ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
ARDS is a type of acute respiratory failure caused by fluid buildup in your lungs. The fluid prevents your lungs from filling with oxygen. Your blood is not able to get the oxygen it needs to carry to your body. Organs such as your kidneys can shut down from a lack of oxygen. ARDS is life-threatening and immediate treatment is needed.
 |
What causes ARDS?
- An illness, such as pneumonia, sepsis (a blood infection), or pancreatitis
- An injury to the chest or the part of the brain that controls breathing, or severe burns
- Inhaling smoke, vomited food, liquids, or harmful gases such as chlorine, or near-drowning
- A drug overdose, multiple transfusions, or a lung injury from a transfusion
What are the signs and symptoms of ARDS?
Signs and symptoms usually start within 72 hours after injury to the lungs. You may have any of the following:
- Shortness of breath and a crackling noise when you breathe
- Fast, difficult breathing and a fast heartbeat
- Moist skin that has a bluish tint
- Extreme fatigue and confusion
- Low blood pressure
How is ARDS diagnosed?
- Blood tests may show if you have an infection.
- A blood gases test is also called an arterial blood gas, or ABG. Blood is taken from an artery (blood vessel) and tested for the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The results can tell healthcare providers how well your lungs are working.
- A chest x-ray or ultrasound may be done to check your lungs and heart. Healthcare providers may use the x-ray to look for signs of infection, such as pneumonia. A chest x-ray may also show signs of ARDS.
- A CT scan may show the cause of your ARDS. You may be given contrast liquid to help the problem show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
How is ARDS treated?
The cause of ARDS must be treated. You will be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) to be cared for in the hospital. You may need any of the following:
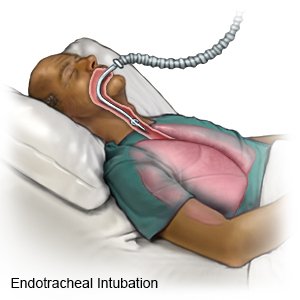
- A ventilator is a machine that will support your breathing and give oxygen while your lungs heal. You will have an endotracheal tube (ET tube) in your mouth or nose that will attach to a ventilator.
- Medicines may be given that cause your muscles to relax and allow the ventilator to work for you. You may also be given medicines to treat an infection or to relieve pain. You may need blood thinning medicine to prevent a pulmonary embolism (blood clot in your lungs). Medicines are sometimes given to decrease swelling in the lungs and other parts of the body.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about ARDS
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
