Diverticulosis Diet
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
A diverticulosis diet
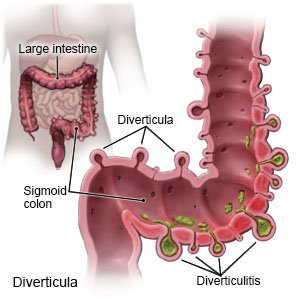
includes high-fiber foods. High-fiber foods help you have regular bowel movements. Extra fiber may decrease your risk of forming new diverticula (small pockets) in your intestine. A high-fiber diet may also help prevent diverticulitis. Diverticulitis is a painful condition that occurs when diverticula become inflamed or infected. You do not need to avoid nuts, seeds, corn, or popcorn while you are on a diverticulosis diet.
 |
Call your doctor or dietitian if:
- You have questions about a high-fiber diet.
- You have a change in your bowel movements.
- You have an upset stomach.
- You have a fever.
- You have pain in your lower abdomen on the left side.
- You have questions about your condition or care.
Amount of fiber you need:
You may need 25 to 35 grams of fiber each day. Ask your dietitian or healthcare provider how much fiber you should have. Increase your intake of fiber slowly. When you eat more fiber, you may have gas and feel bloated. You may need to take a fiber supplement if you do not get enough fiber from food. Drink plenty of liquids as you increase the fiber in your diet. Your dietitian or healthcare provider may recommend 8 eight-ounce cups or more each day. Ask which liquids are best for you.
Foods that are high in fiber:
 |
- Foods with at least 4 grams of fiber per serving:
- ⅓ to ½ cup of high-fiber cereal (check the nutrition label on the box)
- ½ cup of blackberries or raspberries
- 4 dried prunes
- 1 cooked artichoke
- ½ cup of cooked legumes, such as lentils, or red, kidney, and pinto beans
- Foods with 1 to 3 grams of fiber per serving:
- 1 slice of whole-wheat, pumpernickel, or rye bread
- 4 whole-wheat crackers
- ½ cup of cereal with 1 to 3 grams of fiber per serving (check the nutrition label on the box)
- 1 piece of fruit, such as an apple, banana, pear, kiwi, or orange
- 3 dates
- ½ cup of canned apricots, fruit cocktail, peaches, or pears
- ½ cup of raw or cooked vegetables, such as carrots, cauliflower, cabbage, spinach, squash, or corn
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
