Dental Laceration
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is a dental laceration?
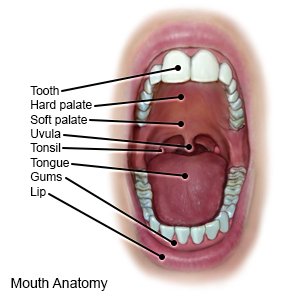
A dental laceration is a cut, gash, or tear in the soft tissue around your teeth. This can include your tongue, gums, lips, or the inside of your cheeks. Trauma is the most common cause of a dental laceration. Some examples include a car accident, a fall, or a sports injury.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of a dental laceration?
- Bleeding from your gums, lips, or mouth
- Swelling of your tongue, gums, or lips
- A tooth that is cracked, chipped, loose, out of place, or missing
- Trouble moving your jaw or mouth
How is a dental laceration diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine your mouth and ask how you were injured. Your provider will check your laceration for foreign objects, such as a piece of tooth. An x-ray or CT may show foreign objects in your laceration. You may be given contrast liquid to help the injured area show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
How is a dental laceration treated?
Treatment depends on how large and deep the laceration is, and where it is located. It also depends on whether you have damage to deeper tissues. You may need any of the following:
- Wound cleaning may be needed to remove dirt or debris. This will decrease the risk for infection. Your healthcare provider may give you medicine to numb the area and decrease pain. Your provider may also give you medicine to help you relax.
- Medicines to treat pain or prevent infection may be given. You may also be given a tetanus shot. Your provider will decide if you need a tetanus shot. Wounds at high risk for tetanus infection include wounds with dirt or saliva in them. You should get a tetanus shot within 72 hours of getting a laceration or wound. Tell your provider if you have had the tetanus vaccine or a booster within the last 5 years.
- Stitches may be needed to close the laceration in your mouth. Your provider may give you medicine to numb the area and to help you relax.
- Surgery may be needed if your laceration needs a lot of cleaning or removal of foreign objects. Surgery may also be needed if you have any broken teeth or a broken jaw.
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Care for your mouth while you heal. Use a soft toothbrush. Rinse your mouth as directed. Your healthcare provider may recommend a solution that contains chlorhexidine 0.1%. This solution will help prevent an infection caused by bacteria. Rinse 2 times each day for 1 week, or as directed.
- Eat soft foods or drink liquids for 1 week or as directed. Soft foods and liquids may be easier to eat until your injury heals. Soft foods include applesauce, pudding, mashed potatoes, gelatin, and ice cream.
- Apply ice to decrease swelling and pain. Apply ice on your jaw or cheek for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you apply it.
- Keep any soft tissue wounds clean. Use prescribed mouthwash as directed. You can also gargle with a salt water solution. To make the solution, mix 1 teaspoon of salt and 1 cup of warm water. Ask your provider for more information on how to clean your wounds.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have heavy bleeding or bleeding that does not stop after 10 minutes of holding firm, direct pressure over the wound.
- Your stitches come apart.
- You have sudden numbness in your face.
- You have severe pain.
- You cannot move part of your face.
When should I call my doctor or dentist?
- You have a fever or chills.
- You have increased swelling, redness, or bleeding.
- You have yellow or green drainage coming out of the laceration.
- You have pain that does not go away or is not helped by pain medicines.
- You have trouble opening your mouth or chewing.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
