Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips (Canada)
This page contains information on Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips for veterinary use.The information provided typically includes the following:
- Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips Indications
- Warnings and cautions for Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips
- Direction and dosage information for Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips
Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips
This treatment applies to the following species:SUMMARY
Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips for Urinalysis are firm plastic strips to which several different reagent areas are affixed. Teco Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips provide tests for Glucose, Bilirubin, Ketone (Acetoacetic acid), Specific Gravity, Blood, pH, Protein, Urobilinogen, and Nitrite in Urine. Test results may provide information regarding the status of carbohydrate metabolism, kidney and liver function, acid-base balance, and bacteriuria. Teco Vet-10 Urine Reagent Strips are packaged along with a drying agent in a plastic bottle with a twist-off cap. Each strip is stable and ready to use upon removal from the bottle. The entire reagent strip is disposable. Results are obtained by direct comparison of the test strip with the color blocks printed on the bottle label. No calculations or laboratory instruments are required.
TEST PRINCIPLE
Glucose: This test is based on a double sequential enzyme reaction. One enzyme, glucose oxidase, catalyzes the formation of gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide from the oxidation of glucose. A second enzyme, peroxidase, catalyzes the reaction of hydrogen peroxide with potassium iodide chromogen to oxidize the chromogen to colors ranging from blue-green to greenish-brown through brown and dark brown.
Bilirubin: This test is based on the coupling of bilirubin with a diazotized dichloroaniline in a strongly acid medium. The colors range from light tan to reddish-brown.
Ketone: This test is based on the reaction of acetoacetic acid with sodium nitroprusside in a strongly basic medium. The colors range from beige or buff-pink color for a “Negative” reading to pink and pink-purple for a “Positive” reading.
Specific Gravity: This test is based on the apparent pKa change of certain pretreated polyelectrolytes in relation to the ionic concentration. In the presence of an indicator, the colors range from dark blue or blue-green in urine of low ionic concentration to green and yellow-green in urine of higher ionic concentration.
Blood: This test is based on the pseudoperoxidase action of hemoglobin and erythrocytes which catalyzes the reaction of 3,3’, 5, 5’-tetramethyl-benzidine and buffered organic peroxide. The resulting colors range from orange to yellow-green and dark green. Very high blood concentration may cause the color development to continue to dark blue.
pH: This test is based on the well known double pH indicator method, where bromothymol blue and methyl red give distinguishable colors over the pH range of 5-9. The colors range from red-orange to yellow and yellow-green to blue-green.
Protein: This test is based on the protein error-of-indicator principle. At a constant pH, the development of any green color is due to the presence of protein. Colors range from yellow for a “Negative” reaction to yellow-green and green to blue-green for a “Positive” reaction.
Urobilinogen: This test is based on a modified Ehrlich reaction in which p-diethylaminobenzaldehyde reacts with urobilinogen in a strongly acid medium. Colors range from light pink to bright magenta.
Nitrite: This test depends on the conversion of nitrate to nitrite by the action of Gram-negative bacteria in the urine. The nitrite reacts with p-arsanilic acid to from a diazonium compound in an acid medium. The diazonium compound in turn couples with 1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo(h) quinolin to produce a pink color.
Leukocytes: This test is based on the action of esterase present in leukocytes, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of an indoxyl ester derivative. The indoxyl ester liberated reacts with a diazonium salt to produce a beige-pink to purple color.
REAGENTS
(Based on dried weight at time of impregnation)
Glucose: 16.3%w/w glucose oxidase (Aspergillus niger, 1.3IU); 0.6%w/w peroxidase (horseradish, 3300 IU); 7.0% w/w potassium iodide; 76.1% w/w buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
Bilirubin: 0.4% w/w 2,4-dichloroaniline diazonium salt, balanced with buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
Ketone: 7.7% w/w sodium nitroprusside balanced with buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
Specific Gravity: 0.2% w/w bromothymol blue, 99.8% buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
Blood: 6.6% w/w cumene hydroperoxide; 4.0% w/w 3, 3’, 5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine; 89.4% w/w buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
pH: 0.2% w/w methyl red; 2.8% w/w bromothymol blue; 97% w/w non-reactive ingredients.
Protein: 0.3% w/w tetrabromophenol blue; 99.7% w/w buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
Urobilinogen: 2.9% w/w p-diethylaminobenzaldehyde balanced with buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
Nitrite: 1.4% w/w p-arsanilic acid, balanced with buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
Leukocytes: 0.4% w/w indoxyl ester derivative; 0.2%w/w diazonium salt; 99.4% w/w buffer and non-reactive ingredients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Do not touch test areas of Urine Reagent Strips.
STORAGE
Store at room temperature between 15°-30°C(59°-86°F) and out of direct sunlight. Do not use after expiration date.
RECOMMENDED HANDLING PROCEDURES
All unused strips must remain in the original bottle. Transfer to any container may cause reagent strips to deteriorate and become non-reactive. Do not remove desiccant from bottle. Do not open container until ready to use. Opened bottles should be used within 3 months after first opening.
SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND PREPARATION
Collect urine in a clean container and test as soon as possible. Do not centrifuge. The use of urine preservatives is not recommended. If testing cannot be performed within one hour after voiding, refrigerate the specimen immediately. Allow refrigerated specimen to return to room temperature before testing.
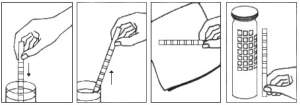
TEST PROCEDURE
1. Remove from the bottle only enough strips for immediate use and replace cap tightly.
2. Completely immerse reagent areas of the strip in fresh, well-mixed urine. Remove the strip immediately to avoid dissolving out the reagent areas.
3. While removing, touch the side of the strip against the rim of the urine container to remove excess urine. Blot the lengthwise edge of the strip on an absorbent paper towel to further remove excess urine and avoid running over (contamination from adjacent reagent pads.)
4. Compare each reagent area to its corresponding color block on the color chart and read at the times specified. Proper read time is critical for optimal results.
5. Obtain results by direct color chart comparison.
RESULTS
Results are obtained by direct comparison of the color blocks printed on the bottle label. The color blocks represent nominal values; actual values will vary around the nominal values.
LIMITATIONS OF PROCEDURE
Comparison to the color chart is dependent on the interpretation of the individual. It is therefore, recommended that all laboratory personnel interpreting the results of these strips be tested for color blindness. As with all laboratory tests, definitive diagnostic or therapeutic decisions should not be based on any single test result or method.
EXPECTED VALUES
Glucose: Small amounts of glucose are normally excreted by the kidney. Concentrations as little as 0.1 g/dl glucose, read either at 10 or 30 seconds, may be significantly abnormal if found consistently. At 10 seconds, results should be interpreted qualitatively; for semi-quantitative results, read at 30 seconds only.
Bilirubin: Normally, no bilirubin is detectable in urine by even the most sensitive method. Even trace amounts of bilirubin are sufficiently abnormal to require further investigation. Atypical colors (colors produced which are different than the negative or positive color blocks shown on the Color Chart) may indicate that bilirubin derived bile pigments are present in the urine sample and are possibly masking the bilirubin reaction.
Ketone: Normally, no ketones are present in urine. Detectable levels of ketone may occur in urine during physiological stress conditions such as pregnancy and frequent strenuous exercise. In starvation diets, or in other abnormal carbohydrate metabolism situations, ketones appear in the urine in excessively large amounts before serum ketones are elevated.
Specific Gravity: Random urine may vary in specific gravity from 1.003-1.060+ and can vary greatly between species.
Blood: Any green spots or green color developing on the reagent area within 40 seconds is significant and the urine should be examined further. Blood is frequently, but not invariably found in the urine of menstruating females.
pH: Urine pH will be affected by many things including the diet, handling of the sample, and acid-base balance of the animal. An alkaline pH is most indicative of an infectious process. Normal pH is between 6 and 8 for most animals depending on their diet.
Protein: In 24-hour urine, 1-14 mg/dl of protein may be excreted by the normal kidney. A color matching any color block greater than trace indicates significant proteinuria. For urine with high specific gravity, the test area may most closely match the trace color block even though only normal concentrations of protein are present. Clinical judgment is needed to evaluate the significance of trace results.
Urobilinogen: In a healthy population, the normal urine urobilinogen range obtained with this test is 0.2-1.0 Ehrlich Unit/dl. A result of 2.0 EU/dl may be of clinical significance and the same patient sample should be evaluated further.
Nitrite: Normally no detectable amount of nitrite is present in urine. The nitrite area will be positive in a proportion of cases of significant infection, depending on how long the urine specimens were retained in the bladder prior to collection. Retrieval of positive cases with the nitrite test range from as low as 40%, in instances where little bladder incubation occurred, to as high as 80% in instances where a minimum of 4 hours incubation occurred.
Leukocytes: Normal urine specimens generally yield negative results with this test. A trace result may be of questionable clinical significance and it is recommended that the test be repeated using a fresh sample from the same patient. Repeated trace and positive results are of clinical significance.
VET-10: 01/2004
TECO DIAGNOSTICS, 1268 N. Lakeview Ave., Anaheim, CA 92807
1-800-222-9880
Presentation: 100 strips per bottle.
CPN: 2031002.0
Distributed by SENSOR HEALTH VET DIAGNOSTICS
110 TURNBULL COURT, UNIT 6, CAMBRIDGE, ON, N1T 1K6
| Telephone: | 519-621-1515 | |
| Toll-Free: | 1-888-777-7080 | |
| Fax: | 519-621-8778 | |
| Website: | www.sensorhealthsciences.com | |
| Email: | info@sensorhealth.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |
Copyright © 2024 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2024-02-27
