Traumatic Pneumothorax
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
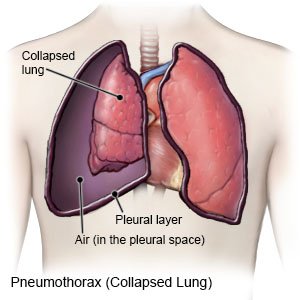
A traumatic pneumothorax is a collapsed lung. All or part of your lung may collapse. A traumatic pneumothorax is caused by an injury that tears your lung and allows air to enter the pleural space. The pleural space is the area between your lungs and your chest wall. The air trapped in your pleural space prevents your lung from filling, and it collapses. A pneumothorax can happen in one or both lungs.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone call if:
- You have new or increased shortness of breath or chest pain.
- Your throat or the front of your neck is pushed to one side.
- You are sweating and feel like you are going to pass out.
- Your fingernails, toenails, or lips begin to turn blue.
- You have trouble thinking clearly.
Call your doctor or pulmonologist if:
- You have a fever.
- You hear a crackling noise or feel popping when you touch your skin.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Antibiotics help prevent or treat a bacterial infection.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Breathing exercises:
You may need to do breathing exercises to strengthen your lungs. Ask your healthcare provider how to do these exercises, and how long you should do them.
Do not smoke:
Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can increase your risk for another pneumothorax. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes and smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
For your safety:
A change of pressure could cause another pneumothorax. Follow these and other safety precautions from your healthcare provider:
- Do not dive under water or climb to high altitudes.
- Do not fly if you have an untreated or recurring pneumothorax.
Follow up with your doctor or pulmonologist as directed:
You may need to return for more chest x-rays. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Traumatic Pneumothorax
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
