Chest Wall Reconstruction
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Chest wall reconstruction
is surgery to repair your chest wall. The chest wall is made of bones, cartilage, and muscles. The chest wall protects your heart and lungs and helps you breathe.
How to prepare for chest wall reconstruction:
- Your surgeon will tell you how to prepare. Your surgeon may tell you not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of your surgery. Arrange to have someone drive you home when you are discharged.
- Tell your surgeon about all your current medicines. Your surgeon will tell you if you need to start or stop any medicine for surgery, and when to do so. You may need to take a blood thinner before your surgery. You may be given antibiotics to help prevent a bacterial infection.
- Tell your surgeon about any allergies you have, including to medicines or anesthesia.
- Your surgeon will tell you if you need tests before your surgery, and when to have them.
- Your surgeon will tell you how long you may need to stay in the hospital after surgery.
What will happen during chest wall reconstruction:
- You will be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and free from pain during surgery. Your surgeon will make an incision near your chest. Your surgeon may insert a soft or hard prosthesis into your chest to create a new wall. The material used will depend on your condition.
- Your surgeon may use muscle from a different part of your body, such as your leg, to create the chest wall. A separate incision will be made. The muscle will be taken out of your body part and sewn into the new chest wall.
What to expect after chest wall reconstruction:
- You will be taken to the intensive care unit (ICU) to be monitored after surgery. Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay.
- A chest tube will be placed during surgery to drain air and extra fluid from around your lungs. The chest tube will be left in place until all the extra fluid and air are gone. Your provider will monitor how much fluid collects and decide when to remove the chest tube.
- A Foley catheter is a tube put into your bladder to drain urine into a bag. Keep the bag below your waist. This will prevent urine from flowing back into your bladder and causing an infection or other problems. Also, keep the tube free of kinks so the urine will drain properly. Do not pull on the catheter. This can cause pain and bleeding, and may cause the catheter to come out.
- Extra oxygen may be needed if your blood oxygen level is low. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils.
- Medicines may be given to prevent or relieve pain, nausea, or a bacterial infection.
- Healthcare providers may help you stand up and walk as soon as possible after surgery. Exercise may help prevent blood clots.
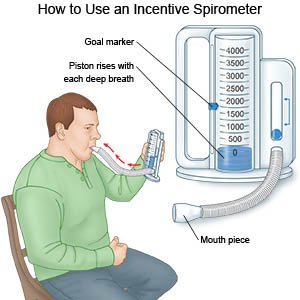
- Deep breathing and coughing may help decrease your risk for a lung infection. Take a deep breath and hold the breath as long as you can. Push the air out of your lungs with a deep, strong cough. Take deep breaths and cough 10 times each hour. Hold a pillow tightly against your incision when you cough to help decrease the pain. You may be given an incentive spirometer to help you take deep breaths. Put the plastic piece in your mouth and take a slow, deep breath. Then let the air out and cough. Repeat these steps 10 times every hour.
- You may not be able to do your regular activities for a few months. For 6 to 8 weeks after surgery, you will need to follow your healthcare provider's activity instructions.
Risks of chest wall reconstruction:
You may bleed more than expected or develop an infection at your incision site. Your body may reject the prosthesis. You may need another surgery to take the prosthesis out. You may need more surgeries if the reconstruction does not work. You may develop life-threatening pneumonia, respiratory failure, or blood clots.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone call if:
- You are short of breath or feel like you cannot get enough air.
- You feel lightheaded and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You feel dizzy or faint and pass out.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- You feel your heart beating in an irregular pattern.
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- Your incision is swollen, red, or has pus coming from it.
- Your stitches or staples come apart.
Call your doctor or surgeon if:
- Your pain does not get better after you take pain medicine.
- You have a fever or chills.
- You cough up yellow, green, or bloody mucus.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Antibiotics help prevent or fight a bacterial infection.
- Nausea medicine may help calm your stomach and prevent vomiting.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for your surgery area as directed:
- Follow your healthcare provider's instructions. Do not get the area wet until your provider says you may. Gently wash the area with soap and water. Pat the area dry and put on clean bandages as directed. Change your bandages when they get wet or dirty. Do not put powders or lotions on the area.
- Check the area every day for signs of infection. Signs of infection include swelling, warmth, redness, or pus.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can prevent the surgery area from healing. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
Activity:
Rest often. Your healthcare provider will tell you when you can start driving and doing your regular activities again. Tell your provider what kind of work you do. You may need specific instructions if you do work that requires lifting objects.
Go to physical therapy as directed:
A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength and to decrease pain.
Follow up with your doctor or surgeon as directed:
You may need to have your surgery site checked and stitches or staples removed. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
