Jaundice in Newborns
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Jaundice
is yellowing of your newborn's eyes and skin. It is caused by too much bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow substance found in red blood cells. It is released when the body breaks down old red blood cells. Bilirubin usually leaves the body through bowel movements. Jaundice happens because your newborn's body breaks down cells correctly, but it cannot remove the bilirubin. Jaundice is common in newborns. It usually happens during the first week of life.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your newborn has a seizure, or you cannot wake him or her.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your newborn has a fever.
- Your newborn is limp (too weak to move).
- Your newborn moves his or her legs in a cycling motion.
- Your newborn changes his or her sleep patterns.
- Your newborn has trouble feeding, or he or she will not feed at all.
- Your newborn is cranky, hard to calm, arches his or her back, or has a high-pitched cry.
Call your newborn's pediatrician if:
- Your newborn has new or worsened yellow skin or eyes.
- You think your newborn is not drinking enough breast milk, or he or she is losing weight.
- Your newborn has pale, chalky bowel movements.
- Your newborn has dark urine that stains his or her diaper.
Treatment
may not be needed. Jaundice often goes away on its own. If it continues or becomes severe, your newborn may need treatment. This may happen at home or in the hospital. You will be able to stay with him or her in the hospital so you can continue to breastfeed. Treatment for jaundice includes the following:
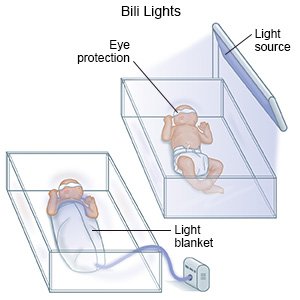
- Phototherapy is a procedure that uses light to turn bilirubin into a form that your newborn's body can remove. One or more lights will be placed above your newborn. He or she will be placed on his or her back to absorb the most light. Your newborn may also lie on a flexible light pad, or his or her healthcare provider may wrap him or her in the light pad. Eye covers may be used to protect his or her eyes from the light. Do not put your newborn in direct sunlight. He or she may get a sunburn or become dehydrated. The only light therapy your newborn should have is phototherapy guided by a healthcare provider.
- Exchange transfusion is a procedure used to replace part of your newborn's blood with blood from a donor. This will be done in the hospital and may be used if your newborn has severe jaundice.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Breastfeed
your newborn as early and as often as possible. Talk to your newborn's healthcare provider about using formula along with breast milk if you do not produce enough breast milk alone. Look for signs of thirst in your newborn, such as lip smacking and restlessness. Try to breastfeed 8 to 12 times daily for the first few days to boost your milk supply. Ask your healthcare provider for help if you have trouble breastfeeding.
Follow up with your newborn's pediatrician as directed:
You may need to follow up with a pediatrician 2 to 3 days after you leave the hospital, following your newborn's birth. Ask for a specific follow-up time. Your newborn may need more blood tests to check his or her bilirubin levels. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
For more information:
- American Academy of Pediatrics
345 Park Boulevard
Itasca , IL 60143
Phone: 1- 800 - 433-9016
Web Address: http://www.aap.org
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Jaundice in Newborns
Treatment options
- Medications for Central Nervous System Disorders
- Medications for Hemolytic Anemia
- Medications for Liver Disease
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
