Atypical Mole
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What do I need to know about an atypical mole?
An atypical mole, or dysplastic nevus, is a mole that usually has an abnormal shape, size, or color. Atypical moles can develop on skin that is protected from the sun and skin that is exposed to sunlight. Your risk is increased if you have a family history of atypical moles. Most atypical moles do not develop into skin cancer. Your risk for skin cancer is higher if you have many atypical moles.
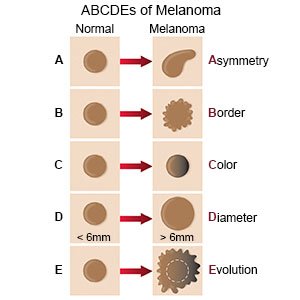
What are the signs and symptoms of an atypical mole?
- Large and flat mole
- Flat area around the outside of the mole with a darker, raised center
- Shape that is lopsided, not even, or not equal
- Mixture of pink, tan, or brown shades within the mole
- Black or much darker mole than other moles nearby
- Dry or scaly skin on a mole
How is an atypical mole diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine your mole. Tell your provider if you have noticed any growth or changes to your mole. Your provider may ask about your and your family's medical history. You may also need any of the following:
- A dermoscopy may be done to examine your mole. A dermoscope is a tool that has a magnifying glass and a light inside. Your dermatologist may use dermoscopy to decide if your mole needs to be removed.
- Mole removal may be done to check for abnormal or cancerous cells. The entire mole must be removed to make sure all of the cells are gone. Your provider may also need to remove some of the skin around the mole.
What do I need to know about skin checks?
- Get regular skin checks by a dermatologist. Full body photos may be taken at each visit to help monitor your moles over time. Your dermatologist will tell you how often to go in to have skin checks.
- Check your skin at home each month. Your dermatologist will show you how to do a self-exam. You may get a copy of your photos to help you monitor your moles. You may get photos of normal and cancerous moles to help you recognize early signs of skin cancer. Choose a day for your self-exams, such as the first day of the month. This will help you remember to do your self-exams.
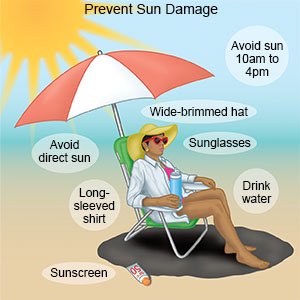
What can I do to protect my skin from sun damage?
Sun damage can lead to skin cancer. The following are ways to protect your skin:
- Avoid sun exposure between 10 am and 4 pm. The sun is most intense during the middle of the day.
- Apply sunscreen to all exposed skin 20 minutes before you go outside. Use a broad spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30. Apply sunscreen to your ears, scalp, back of your hands, and the tops of your feet. These areas are easily forgotten. Use a lip balm that contains at least SPF 30. Use the sunscreen and lip balm even on cloudy days. Apply at least every 2 hours and after you swim or sweat.
- Keep your skin covered while you are outside. Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants or skirts. Wear a hat with a wide brim all the way around. The wide brim shades your face, ears, and the back of your neck. Wear large-framed sunglasses to protect your eyes.
- Stand or sit in the shade while you are outside. Stay under something such as a tree, an umbrella, or a sun shelter as much as possible.
- Do not use tanning beds. Tanning beds are not safer than a tan directly from the sun.
 |
When should I call my doctor?
- You see a new mole that does not look like your other moles.
- You have a mole that changes in height, shape, or texture (feels different).
- You have a mole that changes color.
- You have a mole that starts to itch, bleed, or ooze fluid.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
