Intragastric Balloon (Igb) Procedure for Weight Loss
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What do I need to know about an IGB procedure?
- The IGB procedure uses a balloon that is placed down your throat into your stomach. Placement of the balloon may be through endoscopy, a tube with a light and camera at the end. You may instead swallow a capsule that contains the balloon. The balloon is filled with saline or a gas that causes you to feel full quicker and be less hungry. The balloon takes up space in your stomach and causes food to move through slower than normal.
- You may need more than 1 balloon depending on the type you receive. Some balloons are adjustable so more fluid can be added. The balloon is left in your stomach between 4 and 6 months. IGB is less invasive than other weight loss surgeries. After the procedure, you will follow a supervised 12-month diet and exercise plan and see your weight loss team monthly.
How do I prepare for an IGB procedure?
First you must be able to lose some weight on your own with lifestyle changes. Changes include food choices and physical activity. You will need to be evaluated by a team including a bariatric doctor, dietician, and psychologist. You will have an endoscopy to check for any problems in your esophagus, stomach, and small intestines. Ulcers in your esophagus or stomach, or a large hiatal hernia can prevent you from having the procedure.
- Days before your procedure:
- Arrange to have someone drive you home and stay with you for 24 hours after your procedure.
- You will be given prescriptions for anti-nausea and acid reflux medicines. Make sure you have prescriptions filled before your procedure.
- The day before your procedure: You will be told not to eat 12 hours before your procedure. You may be told not to drink 6 hours before your procedure. Your surgeon will tell you which medicines are okay to take before your procedure.
What will happen during an IGB procedure?
There are 2 types of procedures for the 2 types of balloons.
- Endoscopic placement:
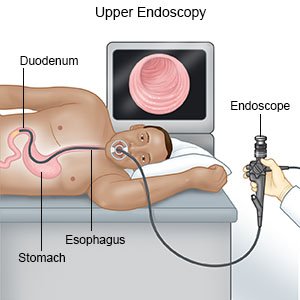
- You will be given a mild sedative. You will not feel pain, but you may feel pressure.
- The surgeon will place an endoscope in your mouth and down into your stomach. The endoscope has a light and camera on the end to help your surgeon see where the balloon will be placed.
- He or she will place the balloon through the endoscope. When the balloon is in your stomach, it is filled with saline.
- The endoscope is removed.
- Pill placement:
- Your surgeon will give you a capsule to swallow that contains the balloon.
- You will swallow the capsule and drink a cup of water.
- The surgeon will inflate the balloon with gas. A second balloon is added in 1 month. A third balloon will be added in 2 months.
What will happen after an IGB procedure?
You should be able to go home 1 to 2 hours after the procedure. You may have some cramping or pain, nausea, and vomiting after placement. These symptoms may last from a few days up to 2 weeks. This is normal. Your weight loss team will give you guidance on taking medicines for your symptoms and your eating plan. You will only be able to drink clear liquids slowly for about 3 to 7 days. You will need follow up with your weight loss team as directed for the next 12 months.
What are the risks of an IGB procedure?
Complications are very rare. Your intragastric balloon may deflate and move into your digestive system. Your balloon may be inflated too much. You may develop inflammation in your pancreas (pancreatitis). You may develop ulcers in your stomach wall. You will need surgery to remove the balloon and fix any of these problems.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
