Abnormal (Dysfunctional) Uterine Bleeding
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
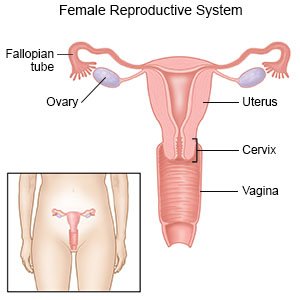
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)
is uterine bleeding that is not usual for you. It may also be called dysfunctional uterine bleeding. You may have bleeding from your uterus at times other than your normal monthly period. Your monthly periods may last longer or shorter, and bleeding may be heavier or lighter than usual. AUB can be acute (lasting a short time) or chronic (lasting longer than 6 months).
 |
Common signs and symptoms of AUB:
- Bleeding or spotting between periods
- Bleeding that starts 12 months or longer after you have been through menopause
- The amount of bleeding during your period is heavier or lighter than usual
- The number of days that you bleed during your regular period is longer than usual, or more than 7 days
- The number of days that you bleed is shorter than usual, or less than 2 days
- The time between your monthly periods is shorter or longer than usual
Seek care immediately if:
- You continue to bleed heavily, or you feel faint.
Call your doctor or gynecologist if:
- You need to change your sanitary pad or tampon more than 1 time each hour.
- Your medicine causes nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment
may include any of the following:
- Medicines may be given to treat a condition causing AUB. An example is medicine to increase or decrease the amount of hormone your thyroid makes. Hormones may be given to help decrease bleeding by making your monthly periods more regular. Sometimes this medicine may be given as birth control pills. Iron supplements may be given if your blood iron level decreases because of heavy bleeding.
- Procedures such as endometrial ablation or dilation and curettage may be used to control your bleeding.
- Surgery may be needed if medicines do not work or cannot be used. You may need an abdominal or vaginal hysterectomy. A hysterectomy is surgery to remove your uterus.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Self-care:
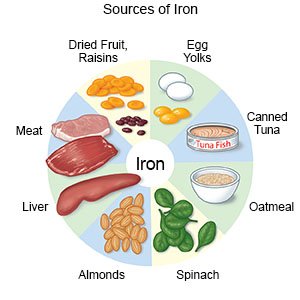
- Include foods high in iron if needed. Examples of foods high in iron are leafy green vegetables, beef, pork, liver, eggs, and whole-grain breads and cereals.
- Keep a diary of your menstrual cycles. Keep track of the number of tampons or pads you use each day.
- Talk to your healthcare provider before you start a weight loss program. You may need to wait until the abnormal bleeding has stopped before you try to lose weight. The amount of iron in your blood should be normal before you lose weight. Ask your provider if weight loss will help your AUB. He or she can tell you what weight is healthy for you. He or she can help you create a safe weight loss plan, if needed.
Follow up with your doctor or gynecologist as directed:
You may need to return in 4 to 6 months so your provider knows if the AUB has stopped. Bring the diary of your menstrual cycles to your follow-up visits. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Treatment options
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
