Blurred Vision
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Blurred vision
is when you cannot see fine details. You may have blurred vision if you are nearsighted or farsighted and you need glasses.
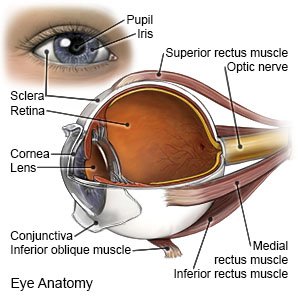 |
Common causes include the following:
- Scratch or open sore on your cornea
- Contact with a chemical
- A foreign object
- An infection
- Medical conditions, such as diabetes, cataracts, or glaucoma
- Trauma, such as a concussion
Seek care immediately if:
- You have weakness in an arm or leg, difficulty speaking or seeing, and a severe headache.
- You have a fever, eye pain, or discharge.
- You have a sudden loss of vision.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- Your blurred vision gets worse.
- Your blurred vision is worse in the morning.
- You have a sudden headache or eye pain.
- Your eye has swelling, redness, or discharge.
- You see floaters, flashes of light, fine dots, or cobweb shapes.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Manage your blurred vision:
Your healthcare provider may ask you to do any of the following:
- Use artificial tears to keep your eye moist or to soothe your irritated eye.
- Apply a cool compress to decrease any swelling or pain. Wet a clean washcloth with cool water and place it on your eye. Use the cool compress as often as directed.
- Wear an eye patch as directed to protect your eye.
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
You may need other eye exams and medicines. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Blurred Vision
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
