Shoulder Dislocation
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
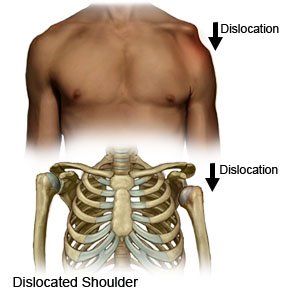
A shoulder dislocation
happens when the top of your arm bone (humerus) moves out of the socket in your shoulder blade.
 |
Common signs and symptoms:
- Shoulder and arm pain that worsens with movement
- A bump in front of or behind your shoulder
- Different shapes for each shoulder
- Redness and swelling in your shoulder
- Muscle spasms in your shoulder
- Weakness, numbness, or tingling in your shoulder and arm
Seek care immediately if:
- Your shoulder and arm become pale or cold.
- You cannot move your shoulder and arm.
- You have more redness or swelling in your shoulder.
- Your shoulder becomes dislocated again.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever.
- You have more pain in your shoulder and arm even after you rest and take your medicine.
- You have new weakness or numbness in your shoulder and arm.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment
depends on how badly your shoulder is dislocated, and if bone or tissue is damaged. You may need any of the following:
- Manual reduction is used to move your dislocated humerus back into place by hand. Weights may also be used to help pull your humerus into place.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Surgery may be needed to repair damaged tissues around your shoulder joint. You may also need a bone graft to repair your shoulder. A bone graft is artificial bone used to replace your damaged bone. You may also need surgery if your shoulder dislocates often.
Rest your shoulder and arm:
Rest helps your muscles and tissues heal. Avoid activities that cause pain or use an overhead arm motion. Your healthcare provider will tell you when it is safe to return to sports or other daily activities.
A sling, splint, or brace
may be needed after your shoulder dislocation is treated. A sling or splint will limit shoulder movement while supporting it. A brace protects your shoulder from injury after treatment.
 |
- Wear your brace, sling, or splint all the time. Take it off only to bathe or do exercises as directed. Ask your healthcare provider how many weeks you should wear it.
- Keep your skin clean and dry. Place padding under your armpit to help absorb sweat and prevent sores on your skin.
- Do not hunch your shoulders. This may cause pain. Keep your shoulders relaxed.
- Support your wrist and hand with the sling. Cover the knuckles on your hand with your sling. Your wrist should be positioned higher than your elbow. Your wrist may start to hurt or go numb if your sling is too short.
Apply ice:
Ice helps decrease swelling and pain. Ice may also help prevent tissue damage. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel before you place it on your shoulder. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed.
Exercises:
Begin gentle exercises as directed. After healing begins, you may start light exercises so your shoulder does not get stiff. Go to physical therapy if directed. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain. Do not lift heavy objects or do any exercise that causes severe pain.
Follow up with your doctor in 5 to 10 days:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Shoulder Dislocation
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
