Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
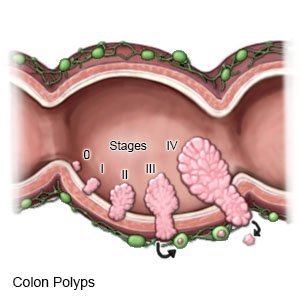
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is a condition that causes multiple polyps to develop in your digestive system. Polyps are lumps of tissue that are usually benign (not cancer). Adenomatous polyps may turn into colorectal cancer if they are not treated. FAP greatly increases your risk for colon cancer. You also have an increased risk for other types of cancer.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- You see blood in your bowel movement.
- You vomit multiple times and cannot keep any food or liquids down.
- Your pain is worse or does not go away after you take your pain medicine.
Call your doctor or gastroenterologist if:
- You have a fever.
- You cannot control your diarrhea or constipation.
- You are losing weight without trying.
- Your abdomen is swollen.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Get screened as directed:
Screening means you are checked for polyps that may be cancer before you have signs or symptoms. Your provider will tell you when screening will start. You may be screened every 1 to 3 years. Timing depends on the number and location of the polyps.
Do not smoke:
Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can damage blood vessels. This increases your risk for cancer and delays healing after surgery. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help quitting.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Limit or do not drink alcohol:
Alcohol can increase your risk for developing new polyps and cancer. It can make symptoms worse. Your provider can give you daily and weekly limits if you choose to drink. Ask your provider for information if you want to quit drinking and need help to quit.
Eat healthy foods:
Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. You may need to change what you eat during treatment. Do not eat foods or drink liquids that cause gas, such as cabbage, beans, onions, or soft drinks. Ask your provider about the best meals and snacks for you.
 |
Maintain a healthy weight:
Ask your provider what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider can help you create a weight loss plan, if needed.
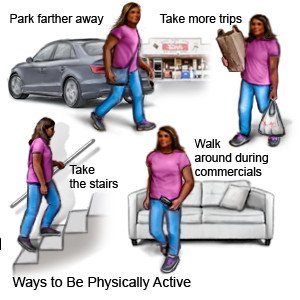
Be physically active as directed:
Ask about the best exercise plan for you. Physical activity, such as exercise, may improve your energy levels and appetite.
 |
Follow up with your doctor or gastroenterologist as directed:
You will need to see your gastroenterologist for ongoing screening tests and treatment. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Treatment options
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
