Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD)?
ETD is a condition that prevents your eustachian tubes from opening properly. It can also cause them to become blocked. Eustachian tubes connect your middle ear to the back of your nose and throat. These tubes open and allow air to flow in and out when you sneeze, swallow, or yawn.
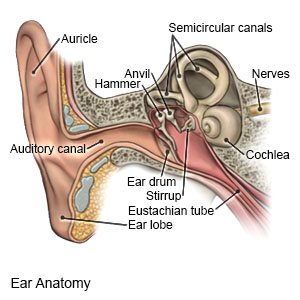 |
What causes or increases my risk for ETD?
ETD may be caused by swelling or buildup of mucus in your eustachian tubes. Pressure can build if you travel in an airplane or go scuba diving. Allergies, a cold, or a sinus infection can cause mucus to build up. The following can also increase your risk:
- Smoking cigarettes
- GERD, chronic sinus inflammation, or a tumor in your nose or throat
- An immune system disorder
- Sleeping on your stomach
- In children, long-term use of a bottle, going to daycare, or a condition such as a cleft palate
What are the signs and symptoms of ETD?
- Fullness or pressure in your ears
- Muffled hearing, or a feeling you are hearing under water or have clogged ears
- Pain in one or both ears
- Ringing in your ears
- Popping, crackling, or clicking feeling in your ears
- Trouble keeping your balance
How is ETD diagnosed?
ETD is most common in children younger than 5 years. Adults with ETD may have had it since childhood. ETD can sometimes begin in adulthood, usually because of certain medical conditions that have developed. Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and when they began. He or she will examine your ears, your nose, and the back of your throat. He or she may also do a hearing test.
How is ETD treated?
ETD may get better on its own without any treatment. If it continues, you may need any of the following:
- Swallow, yawn, or chew gum to help open your eustachian tubes. Your healthcare provider may also recommend you blow with your mouth shut and your nostrils pinched closed.
- Air pressure devices push air into your nose and eustachian tubes to help relieve air pressure in your ear.
- Treatment for allergies such as decongestants, antihistamines, and nasal steroids may improve ETD. They may help decrease swelling of the eustachian tubes.
- A myringotomy is surgery to make a hole in your eardrum. The hole relieves pressure and lets fluid drain from your ear. A pressure equalizing (PE) tube may be used to keep the hole open and to help drain fluid.
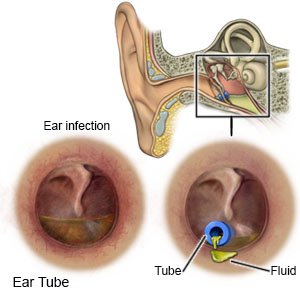
- Tuboplasty is a procedure to widen your eustachian tubes.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
When should I call my doctor?
- Your symptoms do not improve or get worse.
- You have a fever.
- You have any hearing loss.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Treatment options
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
