fertilized egg from attaching to the uterus and developing into a fetus.
 |
What are the most common types of IUDs?
Your healthcare provider will recommend the type of IUD that is right for you. This is based on your age and if you have had a child. If you have not had a child, a smaller IUD will be used.
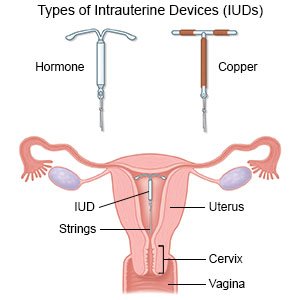 |
- A copper IUD slowly releases a small amount of copper into your uterus. This IUD can remain in place for up to 10 years.
- A hormone-releasing IUD slowly releases a small amount of progesterone into your uterus. Progesterone is a hormone that is made by your body to help control your periods. This IUD can remain in place for 3 to 5 years.
What are the advantages of an IUD?
- An IUD is 98% to 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
- The IUD can be removed by your healthcare provider if you decide to have a baby. You may be able to get pregnant as soon as the IUD is removed.
- An IUD protects you from pregnancy right after it is inserted.
- You do not have to stop sexual activity to insert it. You do not have to remember to take your birth control pill.
- Copper IUDs are safer for some women than oral birth control pills. Examples include women who smoke or have a history of blood clots.
- Hormone-releasing IUDs may decrease certain health problems. Examples include bleeding and cramping that happen with your monthly period.
What are the disadvantages of an IUD?
- There is a small chance that you could get pregnant. Sometimes the IUD cannot be removed after you get pregnant. This increases your risk of a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy is when the fertilized egg starts to grow somewhere other than your uterus.
- An IUD does not protect you from sexually transmitted infections.
- You may have cramps during the first weeks after you get the IUD.
- A copper IUD may cause your monthly period to be heavier or more painful. This is more common within the first 3 months after you get the IUD. You may need to have your IUD removed if your bleeding or pain becomes severe. You may have spotting between periods.
- There is a small risk of an infection within the first 20 days after the IUD is placed. Infection can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease. This can cause infertility.
- Your uterus may tear when the IUD is inserted. The IUD may slip part or all of the way out of your uterus.
How is the IUD inserted?
- The IUD is usually inserted during your monthly period. This may help decrease the amount of discomfort you have during the procedure. It also helps make sure that you are not pregnant. You will be asked to lie down and place your feet in stirrups. Your healthcare provider will gently insert a speculum into your vagina. This is the same tool used during a Pap smear. The speculum allows your healthcare provider to see inside your vagina to your cervix. The cervix is the opening of your uterus.
- Your healthcare provider will clean your cervix with an antiseptic solution to prevent infection. You may be given numbing medicine. A long plastic tube is gently passed through your cervix and into your uterus. This tube has the IUD inside of it. The IUD is pushed out of the tube and into your uterus. You may have cramps as the IUD is inserted. The tube is removed after the IUD is in place.
How can I make sure my IUD is still in place?
An IUD has a string made of plastic thread. One to 2 inches of this string hangs into your vagina. You cannot see this string, and it should not cause problems when you have sex. Check your IUD string every 3 days for the first 3 months after it is inserted. After that, check the string after each monthly period. Do the following to check the placement of your IUD:
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water. Dry them with a clean towel.
- Bend your knees and squat low to the ground.
- Gently put your index finger inside your vagina. The cervix is at the top of the vagina and feels like the tip of your nose. Feel for the IUD string. Do not pull on the string. You should not be able to feel the firm plastic of the IUD itself.
- Wash your hands after you check your IUD string.
Where can I find more information?
- Planned Parenthood Federation of America
434 West 33rd St.
New York City , NY 10001
Phone: 1- 800 - 230-7526
Web Address: http://www.plannedparenthood.org
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have severe pain or bleeding during your period.
- You have a fever and severe abdominal pain.
When should I call my doctor?
- You think you are pregnant.
- The IUD has come out.
- You have bleeding from your vagina after you have sex, and it is not your period.
- You have pain during sex.
- You cannot feel the IUD string, the string feels longer, or you feel the plastic of the IUD itself.
- You have vaginal discharge that is green, yellow, or has a foul odor.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
