Dcr (Dacryocystorhinostomy)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2025.
DCR is surgery to open a blocked tear duct. During surgery, a new path is created from the inner corner of your eye into your nose. This helps tears drain directly into your nose.
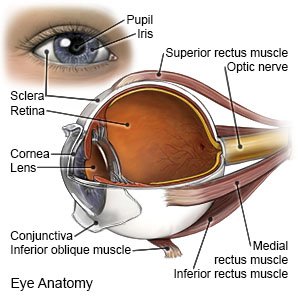 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone call if:
- You have trouble breathing.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have severe pain.
- You have red streaks on the skin around your nose or eye.
Call your surgeon if:
- Your symptoms do not improve within 1 week.
- Your nose bleeds more than you were told to expect.
- You have a fever.
- Your nose or eye is red, swollen, and draining pus.
- Your upper teeth, gum, or nose is numb.
- Your sense of smell or taste is different than before surgery.
- You have a change in your vision.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics help prevent or treat an infection. These may be given as a nasal spray, eyedrops, or a pill.
- Steroids help prevent or treat inflammation. These may be given as a nasal spray, eyedrops, or a pill.
- Decongestants help reduce nasal congestion and help you breathe more easily. These may be given as a nasal spray or a pill.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Do not blow your nose. The increase in pressure can cause your nose to bruise, swell, or bleed. Try not to sneeze. If you have to sneeze, keep your mouth open to decrease pressure in your nose.
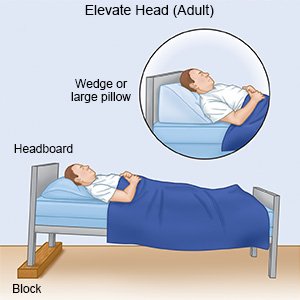
- Elevate your head and upper back. Place extra pillows under your head, neck, and shoulders when you sleep in bed. Try not to bend your neck. Elevation will help decrease swelling.
- Apply ice. Do this for 15 to 20 minutes every hour for the first day. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you apply it on your nose. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
- Rinse your nose with saline, as directed. Mix ½ teaspoon of salt and ¼ teaspoon of baking soda with 1 cup of warm distilled water. Nose rinses help remove crusts and prevent infection. Apply petroleum jelly to your nostrils after you rinse your nose. You may have gauze taped under your nostril openings. Change the gauze if it gets wet or dirty.
- Use a cool mist humidifier. A cool mist humidifier will increase air moisture in your home. This will help keep your nose and throat moist and prevent irritation.
- Limit activity for 3 days or as directed. Do not lift objects heavier than 20 pounds. Ask when you can return to your usual daily activities.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can irritate your nose and eye, and delay healing. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
Follow up with your surgeon as directed:
You may need to return to have your stitches or stents removed. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
