Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class: Laxatives
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Feb 4, 2024.
On This Page
Highlights of Prescribing Information
Monobasic Sodium
Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval:2006
WARNING: ACUTE PHOSPHATE NEPHROPATHY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Rare, serious reports of acute phosphate nephropathy in patients who received oral sodium phosphate products, including Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, for colon cleansing prior to colonoscopy. Some cases have resulted in permanent impairment of renal function and some patients required long-term dialysis. (5.1)
- Patients at increased risk include those with increased age, hypovolemia, increased bowel transit time (such as bowel obstruction), active colitis, or baseline kidney disease, and those using medicines that affect renal perfusion or function (such as diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs], and possibly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs]). (5.1)
- Advise patients of the importance of following the recommended split dosage regimen and the importance of adequate hydration before, during and after the use of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. Avoid additional sodium phosphate-based products. (2.1,2.2)
Recent Major Changes
Warnings and Precautions (5.7) 11/2018
Indications and Usage for Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are an osmotic laxative indicated for cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy in adults. (1)
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets Dosage and Administration
Important Administration Instructions:
- Two doses of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy: the first dose the evening before the colonoscopy and the second dose on the morning of the colonoscopy. (2.1 )
- Do not take other laxatives, particularly additional sodium phosphate- based purgative or enema products. (2.1,7.3 )
- Do not take oral medications within 1 hour before or after starting each dose. (2.1 , 7.2 )
Dosage Regimen (2.2)
The recommended adult dosage is 32 tablets taken orally with a total of 2 quarts of clear liquids in the following manner:
- Evening before colonoscopy: 4 tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids every 15 minutes for a total of 20 tablets.
- Next morning: 4 tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids every 15 minutes for a total of 12 tablets.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 1.5 g of sodium phosphate (3) (3)
Contraindications
- Biopsy-proven acute phosphate nephropathy (4, 5.1 )
- Gastrointestinal (GI) obstruction (4, 5.7 )
- Gastric bypass or stapling surgery (4 )
- Bowel perforation (4 )
- Toxic colitis (4)
- Toxic megacolon (4 )
- Hypersensitivity to sodium phosphate salts or any components of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets (4, 5.7 )
Warnings and Precautions
- Renal disease and electrolyte disorders : Use caution in severe renal impairment and those taking concurrent medications that increase risk, ensure adequate hydration, and consider laboratory assessments prior to and after use. (5.1, 7.1 )
- Cardiac arrhythmias : Consider pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs in patients at increased risk. (5.2 )
- Seizures : Use caution in patients with a history of seizures and patients at increased risk of seizure, including medications that lower the seizure threshold. (5.3, 7.1 )
- Suspected GI obstruction or perforation : Rule out diagnosis before administration. (4, 5.4 )
- Colonic mucosal ulceration : Consider potential for mucosal ulcerations when interpreting colonoscopy findings in patients with known or suspected inflammatory bowel disease. Use with caution in patients with an acute exacerbation of chronic inflammatory bowel disease (5.5 )
- Patients at risk for aspiration : Observe during administration. (5.6 )
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis : Inform patients to seek immediate medical care if symptoms occur. (5.7 )
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥3%) are: bloating, nausea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lupin Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-866-403-7592 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that increase risks due to fluid and electrolyte changes. (7.1 )
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 10/2020
Full Prescribing Information
BOXED WARNING
WARNING: ACUTE PHOSPHATE NEPHROPATHY
- There have been rare, but serious reports of acute phosphate nephropathy in patients who received oral sodium phosphate products, including Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, for colon cleansing prior to colonoscopy. Some cases have resulted in permanent impairment of renal function and some patients required long-term dialysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
- While some cases have occurred in patients without identifiable risk factors, patients at increased risk of acute phosphate nephropathy may include those with increased age, hypovolemia, increased bowel transit time (such as bowel obstruction), active colitis, or baseline kidney disease, and those using medicines that affect renal perfusion or function (such as diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs], and possibly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs]) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
- Advise patients of the importance of following the recommended split dosage regimen and the importance of adequate hydration before, during and after the use of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. Avoid additional sodium phosphate- based purgative or enema products [see Dosage and Administration (2.1,2.2 )] .
1. Indications and Usage for Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are indicated for cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy in adults.
2. Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
- Correct fluid and electrolyte abnormalities before treatment with Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
- Clear liquids must be consumed before, during and after taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
- Do not administer Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets within 7 days of a previous use.
- Two doses of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy: the first dose the evening before the colonoscopy and the second dose on the morning of the colonoscopy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Consume only clear liquids (no solid food) from the start of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets treatment until after the colonoscopy.
- Do not eat or drink alcohol, milk, anything colored red or purple or any other foods containing pulp material.
- Do not take other laxatives while taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, particularly additional sodium phosphate-based purgative or enema products [see Drug Interactions (7.3)] .
- Do not take oral medications within 1 hour before or after starting each dose of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets[see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
2.2 Dosage Regimen
Instruct adult patients that on the day before their colonoscopy, they can consume a light breakfast consisting of clear soup and/or plain yogurt (no solid foods) before noon, followed by only clear liquids until after the colonoscopy.
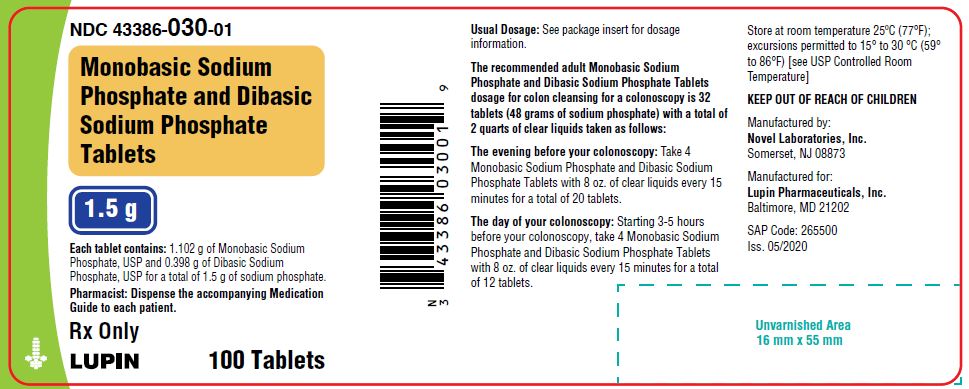
The recommended dose of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets for colon cleansing for adult patients is 32 tablets (48 grams of sodium phosphate) taken orally with a total of 2 quarts of clear liquids in the following manner:
The evening before the colonoscopy: Take 4 Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids every 15 minutes for a total of 20 tablets.
On the day of the colonoscopy starting 3 to 5 hours before the procedure: Take 4 Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids every 15 minutes for a total of 12 tablets.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
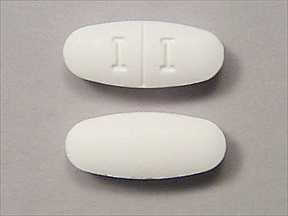
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are supplied as white to off-white uncoated tablet, modified oval shaped, biconvex, bisect on one side and plain on the other. Debossed "N" on the left side of the bisect and "03" on the right side of the bisect. Each Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets contains 1.102 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate, USP and 0.398 grams of Dibasic Sodium Phosphate, USP for a total of 1.5 grams of sodium phosphate per tablet. Inert ingredients include polyethylene glycol 8000, NF; and magnesium stearate, NF.
4. Contraindications
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are contraindicated in the following conditions:
- History of acute phosphate nephropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Gastrointestinal (GI) obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Gastric bypass or stapling surgery
- Bowel perforation
- Toxic colitis
- Toxic megacolon
- Hypersensitivity to sodium phosphate salts or any component of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Renal Disease, Acute Phosphate Nephropathy, and Electrolyte Disorders
Renal Disease and Acute Phosphate Nephropathy
There have been rare, but serious, reports of renal failure, acute phosphate nephropathy, and nephrocalcinosis in patients who received oral sodium phosphate products, including Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, for colon cleansing prior to colonoscopy. These cases often resulted in permanent impairment of renal function and several patients required long-term dialysis. The time to onset is typically within days; however, in some cases, the diagnosis of these events has been delayed up to several months after the ingestion of these products. Patients at increased risk of acute phosphate nephropathy may include patients with the following: hypovolemia, baseline kidney disease, increased age, and patients using medicines that affect renal perfusion or function [such as diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and possibly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Electrolyte Disorders
Bowel preparations, including Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tabletscan cause fluid and electrolyte disturbances, which can lead to serious adverse reactions including cardiac arrhythmias, seizures and renal impairment [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Patient Management
- Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of acute phosphate nephropathy [see Contraindications (4)]. Use Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with caution in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute), with conditions, or who are taking medications, that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or may increase the risk of arrhythmias, seizures, or renal impairment. Consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy labs (phosphate, calcium, potassium, sodium, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
- Correct electrolyte abnormalities such as hypernatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hypokalemia, or hypocalcemia before treatment with Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] .
- Avoid additional sodium phosphate-based purgative or enema products [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
- Advise all patients to hydrate adequately before, during, and after the use of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets[see Dosage and Administration (2.1,2.2)] .
- If a patient develops significant vomiting or signs of dehydration while or after taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, consider performing post-colonoscopy lab tests [electrolytes, creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)].
5.2 Cardiac Arrhythmias
There have been rare reports of serious arrhythmias associated with the use of ionic osmotic laxative products for bowel preparation. QT prolongation with sodium phosphate tablets has been associated with electrolyte imbalances, such as hypokalemia and hypocalcemia.
Use caution when prescribing Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets for patients at increased risk of arrhythmias (e.g., patients with a history of prolonged QT, uncontrolled arrhythmias, recent myocardial infarction, unstable angina, congestive heart failure, or cardiomyopathy) and those taking medications known to prolong the QT interval, since serious complications may occur. Consider pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs in patients at increased risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias.
5.3 Seizures
There have been rare reports of generalized tonic-clonic seizures and/or loss of consciousness associated with use of sodium phosphate osmotic laxative products, such as Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, in patients with no prior history of seizures. The seizure cases were associated with electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia) and low serum osmolality. The neurologic abnormalities resolved with correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities.
Use Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with caution in patients with a history of seizures and in patients at higher risk of seizure, such as patients taking medications that lower the seizure threshold (such as tricyclic antidepressants), patients withdrawing from alcohol or benzodiazepines, or patients with known or suspected hyponatremia [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.4 Use in Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease
If gastrointestinal obstruction or perforation is suspected, perform appropriate diagnostic studies to rule out these conditions before administering Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets [see Contraindications (4)].
Use with caution in patients with severe active ulcerative colitis.
5.5 Colonic Mucosal Ulceration and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Osmotic laxatives, including Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, may induce colonic mucosal aphthous ulcerations. In the Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets clinical program, aphthous ulcers were observed in 3% of patients who took the recommended Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets dosing regimen.
Consider the potential for mucosal ulcerations resulting from bowel preparation when interpreting colonoscopic finding should in patients with known or suspected inflammatory bowel disease.
Use Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with caution in patients experiencing an acute exacerbation of chronic inflammatory bowel disease as published data suggest that sodium phosphate absorption may be enhanced in such patients.
5.6 Aspiration
Patients with impaired gag reflex or other swallowing abnormalities are at risk for regurgitation or aspiration of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. Observed these patients during administration of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
5.7 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets may cause serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, urticaria, and throat tightness [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis and instruct them to seek immediate medical care should signs and symptoms occur.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious or otherwise important adverse reactions for bowel preparations are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Renal Disease, Acute Phosphate Nephropathy, and Electrolyte Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cardiac Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Use in Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Colonic Mucosal Ulceration and Inflammatory Bowel Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Aspiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets was evaluated in two randomized, investigator-blinded, active controlled trials in 931 adult patients undergoing elective colonoscopy. The mean age of the study population was 60 years (range 20 to 89 years), 88% of patients were Caucasian and 55% were female [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Table 1 shows the most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 3% of patients by treatment group in Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Since diarrhea was considered as a part of the efficacy of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, diarrhea was not defined as an adverse event in this clinical trial.
|
1Reported in more than 3% of patients in at least one treatment group |
|||
|
2Another oral formulation of monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate |
|||
| Table 1: Common Adverse Reactions1 in Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy in Study 1
|
|||
| Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 32 tabs (48 g) N=272
| Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 40 tabs (60 g) N=265
| Sodium Phosphate2
40 tabs (60 g) N=268 |
|
| Bloating | 31% | 39% | 41% |
| Nausea | 26% | 37% | 30% |
| Abdominal Pain | 23% | 24% | 25% |
| Vomiting | 4% | 10% | 9% |
Electrolyte Abnormalities in Study 1
Hyperphosphatemia
A total of, 96%, 96%, and 93% of patients who took 60 grams of oral sodium phosphate, 60 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, and 48 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, respectively, developed hyperphosphatemia (defined as phosphate level > 5.1 mg/dL) on the day of the colonoscopy. In this study, patients who took 60 grams of oral sodium phosphate, 60 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, and 48 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets had baseline mean phosphate levels of 3.5, 3.5, and 3.6 mg/dL and subsequently developed mean phosphate levels of 7.6, 7.9, and 7.1 mg/dL, respectively, on the day of the colonoscopy.
Hyperkalemia
A total of 20%, 22%, and 18% of patients who took 60 grams of oral sodium phosphate, 60 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, and 48 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, respectively, developed hypokalemia (defined as a potassium level < 3.4 mEq/L) on the day of the colonoscopy. In this study, patients who took 60 grams of oral sodium phosphate, 60 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, and 48 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets all had baseline potassium levels of about 4.3 mEq/L and then developed a mean potassium level of 3.7 mEq/L on the day of the colonoscopy.
Several patients on all three sodium phosphate regimens developed hypocalcemia and hypernatremia that did not require treatment.
The Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 60-gram dosage regimen was associated with an increased risk of adverse reactions compared to the 48- gram dosage regimen and a similar overall response rate [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Therefore, the Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 60-gram dosage is not a recommended regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity reactions: anaphylaxis, angioedema (swelling of the lips, tongue and face), rash, pruritus, urticaria, throat tightness, bronchospasm, dyspnea, pharyngeal edema, dysphagia, and paresthesia.
Cardiovascular: Arrhythmias
Nervous system: Seizures
Renal: Renal impairment, increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN), increased creatinine, acute renal failure, acute phosphate nephropathy, nephrocalcinosis, and renal tubular necrosis.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs That May Increase Risks due to Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities
Use caution when prescribing Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets for patients with conditions, or who are using medications, that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or may increase the risk of renal impairment, seizures, arrhythmias, or prolonged QT in the setting of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities. Consider additional patient evaluations as appropriate in patients taking these concomitant medications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1,5.2,5.3)].
7.2 Potential for Reduced Drug Absorption
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets can reduce the absorption of other coadministered oral medications. Administer oral medications at least 1 hour before or 1 hour after starting each Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
7.3 Other Sodium Phosphate-Based Laxatives
Administration of additional sodium phosphate-based purgative or enema products with Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets may increase the risk of acute phosphate nephropathy. Avoid concomitant use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
There are no available data on sodium phosphate use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk for adverse developmental outcomes.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with sodium phosphate.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
There are no data available to assess the presence of sodium phosphate in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production.
The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets to a child during lactation; therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 599 patients in clinical trials receiving at least 48 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, 134 (22%) were 65 years of age or older, while 27 (5%) were 75 years of age or older.
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between geriatric patients and younger patients. However, the mean phosphate levels in geriatric patients were greater than the phosphate levels in younger patients after Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets administration. The mean colonoscopy-day phosphate levels in patients 18-64, 65-74, and ≥ 75 years old who received the recommended Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets dosage regimen in Study 1were 7.0, 7.3, and 8.0 mg/dL, respectively. After Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets administration, the mean phosphate levels in patients 18-64, 65-74, and ≥ 75 years old were 7.4, 7.9, and 8.0 mg/dL, respectively. Greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out; therefore, use Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with caution in geriatric patients. Advise geriatric patients to adequately hydrate before, during, and after the use of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
Sodium phosphate is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions with sodium phosphate may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Since geriatric patients are more likely to have impaired renal function, consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy labs (phosphate, calcium, potassium, sodium, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Sodium phosphate is substantially excreted by the kidney. Use Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with caution in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min) or patients taking concomitant medications that may affect renal function. These patients may be at risk for renal injury. Advise these patients of the importance of adequate hydration before, during and after the use of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, and consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy labs (phosphate, calcium, potassium, sodium, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
10. Overdosage
Overdosage of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets may lead to severe electrolyte disturbances, including hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, hypernatremia, or hypokalemia, as well as dehydration and hypovolemia, with attendant signs and symptoms of these disturbances. Certain severe electrolyte disturbances resulting from overdose may lead to cardiac arrhythmias, seizure, renal failure, and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3)]. Monitor for fluid and electrolyte disturbances and treated symptomatically.
11. Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets Description
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets (sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate and sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous) is an osmotic laxative used to clean the colon prior to colonoscopy. Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets is manufactured with a highly soluble tablet binder and does not contain microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are white to off-white uncoated tablet, modified oval shaped, biconvex, bisect on one side and plain on the other. Debossed "N" on the left side of the bisect and "03" on the right side of the bisect. Each Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablet contains 1.102 grams of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate, USP and 0.398 grams of Dibasic Sodium Phosphate, USP for a total of 1.5 grams of sodium phosphate per tablet. Inert ingredients include polyethylene glycol 8000, NF; and magnesium stearate, NF. Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets is gluten-free.
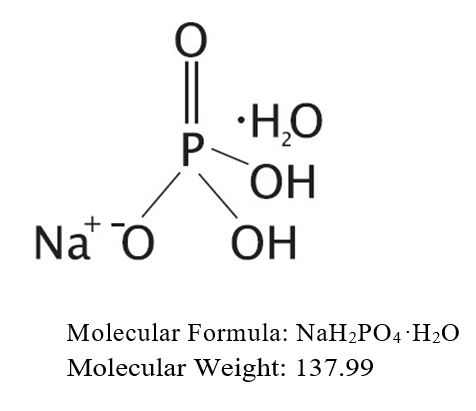
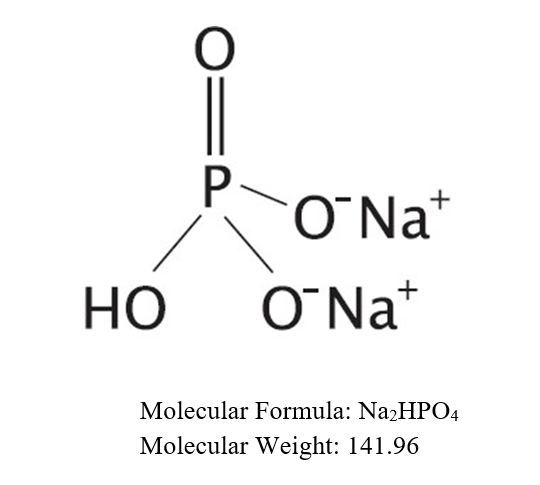
The structural and molecular formulae and molecular weights of the active ingredients are shown below:
- Monobasic sodium phosphate, USP
- Dibasic sodium phosphate, USP
12. Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The primary mode of action is the osmotic effect of sodium, which induces a laxative effect. The physiological consequence is increased water retention in the lumen of the colon, resulting in loose stools.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Administration of the recommended Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets dosage regimen has a purgative effect for approximately 1 to 3 hours.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic studies with Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets have not been conducted. However, the following pharmacokinetic study was conducted with another oral tablet formulation of sodium phosphate which contain the same active ingredients as Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets at a dose that is 25% greater than the Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets dose.
Absorption
An open-label pharmacokinetic study of oral sodium phosphate in healthy subjects was performed to determine the concentration-time profile of serum inorganic phosphorus levels after oral sodium phosphate administration. All subjects received the approved dosing regimen for colon cleansing of 60 grams of sodium phosphate with a total liquid volume of
3.6 quarts. A 30-gram dose (20 tablets given as 3 tablets every 15 minutes with 8 ounces of clear liquids) was given beginning at 6 PM in the evening. The 30-gram dose (20 tablets given as 3 tablets every 15 minutes with 8 ounces of clear liquids) was repeated the following morning beginning at 6 AM.
Twenty-three healthy subjects (mean age 57 years old; 57% male and 43% female; and 65% Hispanic, 30% Caucasian, and 4% African-American) participated in this pharmacokinetic study. The serum phosphorus level rose from a mean
(± standard deviation) baseline of 4.0 (± 0.7) mg/dL to 7.7 (± 1.6 mg/dL), at a median of 3 hours after the administration of the first 30-gram dose of sodium phosphate tablets (see Figure 1). The serum phosphorus level rose to a mean of 8.4 (± 1.9) mg/dL, at a median of 4 hours after the administration of the second 30-gram dose of sodium phosphate tablets. The serum phosphorus level remained above baseline for a median of 24 hours after the administration of the initial dose of sodium phosphate tablets (range 16 to 48 hours).
Figure 1. Mean (±Standard Deviation) Serum Phosphorus Concentrations
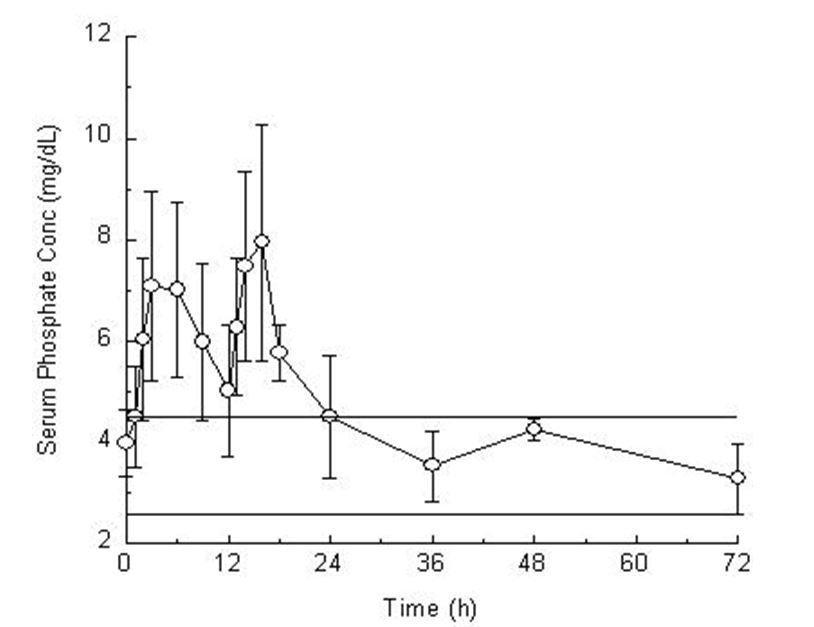
The upper (4.5 mg/dL) and lower (2.6 mg/dL) reference limits for serum phosphate are represented by solid bars.
Specific Populations
Male and Female Patients: No difference in serum phosphate AUC values were observed in the single pharmacokinetic study conducted with sodium phosphate tablets in 13 male and 10 female healthy subjects.
Elderly Patients: In a single pharmacokinetic study of sodium phosphate tablets, which included 6 elderly subjects, plasma half-life increased two-fold in subjects > 70 years of age compared to subjects < 50 years of age (3 subjects and 5 subjects, respectively) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Patients with Renal Impairment: The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets has not been studied. The inorganic form of phosphate in the circulating plasma is excreted almost entirely by the kidneys [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
14. Clinical Studies
The colon cleansing efficacy and safety of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets was evaluated in a randomized, investigator-blinded, actively controlled, multicenter, U.S. trial in patients scheduled to have an elective colonoscopy (Study 1).
In Study 1, patients were randomized into one of the following three sodium phosphate treatment groups:
- An oral tablet formulation of sodium phosphate containing 60 grams of sodium phosphate given in split doses (30 grams in the evening before the colonoscopy and 30 grams on the next day) with at least 3.6 quarts of clear liquids;
- Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets containing 60 grams of sodium phosphate given in split doses (30 grams in the evening before the colonoscopy and 30 grams on the next day) with 2.5 quarts of clear liquids; and
- Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets containing 48 grams of sodium phosphate (30 grams in the evening before the colonoscopy and 18 grams on the next day) with 2 quarts of clear liquids.
Patients were instructed to eat a light breakfast before noon on the day prior to the colonoscopy and then were told to drink only clear liquids after noon on the day prior to the colonoscopy.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the overall colon cleansing response rate in the 4-point Colonic Contents Scale. Response was defined as a rating of "excellent" or "good" on the 4-point scale as determined by the blinded colonoscopist. This trial was designed to assess the non-inferiority of the two Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets groups compared to the active control group.
The efficacy analysis included 704 adult patients who had an elective colonoscopy. Patients ranged in age from 21 to 89 years old (mean age 56 years old) with 55% female and 45% male patients. Race was distributed as follows: 87% Caucasian, 10% African American, and 3% other race. The Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 60-gram and 48-gram treatment groups demonstrated non-inferiority compared to the active control. See Table 2 for the results.
|
1Colon cleansing efficacy was based on response rate to treatment. A patient was considered to be a responder if overall colon cleansing was rated as "excellent" or "good" on a 4-point scale based on the amount of retained "colonic contents". Excellent was defined as >90% of mucosa seen, mostly liquid stool, minimal suctioning needed for adequate visualization. Good was defined as >90% of mucosa seen, mostly liquid stool, significant suctioning needed for adequate visualization. Fair was defined as >90% of mucosa seen, mixture of liquid and semisolid stool, could be suctioned and/or washed. Inadequate was defined as <90% of mucosa seen, mixture of semisolid and solid stool which could not be suctioned or washed. |
||||||||
|
2On the day of the colonoscopy, study medication was taken 3 to 5 hours before the start of the colonoscopy. |
||||||||
| Table 2: Phase 3 Study – Overall Colon Content Cleansing Response Rates1
|
||||||||
| Treatment Arm (grams of sodium phosphate)
| No. of tablets taken at 6 PM on the
day prior to colonoscopy | No. of tablets taken the next day2
| Excellent
| Good
| Fair
| Inadequate
| Overall Response Rate (Excellent or Good)
| |
| Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 32 tabs (48 g) n=236 | 20 | 12 | 76% | 19% | 3% | 2% | 95% | |
| Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 40 tabs (60 g) n=233 | 20 | 20 | 73% | 24% | 2% | 1% | 97% | |
| Sodium Phosphate Tablets 40 tabs (60 g) n=235 | 20 | 20 | 51% | 43% | 6% | 0% | 94% | |
The Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 60-gram dosage regimen had a similar overall response rate as the 48-gram dosage regimen and was associated with an increased risk of adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Therefore, the Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets 60-gram dosage is not a recommended regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
16. How is Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets supplied
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are white to off-white uncoated tablet, modified oval shaped, biconvex, bisect on one side and plain on the other. Debossed "N" on the left side of the bisect and "03" on the right side of the bisect. Each Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablet contains 1.102 grams of monobasic sodium phosphate, USP and 0.398 grams of dibasic sodium phosphate, USP for a total of 1.5 grams of sodium phosphate per tablet. Inert ingredients include polyethylene glycol 8000, NF; and magnesium stearate, NF.
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets is packaged in a multi-dose, child-resistant bottle containing 100 tablets: NDC 43386-030-01.
Each bottle contains two silica desiccant packets, which should not be ingested.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Discard any unused portion.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Instruct patients:
- On the importance of taking the recommended fluid regimen. Advise them to hydrate adequately with clear liquids before, during, and after the use of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] . Examples of clear liquids can be found in the Medication Guide.
- Two doses of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy.
- Do not eat or drink alcohol, milk, anything colored red or purple or any other foods containing pulp material.
- Not to take other laxatives or enemas made with sodium phosphate while they are taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets [see Drug Interactions (7.3)] .
- Not to take oral medications within one hour before or after starting each dose of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
- To contact their healthcare provider if they develop significant vomiting or signs of dehydration after taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets or if they experience cardiac arrhythmias or seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1,5.2,5.3)].
- To seek immediate medical care should signs and symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] .
Novel Laboratories, Inc.
Somerset, NJ 08873
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Baltimore, MD 21202
SAP Code: 265501
Iss. 05/2020
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets s
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets can cause serious side effects, including:
Serious kidney problems. Rare, but serious kidney problems can happen in people who take medicines made with sodium phosphate, including Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, to clean the colon before colonoscopy. These kidney problems can sometimes lead to kidney failure or the need for dialysis for a long time. These problems often happen within a few days, but sometimes may happen several months after taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
Conditions that can make you more at risk for having serious kidney problems with Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets include if you:
- lose too much body fluid (dehydration)
- have slow moving bowels
- have a blockage in your intestine (bowel obstruction)
- have any disease that causes bowel inflammation (colitis)
- have kidney disease or kidney problems
- have heart failure
- take water pills, high blood pressure medicine, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Increased age may increase your risk for having serious kidney problems with Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
Severe fluid loss (dehydration) and severe changes in body salts in the blood (electrolytes). People who take medicines to clean their colon before a colonoscopy, including Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, can have severe loss of body fluid, with severe changes in body salts in the blood. These changes can be serious and can cause:
- abnormal heart rhythms
- kidney problems
- seizures. This can happen even if you have never had a seizure.
Tell your doctor if you have any of these symptoms of loss of too much body fluid (dehydration) while taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets:
- vomiting
- urinating less often than normal
- dizziness
- headache
See "What are the possible side effects of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?" for more information about side effects.
Important information about taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets:
- Two doses of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are needed to completely prepare for your colonoscopy. Take your first dose of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets on the evening before your colonoscopy. Take your second dose of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets on the morning of your colonoscopy.
- Drink plenty of clear liquids before, during, and after taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
- Do not take another laxative or enema that contains sodium phosphate while taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. See "How should I take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?" for more information about how to take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
What is Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets is a prescription medicine used in adults to clean your colon before a colonoscopy. Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets cleans your colon by causing you to have diarrhea. Cleaning your colon helps your doctor see the inside of your colon more clearly during the colonoscopy.
It is not known if Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are safe and effective in children.
Who should not take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
Do not take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets if you:
- have had a kidney biopsy that shows you have kidney problems because of too much phosphate.
- have stomach or bowel (intestine) blockage.
- had stomach surgery involving stapling or bypass.
- have an opening in the wall of your intestine (bowel perforation).
- have a severely inflamed colon (toxic colitis).
- have a very dilated intestine (toxic megacolon).
- are allergic to sodium phosphate salts or any of the ingredients in Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
What should I tell my doctor before taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
Before you take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have problems with serious loss of body fluid (dehydration) and changes in blood salts (electrolytes).
- have kidney problems.
- have heart problems.
- have a history of seizures.
- have had stomach surgery.
- have stomach or bowel problems.
- have ulcerative colitis.
- have problems with swallowing, gastric reflux, or if you inhale food or fluid into your lungs when eating or drinking (aspirate).
- are withdrawing from alcohol use.
- are withdrawing from the use of a type of medicine called a benzodiazepine.
- are on a low salt diet.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets while breastfeeding.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets may affect how other medicines work. Do not take medicines by mouth within 1 hour of starting each dose of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets or 1 hour after you start taking each dose of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- water pills (diuretics).
- medicines for blood pressure or heart problems.
- medicines for kidney problems.
- medicines for pain, such as aspirin or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
- medicine for seizures.
- a laxative for constipation. Do not take other laxatives while taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, especially a laxative or enema that contains sodium phosphate.
- medicine for depression or other mental health problem called a benzodiazepine.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take any of the medicines listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines to show your doctor or pharmacist when you get a new prescription.
How should I take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
- Take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- On the day before your colonoscopy , you can eat a light breakfast before 12:00 PM (noon). Examples of foods that you can eat include: clear liquids and plain yogurt. Do not eat any solid foods on the day before your colonoscopy. After your light breakfast, eat or drink only clear liquids until after your colonoscopy.
- It is important for you to drink plenty of clear liquids before, during, and after taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. This may help prevent kidney damage. Examples of clear liquids are:
- water
- clear soda
- clear broth soups
- gelatin (without added fruit or topping)
- herbal tea, black tea or coffee
- popsicles (without pieces of fruit or fruit pulp)
- watered down (diluted) (from concentrate) clear white grape juice
- strained limeade or lemonade fruit juices (without pulp) including apple juice or
- Eat or drink only clear liquids after 12:00 PM (noon) on the day before your colonoscopy until after your colonoscopy.
- Do not eat solid food starting on the day before your colonoscopy until after your colonoscopy.
- Do not eat or drink alcohol, milk, anything colored red or purple or any foods that have pulp.
You must read, understand, and follow these instructions to take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets the right way:
On the evening before your colonoscopy, take a total of 20 Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, as follows: Step 1. Take 4 Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids.
Step 2. Wait 15 minutes.
Step 3. Take 4 more Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids.
Step 4. Repeat Steps 2 and 3 above, three more times. Make sure you wait 15 minutes after each time.
On the day of your colonoscopy, take a total of 12 Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets starting about 3 to 5 hours before your colonoscopy, as follows:
Step 1. Take 4 Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids.
Step 2. Wait 15 minutes
Step 3. Take 4 more Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids.
Step 4. Repeat Steps 2 and 3 one more time.
If you take too much Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, call your doctor or get medical help right away.
What should I avoid while taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
- Do not take other laxatives or enemas made with sodium phosphate while taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
- Do not use Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets if you have already used it in the last 7 days.
What are the possible side effects of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets can cause serious side effects, including:
- See "What is the most important information I should know about Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?"
- Changes in certain blood tests. Your doctor may do blood tests before and after you take Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets to check your levels of calcium, phosphate, potassium, and sodium in your blood. Tell your doctor if you have any symptoms of too much fluid loss, including:
- vomiting o urinating less often than normal
- dizziness o headache
- Abnormal heartbeat (arrhythmias). Tell your doctor if you have an abnormal or irregular heartbeat while taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
- Seizures or fainting (loss of consciousness). People who take a medicine that contains sodium phosphate, such as Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets, can have seizures or faint even if they have not had seizures before. Tell your doctor right away if you have a seizure or faint while taking Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
- Sores (ulcers) in the lining of the colon. Tell your doctor right away if you have severe stomach-area (abdomen) pain or rectal bleeding.
- Serious allergic reaction. Get emergency medical care right away if you have symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including:
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat o dizziness or lightheadedness
- problems breathing or wheezing o skin rash
- throat tightness o raised red patches on your skin (hives)
- fainting
- The most common side effects of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are:
- bloating stomach (abdominal) pain
- nausea vomiting
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
- Store Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets at room temperature, between 68° F to 77° F (20° C to 25° C).
- Throw away any Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets that is not needed.
Keep Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets to other people, even if they are going to have the same procedure that you are. It may harm them. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets?
Active ingredients: monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate
Inactive ingredients: polyethylene glycol 8000 and magnesium stearate.
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets is gluten-free.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Novel Laboratories, Inc.
Somerset, NJ 08873
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Baltimore, MD 21202
SAP Code: 265501
Iss. 05/2020
| MONOBASIC SODIUM PHOSPHATE AND DIBASIC SODIUM PHOSPHATE
monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Lupin Pharmaceuticals,Inc. (089153071) |
| Registrant - Novel Laboratories, Inc. (793518643) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novel Laboratories, Inc. | 793518643 | ANALYSIS(43386-030) , MANUFACTURE(43386-030) , PACK(43386-030) | |
More about sodium biphosphate / sodium phosphate
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (120)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: laxatives