Short Bowel Syndrome
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Short bowel syndrome
is a condition that prevents your intestines from absorbing nutrients. Short bowel syndrome occurs when the intestine is shorter than normal or does not work the way it should. You may have been born with a short bowel. Causes include tumors, radiation, infections, surgery to remove part of the intestine, and conditions such as Celiac disease.
 |
Common signs and symptoms of short bowel syndrome:
Diarrhea is the most common symptom of short bowel syndrome. You may also have any of the following:
- Abdominal cramps
- Bloated abdomen
- Rapid weight loss
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Rash around your rectum
Seek care immediately if:
- You have severe abdominal pain.
- Your bowel movements are dark or have blood in them.
- You are lightheaded and feel like you are going to faint.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever.
- You feel achy, or have chills, weakness, or a cough.
- Your abdominal pain does not go away, even after treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment
may include any of the following:
- Medicines may help treat or prevent a bacterial infection, diarrhea, or too much stomach acid. You may also need vitamin and mineral supplements because your intestines cannot absorb these nutrients from food.
- Surgery may be needed if your intestines become blocked or your bowel is very short. Healthcare providers will lengthen your bowel or remove the blockage. You may need a bowel transplant.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Nutrition
may depend on the cause of your short bowel syndrome or how much bowel is left. You may need to meet with a dietitian to talk about the best foods for you.
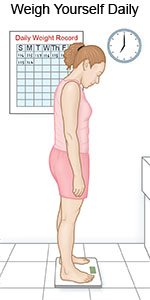
Weigh yourself daily before breakfast:
Record your weight in a journal. Healthcare providers may need to compare your weight from day to day. This helps them determine the amount of body fluid you have. If you lose too much body fluid, you can become dehydrated. If you have too much body fluid, you may have trouble breathing. Ask what your weight should be.
 |
Follow up with your doctor or gastroenterologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Short Bowel Syndrome
Treatment options
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
