Croup in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is croup?
Croup is a respiratory infection. It causes your child's throat and upper airways to swell and narrow. It is also called laryngotracheobronchitis. Croup is most common in children ages 6 months to 3 years. Your child may get croup more than once.
What increases my child's risk for croup?
Croup is commonly caused by a virus. It usually occurs during the common cold season. Croup is spread by breathing in germs from infected people when they cough or sneeze. Croup can also spread if your child touches contaminated items and then touches his or her mouth, nose, or eyes.
What are the signs and symptoms of croup?
Croup begins like a cold with cough, fever, and a runny nose. As your child's airway becomes swollen, he or she may have any of the following:
- Barking cough that is worse at night
- Noisy, fast, or difficult breathing
- Hoarse or raspy voice
How is croup treated?
Treatment can usually be done at home. Your child's healthcare provider may recommend any of the following:
- Medicines, such as acetaminophen, steroids, and NSAIDs, may be recommended. These medicines help decrease fever and inflammation, and open your child's airway. Ask your child's healthcare provider which cough medicine may help with your child's cough.
- Help your child rest and keep calm as much as possible. Stress can make your child's cough worse.
- Moist air may help your child breathe easier and decrease his or her cough. Take your child outside for 5 minutes if it is humid. Or, take your child into the bathroom and turn on a hot shower or bathtub. Do not put your child into the shower or bathtub. Sit with your child in the warm, moist air for 15 to 20 minutes.
- Use a cool mist humidifier to increase air moisture in your home. This may make it easier for your child to breathe and help decrease his or her cough.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I prevent the spread of croup?
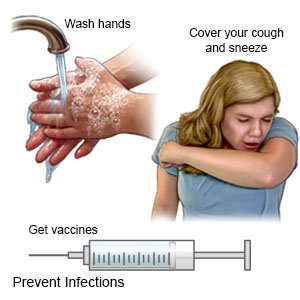 |
- Have your child wash his or her hands often with soap and water. Carry germ-killing hand lotion or gel with you. Have your child use the lotion or gel to clean his or her hands when soap and water are not available.

- Remind your child to cover his or her mouth while coughing or sneezing. Have your child cough or sneeze into a tissue or the bend of his or her arm. Ask those around your child to cover their mouths when they cough or sneeze.
- Do not let your child share cups, silverware, or dishes with others.
- Keep your child home from school or daycare.
- Get the vaccinations your child needs. Take your child to get a flu vaccine as soon as recommended each year, usually in September or October. Ask your child's healthcare provider if your child needs other vaccines.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child stops breathing or breathing becomes difficult.
- Your child faints.
- Your child's lips or fingernails turn blue, gray, or white.
- The skin between your child's ribs or around his or her neck goes in with every breath.
- Your child is dizzy or sleeping more than what is normal for him or her.
- Your child drools or has trouble swallowing his or her saliva.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child has no tears when he or she cries.
- The soft spot on the top of your baby's head is sunken in.
- Your child has wrinkled skin, cracked lips, or a dry mouth.
- Your child urinates less than what is normal for him or her.
When should I call my child's doctor?
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child does not get better after sitting in a steamy bathroom for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Your child's cough does not go away.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Croup
Treatment options
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
