Esophageal Cancer
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Esophageal cancer starts in the cells that line the esophagus.
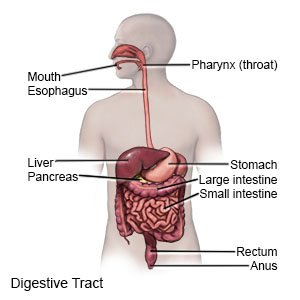 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Nutrition:
If you have trouble swallowing, you may be given foods that are soft or in liquid form. Ask your healthcare provider about any extra nutrition you may need, such as nutrition shakes. Tell your healthcare provider if you have problems eating, or you feel sick after you eat.
Medicines:
- Antinausea medicine may be given to calm your stomach and prevent vomiting.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
Tests:
- A barium swallow is an x-ray of your esophagus and stomach. You will drink a white chalky liquid called barium to help your esophagus show up better on an x-ray.
- A CT or MRI may show cancer and if it has spread. You may be given contrast liquid to help the cancer show up better. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- Endoscopy is used to examine the lining of your esophagus, stomach, and part of your small intestine. Your healthcare provider uses a small tube with a camera on the end.
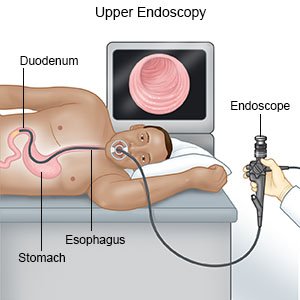
Treatment:
- Surgery may be needed to remove part of your esophagus or lymph nodes. This may help stop the cancer from spreading.
- Chemotherapy is used to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy may also be used to shrink the tumor or lymph nodes before surgery. Once the tumor is smaller, surgery can be done to remove the cancer.
- Radiation therapy is used to kill cancer cells with x-rays or gamma rays. Radiation may be given after surgery to kill cancer cells that were not removed. It may be given alone or with chemotherapy.
RISKS:
You may get a blood clot in your leg or arm. The clot may travel to your heart or brain and cause life-threatening problems, such as a heart attack or stroke. Treatment may cause pain when you eat or swallow liquids. If the cancer is not treated, it can spread to other parts of your body and be life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
