The originating document has been archived. We cannot confirm the completeness, accuracy, or currency of the content.
Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) 100 mg/mL Antimicrobial Injectable Solution
This page contains information on Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) 100 mg/mL Antimicrobial Injectable Solution for veterinary use.The information provided typically includes the following:
- Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) 100 mg/mL Antimicrobial Injectable Solution Indications
- Warnings and cautions for Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) 100 mg/mL Antimicrobial Injectable Solution
- Direction and dosage information for Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) 100 mg/mL Antimicrobial Injectable Solution
Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) 100 mg/mL Antimicrobial Injectable Solution
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Elanco US
Company: Elanco US
 |
Current label information has not been provided by the product owner. This information is provided as a service to our users. |
 |
For subcutaneous use in replacement dairy heifers under 20 months of age and all classes of beef cattle except beef calves less than 2 months of age and beef bulls intended for breeding (any age).
Not for use in any other class of dairy cattle or in veal calves.
Conditionally approved by FDA pending a full demonstration of effectiveness under application number 141-527.
Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) 100 mg/mL Antimicrobial Injectable Solution Caution
Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Federal (U.S.A.) law prohibits the extra-label use of this drug in food-producing animals.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION:
Baytril 100-CA1 is a sterile, ready-to-use injectable antimicrobial solution that contains enrofloxacin, a broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent.
Each mL of Baytril 100-CA1 contains 100 mg of enrofloxacin. Excipients are L-arginine base 200 mg, n-butyl alcohol 30 mg, benzyl alcohol (as a preservative) 20 mg and water for injection q.s.
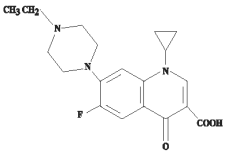
CHEMICAL NOMENCLATURE AND STRUCTURE:
1-cyclopropyl-7-(4-ethyl-1-piperazinyl)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid.
Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) 100 mg/mL Antimicrobial Injectable Solution Indications
Baytril 100-CA1 is indicated for the treatment of clinical anaplasmosis associated with Anaplasma marginale in replacement dairy heifers under 20 months of age and all classes of beef cattle except beef calves less than 2 months of age and beef bulls intended for breeding (any age). Not for use in any other class of dairy cattle or in veal calves.
Dosage and Administration
Baytril 100-CA1 should be administered as a single dose for treatment of clinical anaplasmosis. Administer, by subcutaneous injection, a single dose of 12.5 mg/kg of body weight (5.7 mL/100 lb). Administered dose volume should not exceed 20 mL per injection site.
Baytril 100-CA1 Dose for Anaplasmosis*
|
Weight (lb) |
Single-Dose Therapy 12.5 mg/kg Dose Volume (mL) |
|
500 |
28.5 |
|
600 |
34.0 |
|
700 |
40.0 |
|
800 |
45.5 |
|
900 |
51.5 |
|
1000 |
57.0 |
|
1100 |
62.5 |
|
1200 |
68.5 |
|
1300 |
74.0 |
|
1400 |
80.0 |
|
1500 |
85.5 |
|
1600 |
91.0 |
|
1700 |
97.0 |
|
1800 |
102.5 |
|
1900 |
108.5 |
|
2000 |
114.0 |
*Dose volumes have been rounded to the nearest 0.5 mL.
Use within 30 days of first puncture and puncture a maximum of 30 times with a needle or 4 times with a dosage delivery device.
Any product remaining beyond these parameters should be discarded.
 |
RESIDUE WARNINGS: Cattle intended for human consumption must not be slaughtered within 28 days from the last treatment. This product is not approved for use in female dairy cattle 20 months of age or older including dry dairy cows. Use in these cattle may cause drug residues in milk and/or in calves born to these cows. A withdrawal period has not been established for this product in pre-ruminating calves. Do not use in calves to be processed for veal. |
 |
HUMAN WARNINGS:
Not for use in humans. Keep out of reach of children. Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for 15 minutes. In case of dermal contact, wash skin with soap and water. Consult a physician if irritation persists following ocular or dermal exposures. Individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to quinolones should avoid this product. In humans, there is a risk of user photosensitization within a few hours after excessive exposure to quinolones. If excessive accidental exposure occurs, avoid direct sunlight.
Precautions
The effects of enrofloxacin on bull reproductive performance have not been adequately determined.
Subcutaneous injection in cattle can cause a transient local tissue reaction that may result in trim loss of edible tissue at slaughter.
Baytril 100 and Baytril 100-CA1 contain different excipients than other Baytril products. The safety and efficacy of this formulation in species other than cattle has not been determined.
Quinolone-class drugs should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected Central Nervous System (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation which may lead to convulsive seizures. Quinolone-class drugs have been shown to produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species. See Animal Safety section for additional information.
Adverse Reactions
No adverse reactions were observed during Baytril 100 clinical trials.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics: Following a single subcutaneous dose of 12.5 mg/kg body weight in eight beef heifers and steers, enrofloxacin reached a mean maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of 1.39 mg/L at 4.25 hours after dosing. Ciprofloxacin, which is the main active metabolite of enrofloxacin, started appearing in the blood approximately 20 minutes after dosing and had a Cmax of 0.59 mg/L at 6.25 hours after dosing. The mean area under the concentration curve to the last quantifiable concentration timepoint (AUClast) for enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin was 12.38 and 7.13 mg*hr/L, respectively. The mean half-life was 4.15 hours for enrofloxacin and 5.15 hours for ciprofloxacin.
Mechanism of Action: Enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin work by inhibiting the function of the topoisomerases gyrase and topoisomerase IV in the bacterial cell. Typically, gyrase is the primary target in Gram-negative bacteria, and topoisomerase IV is the primary target in Gram-positive bacteria. These enzymes are necessary for bacterial DNA synthesis. Their inhibition by these drugs leads to several types of lethal cell damage by mechanisms that are complex and not completely understood, and results in cessation of cell respiration and division.
MICROBIOLOGY:
Enrofloxacin is bactericidal and exerts its antibacterial effect by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase (a type II topoisomerase) thereby preventing DNA supercoiling and replication which leads to cell death.1 Enrofloxacin is active against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
REASONABLE EXPECTATION OF EFFECTIVENESS:
Baytril 100-CA1 is conditionally approved pending a full demonstration of effectiveness. Additional information for conditional approvals can be found by searching https://www.fda.gov for “conditional approval”. Baytril 100-CA1 (enrofloxacin) has a reasonable expectation of effectiveness for treatment of clinical anaplasmosis in the conditionally approved classes of cattle when administered for the conditionally approved dosage regimen based on published scientific literature and reports from studies conducted by the sponsor. The information evaluated effectiveness across a variety of study designs, including differences in: dose, frequency, duration, and route of administration; animal class and age (including young calves and adult cows); infection method (natural vs. challenge); and product formulation. Despite the variation in study design, the studies consistently showed that administration of enrofloxacin in A. marginale-infected cattle resulted in a decrease in parasitemia and, when evaluated, improvement in clinical variables (hematocrit and rectal temperatures).
ANIMAL SAFETY:
Safety studies were conducted in feeder calves using single doses of 5, 15 and 25 mg/kg for 15 consecutive days and 50 mg/kg for 5 consecutive days. No clinical signs of toxicity were observed when a dose of 5 mg/kg was administered for 15 days. Clinical signs of depression, incoordination and muscle fasciculation were observed in calves when doses of 15 or 25 mg/kg were administered for 10 to 15 days. Clinical signs of depression, inappetance and incoordination were observed when a dose of 50 mg/kg was administered for 3 days. No drug-related abnormalities in clinical pathology parameters were identified. No articular cartilage lesions were observed after examination of stifle joints from animals administered 25 mg/kg for 15 days.
A safety study was conducted in 23-day-old calves using doses of 5, 15 and 25 mg/kg for 15 consecutive days. No clinical signs of toxicity or changes in clinical pathology parameters were observed. No articular cartilage lesions were observed in the stifle joints at any dose level at 2 days and 9 days following 15 days of drug administration.
An injection site study conducted in feeder calves demonstrated that the formulation may induce a transient reaction in the subcutaneous tissue and underlying muscle. No painful responses to administration were observed.
Reproductive Safety: Two reproductive safety studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of enrofloxacin administered to pregnant cows. In one study, enrofloxacin was administered to 347 beef cows at critical times (folliculogenesis, and early, middle, and late organogenesis) during the first trimester of pregnancy. In the second study, enrofloxacin was administered to 30 late gestation (third trimester) dairy cows. A nontreated control group was included in both studies. Reproductive efficiencies (conception rate and pregnancy attrition rate for the first trimester study; and calving rate, calving failure rate, abortion rate, stillborn rate, and dystocia scores for both studies) and cow health were evaluated. Calves born to study cows were assessed for congenital anomalies, body weight, and general health through 60 days post-partum. Enrofloxacin treatment had no adverse effect on reproduction or cow health in either study. Three calves in the first trimester study that were born to enrofloxacin-treated cows died due to perforating gastrointestinal ulcers. No congenital anomalies were observed in either study, and calf body weights and general health were otherwise normal.
STORAGE CONDITIONS:
Protect from direct sunlight. Do not refrigerate or freeze. Store at 20-30°C (68-86°F), excursions permitted up to 40°C (104°F). Precipitation may occur due to cold temperature. To redissolve, warm and then shake the vial.
How Supplied
Baytril 100-CA 1: 100 mg/ml 250 ml Bottle
REVISED:
January 2022
References
1. Hooper, D. C., Wolfson, J. S., Quinolone Antimicrobial Agents, 2nd ed., ASM Press, 59-75, 1993.
For product questions, to report adverse reactions, or for a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), call Elanco Product & Veterinary Support at 1-800-428-4441.
Baytril is sold by Elanco or its affiliates and is not a product of Bayer. The product name Baytril is owned by Bayer and used under license.
Elanco and the diagonal bar logo are trademarks of Elanco or its affiliates.
© 2022 Elanco or its affiliates
Manufactured for:
Elanco US Inc., Greenfield, IN 46140 U.S.A.
Made in Germany
90207034_PA600207X
W1a
CPN: 1131117.0
2500 INNOVATION WAY, GREENFIELD, IN, 46140
| Customer Service: | 317-276-1262 | |
| Technical Service: | 800-428-4441 | |
| Website: | www.elanco.us | |
| Email: | elanco@elanco.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". DVMetrics assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the DVMetrics service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2024 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2024-02-27
