Cetylev Dosage
Generic name: acetylcysteine 500mg
Dosage form: tablet, effervescent
Drug class: Antidotes
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 10, 2024.
Pretreatment Assessment and Testing Following Acute Acetaminophen Ingestion
The following recommendations are related to acute acetaminophen ingestion. For recommendations related to repeated supratherapeutic exposure see Dosage and Administration (2.4).
- Assess the history and timing of acetaminophen ingestion as an overdose.
- The reported history of the quantity of acetaminophen ingested as an overdose is often inaccurate and is not a reliable guide to therapy.
- Obtain the following laboratory tests to monitor hepatic and renal function and electrolyte and fluid balance: aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), bilirubin, international normalized ratio (INR), creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), blood glucose, and electrolytes.
- Obtain a plasma or serum sample to assay for acetaminophen concentration at least 4 hours after ingestion. Acetaminophen concentrations obtained earlier than 4 hours post-ingestion may be misleading as they may not represent maximum acetaminophen concentrations.
- If the time of acute acetaminophen ingestion is unknown:
- Administer a loading dose of CETYLEV immediately [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
- Obtain an acetaminophen concentration to determine need for continued treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- If the acetaminophen concentration cannot be obtained (or is unavailable or uninterpretable) within the 8-hour time interval after acetaminophen ingestion or there is clinical evidence of acetaminophen toxicity:
- Administer a loading dose of CETYLEV immediately and continue treatment for a total of 17 doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- If the patient presents more than 8 hours after ingestion and the time of acute acetaminophen ingestion is known:
- Administer a loading dose of CETYLEV immediately [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Obtain acetaminophen concentration to determine need for continued treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- If the patient presents less than 8 hours after ingestion and the time of acute acetaminophen ingestion is known and the acetaminophen concentration is known:
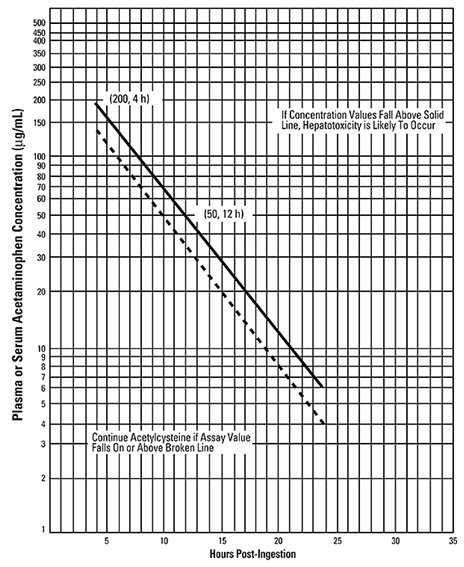
- Use the Rumack-Matthew nomogram (Figure 1) to determine whether or not to initiate treatment with CETYLEV [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Nomogram for Estimating Potential for Hepatotoxicity from Acute Acetaminophen Ingestion and Need for CETYLEV Treatment
If the timing of the acute acetaminophen ingestion is known and the results of the acetaminophen assay are available within 8 hours:
- Refer to the Rumack-Matthew nomogram (see Figure 1) to determine whether or not to initiate treatment with CETYLEV.
- Initiation of CETYLEV depends on the acetaminophen concentration and also the clinical presentation of the patient.
The nomogram may underestimate the hepatotoxicity risk in patients with chronic alcoholism, malnutrition, or CYP2E1 enzyme inducing drugs (e.g., isoniazid), and consideration should be given to treating these patients even if the acetaminophen concentrations are in the nontoxic range.
Loading Dose
For patients whose acetaminophen concentrations are at or above the "possible" toxicity line (dotted line in nomogram):
- Administer a loading dose of CETYLEV [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
For patients with an acute overdose due to an extended-release acetaminophen, if the acetaminophen concentration at 4 hours post ingestion is below the possible toxicity line then obtain a second sample for acetaminophen concentration 8 to 10 hours after the acute ingestion. If the second value is at or above the "possible" toxicity line (dotted line in nomogram):
- Administer a loading dose of CETYLEV [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
For patients whose values are below the "possible" toxicity line, but time of ingestion was unknown or sample was obtained less than 4 hours after ingestion:
- Administer a loading dose of CETYLEV [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
For patients whose values are below the "possible" toxicity line and time of ingestion is known and the sample was obtained more than 4 hours after ingestion, do not administer CETYLEV because there is minimal risk of hepatotoxicity.
| Figure 1: Rumack-Matthew Nomogram for Estimating Potential for Hepatotoxicity from Acetaminophen Poisoning – Plasma or Serum Acetaminophen Concentration versus Time (hours) Post-acetaminophen Ingestion (Adapted from Rumack and Matthew, Pediatrics 1975; 55:871−876.) | |
 |
|
Maintenance Dose
Determine need for continued treatment with CETYLEV after the loading dose. Choose ONE of the following based on the acetaminophen concentration:
The acetaminophen concentration is above the possible toxicity line according to the nomogram (see Figure 1):
- Continue CETYLEV treatment with the maintenance dose for 17 doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Monitor hepatic and renal function and electrolytes throughout treatment.
The acetaminophen concentration could not be obtained:
- Continue CETYLEV treatment with the maintenance dose for 17 doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Monitor hepatic and renal function and electrolytes throughout treatment.
For patients whose acetaminophen concentration is below the "possible" toxicity line (see Figure 1) and time of ingestion is known and the sample was obtained more than 4 hours after ingestion:
- Discontinue CETYLEV.
The acetaminophen concentration was in the non-toxic range, but time of ingestion was unknown or less than 4 hours:
- Obtain a second sample for acetaminophen concentration and consider the patient's clinical status to decide whether or not to continue CETYLEV treatment.
- If there is any uncertainty as to patient's risk of developing hepatotoxicity, it is recommended to administer a complete treatment course under medical observation with appropriate monitoring.
Continued Therapy After Completion of Loading and Maintenance Doses
In cases of suspected massive overdose, or with concomitant ingestion of other substances, or in patients with preexisting liver disease; the absorption and/or the half-life of acetaminophen may be prolonged. In such cases, consideration should be given to the need for continued treatment with CETYLEV beyond a total of 17 maintenance doses.
Acetaminophen levels and ALT/AST and INR should be checked after the last maintenance dose. If acetaminophen levels are still detectable, or if the ALT/AST are still increasing or the INR remains elevated; the maintenance doses should be continued and the treating physician should contact a US regional poison center at 1-800-222-1222, or alternatively, a "special health professional assistance line for acetaminophen overdose" at 1-800-525-6115 for assistance with dosing recommendations.
Recommended Dosage and Preparation and Administration Instructions in Adults and Pediatrics for Acute Acetaminophen Ingestion
- CETYLEV is for oral administration only; not for nebulization or intratracheal instillation.
- After appropriate preparation and dilution, CETYLEV is interchangeable with 20% acetylcysteine solution, when given at the same acetylcysteine dosage.
- Adults and Pediatrics: The recommended loading dose of CETYLEV is 140 mg/kg. Administer a first maintenance dose of 70 mg/kg 4 hours after the loading dose. Repeat 70 mg/kg maintenance dose every 4 hours for a total of 17 maintenance doses.
Preparation and Administration Instructions
- Dissolve the appropriate number of 2.5 gram and/or 500 mg CETYLEV effervescent tablets in the volume of water indicated in dosing tables and text below, based upon patient weight.
- Once the tablets are dissolved, administer the oral solution immediately.
- Solutions should be freshly prepared for each dose and utilized within 2 hours.
- If the patient vomits an oral dose of CETYLEV within 1 hour of administration, repeat that dose.
- If the patient is persistently unable to retain the orally administered acetylcysteine, CETYLEV may be administered by nasoduodenal tube. An intravenous formulation of acetylcysteine may also be considered.
Patients Weighing 20 kg and Greater
Tables 1 and 2 provide the weight-based loading and maintenance doses, respectively, of CETYLEV for patients weighing 20 kg and greater. For patients weighing 20 to 59 kg dissolve CETYLEV tablets in 150 mL of water. For patients weighing 60 kg and greater dissolve CETYLEV tablets in 300 mL of water.
| *No specific studies have been conducted to evaluate the necessity of dose adjustments in patients weighing over 100 kg. Limited information is available regarding the dosing requirements of patients that weigh more than 100 kg. | |||
| Dissolve CETYLEV Tablets in 300 mL of Water | |||
| Body weight (Kg) |
Actual Acetylcysteine Dose to be Administered (grams) |
Number of CETYLEV Tablets to Dissolve in Water | |
| 2.5 gram tablets | 500 mg tablets | ||
| 100 or greater | 15 | 6 | 0 |
| 90 to 99 | 14 | 5 | 3 |
| 80 to 89 | 13 | 5 | 1 |
| 70 to 79 | 11 | 4 | 2 |
| 60 to 69 | 10 | 4 | 0 |
| Dissolve CETYLEV Tablets in 150 mL of Water | |||
| 50 to 59 | 8 | 3 | 1 |
| 40 to 49 | 7 | 2 | 4 |
| 30 to 39 | 6 | 2 | 2 |
| 20 to 29 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
|
|||
| Dissolve CETYLEV Tablets in 300 mL of Water | |||
| Body weight (Kg) |
Actual Acetylcysteine Dose to be Administered (grams) |
Number of CETYLEV Tablets to Dissolve in Water | |
| 2.5 gram tablets | 500 mg tablets | ||
| 100 or greater* | 7.5 | 3 | 0 |
| 90 to 99 | 7 | 2 | 4 |
| 80 to 89 | 6.5 | 2 | 3 |
| 70 to 79 | 5.5 | 2 | 1 |
| 60 to 69 | 5 | 2 | 0 |
| Dissolve CETYLEV Tablets in 150 mL of Water | |||
| 50 to 59 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| 40 to 49 | 3.5 | 1 | 2 |
| 30 to 39 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 20 to 29 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
Patients Weighing 1 to 19 kg
Dissolve two 2.5 gram CETYLEV effervescent tablets in 100 mL of water to create a 50 mg/mL solution. Calculate the loading and maintenance doses using the patient's kilogram weight:
Recommendations for Repeated Supratherapeutic Acetaminophen Ingestion
Repeated supratherapeutic acetaminophen ingestion (RSI) is an ingestion of acetaminophen at dosages higher than those recommended for extended periods of time. The risk of hepatotoxicity and the recommendations for treatment of acute acetaminophen ingestion (i.e., the Rumack-Matthew nomogram) do not apply to patients with RSI. Therefore, obtain the following information to guide CETYLEV treatment for RSI.
- Acetaminophen serum or plasma concentrations. A reported history of the quantity of acetaminophen ingested is often inaccurate and is not a reliable guide to therapy.
- Laboratory tests to monitor hepatic and renal function and electrolyte and fluid balance: AST, ALT, bilirubin, INR, creatinine, BUN, blood glucose, and electrolytes.
For specific CETYLEV dosage and administration information in patients with RSI, consider contacting your regional poison center at 1-800-222-1222, or alternatively, a special health professional assistance line for acetaminophen overdose at 1-800-525-6115.
Frequently asked questions
More about Cetylev (acetylcysteine)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Imprints, shape & color data
- Side effects
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: antidotes
- Breastfeeding
Patient resources
Other brands
NAC, Mucomyst, Acetadote, N-A-C Sustain, Acys-5
Professional resources
Other brands
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
