RhoGAM Ultra-Filtered PLUS Dosage
Generic name: HUMAN RHO(D) IMMUNE GLOBULIN 300ug
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Immune globulins
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 24, 2023.
For intramuscular use only.
Dose
Pregnancy and other obstetrical conditions
| Dose | Indication | Notes* |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| RhoGAM (300 µg) (1500 IU) |
Postpartum (if the newborn is Rh-positive) Administer within 72 hours of delivery. |
Additional doses of RhoGAM are indicated when the patient has been exposed to > 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. This may be determined by use of qualitative or quantitative tests for fetal-maternal hemorrhage. |
Antepartum:
|
If antepartum prophylaxis is indicated, it is essential that the mother receive a postpartum dose if the infant is Rh-positive. If RhoGAM is administered early in pregnancy (before 26 to 28 weeks), there is an obligation to maintain a level of passively acquired anti-D by administration of RhoGAM at 12-week intervals. |
|
| MICRhoGAM (50 µg) (250 IU) |
Actual or threatened termination of pregnancy (spontaneous or induced) up to and including 12 weeks gestation Administer within 72 hours |
RhoGAM may be administered if MICRhoGAM is not available. |
- Administer RhoGAM every 12 weeks starting from first injection to maintain a level of passively acquired anti-D.
- If delivery occurs within three weeks after the last antepartum dose, the postpartum dose may be withheld, but a test for fetal-maternal hemorrhage should be performed to determine if exposure to > 15 mL of red blood cells has occurred.
- If delivery of the baby does not occur 12 weeks after the administration of the standard antepartum dose (at 26 to 28 weeks), a second dose is recommended to maximize protection antepartum.
RhoGAM dosage
Each single dose prefilled syringe of RhoGAM contains 300 μg (1500 IU) of Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human). This is the dose for the indications associated with pregnancy at or beyond 13 weeks unless there is clinical or laboratory evidence of a fetal-maternal hemorrhage (FMH) in excess of 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells.
MICRhoGAM dosage
Each single dose prefilled syringe of MICRhoGAM contains 50 μg (250 IU) of Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human). This dose will suppress the immune response to up to 2.5 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. MICRhoGAM is indicated within 72 hours after termination of pregnancy up to and including 12 weeks gestation. At or beyond 13 weeks gestation, RhoGAM should be administered instead of MICRhoGAM.
Multiple Dosage
Multiple doses of RhoGAM are required if a FMH exceeds 15 mL, an event that is possible but unlikely prior to the third trimester of pregnancy and is most likely at delivery. Patients known or suspected to be at increased risk of FMH should be tested for FMH by qualitative or quantitative methods.3 In efficacy studies, RhoGAM was shown to suppress Rh immunization in all subjects when given at a dose of > 20 μg per mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. Thus, a single dose of RhoGAM will suppress the immune response after exposure to < 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. However, in clinical practice, laboratory methods used to determine the amount of exposure (volume of transfusion or FMH) to Rh-positive red blood cells are imprecise. Therefore, administration of more than 20 μg of RhoGAM per mL of Rh-positive red blood cells should be considered whenever a large FMH or red blood cell exposure is suspected or documented. Multiple doses may be administered at the same time or at spaced intervals, as long as the total dose is administered within three days of exposure.1
Transfusion of Rh-incompatible blood or blood products
Administer within 72 hours of suspected or proven exposure to Rh-positive red blood cells.
| Dose | Indication | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| MICRhoGAM (50 µg) (250 IU) |
< 2.5 mL Rh-positive red blood cells | RhoGAM may be administered if MICRhoGAM is not available. |
| RhoGAM (300 µg) (1500 IU) |
2.5 - 15.0 mL Rh-positive red blood cells | |
| RhoGAM (300 µg) (1500 IU) (multiple syringes) |
> 15.0 mL Rh-positive red blood cells | Additional doses of RhoGAM are indicated when the patient has been exposed to > 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. Administer 20 µg of RhoGAM per mL of Rh-positive red blood cell exposure, rounding up to the next whole syringe. Multiple doses may be administered at the same time or at spaced intervals, as long as the total dose is administered within three days of exposure. |
Administration
- Visually inspect RhoGAM and MicRhoGAM for particulate matter, discoloration and syringe damage prior to administration.
- Do not use if particulate matter is observed.
- RhoGAM and MicRhoGAM are clear or slightly opalescent. Do not use if discolored.
- Administer injection per standard protocol.
| Note: When administering RhoGAM intramuscularly, place fingers in contact with glass syringe barrel through windows in shield to prevent possible premature activation of safety guard. | 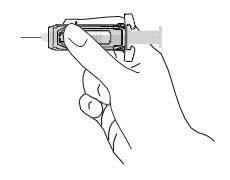 |
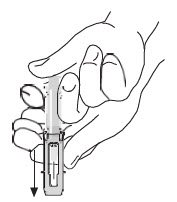 |
After injection, to engage the safety guard, use free hand to slide safety guard over needle. An audible "click" indicates proper activation. Keep hands behind needle at all times. Dispose of the syringe in accordance with local regulations. |
As with all blood products, patients should be observed for at least 20 minutes following administration of RhoGAM or MICRhoGAM.
More about RhoGAM Ultra-Filtered Plus (rho (d) immune globulin)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: immune globulins
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Patient resources
Other brands
RhoGAM, Rhophylac, HyperRHO S/D Full Dose, WinRho SDF, ... +4 more
Professional resources
Other brands
Rhophylac, HyperRHO S/D Full Dose, HyperRHO S/D Mini-Dose
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.

