Elbow Fracture in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
An elbow fracture is a break in one or more of the bones that form your child's elbow joint.
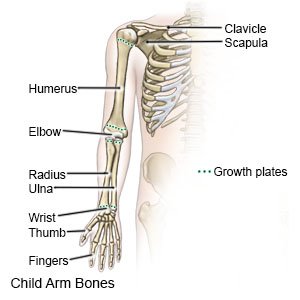 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child's elbow, arm, or fingers are numb.
- Your child's skin is swollen, cold, or pale.
Call your child's doctor if:
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child's pain gets worse, even after he or she rests and takes pain medicine.
- Your child has new or increased trouble moving his or her arm.
- Your child has new sores around the area of his or her splint or cast.
- Your child's cast or splint becomes damaged.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Medicines:
Your child may need any of the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given to your child. Ask how to give your child this medicine safely.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If your child takes blood thinner medicine, always ask if NSAIDs are safe for him or her. Always read the medicine label and follow directions. Do not give these medicines to children younger than 6 months without direction from a healthcare provider.
- Do not give aspirin to children younger than 18 years. Your child could develop Reye syndrome if he or she has the flu or a fever and takes aspirin. Reye syndrome can cause life-threatening brain and liver damage. Check your child's medicine labels for aspirin or salicylates.
- Give your child's medicine as directed. Contact your child's healthcare provider if you think the medicine is not working as expected. Tell the provider if your child is allergic to any medicine. Keep a current list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs your child takes. Include the amounts, and when, how, and why they are taken. Bring the list or the medicines in their containers to follow-up visits. Carry your child's medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage your child's symptoms:
- Elevate your child's elbow above the level of his or her heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop your child's elbow on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably. Have your child wiggle his or her fingers and open and close them to prevent hand stiffness.
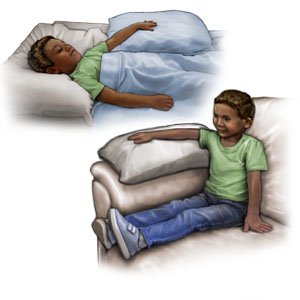
- Apply ice on your child's elbow for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you put it on your child's elbow. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
- Take your child to physical therapy as directed. A physical therapist can teach your child exercises to help improve movement and strength and to decrease pain.
Care for your child's cast or splint:
Follow instructions about when your child may take a bath or shower. It is important not to get the cast or splint wet. Cover the device with 2 plastic bags before you let your child bathe. Tape the bags to your child's skin above the device to help keep out water. Have your child keep his or her arm out of the water in case the bag breaks.
- Check the skin around your child's cast or splint daily for any redness or open skin.
- Do not let your child use a sharp or pointed object to scratch the skin under the cast or splint.
- Do not let your child push down or lean on any part of the cast, because it may break.
Follow up with your child's doctor as directed:
Your child may need to have the splint, cast, or stitches removed. He or she may need x-rays to check how well the bones are healing. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
