Asymptomatic bacteriuria
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 17, 2023.
What is asymptomatic bacteriuria?

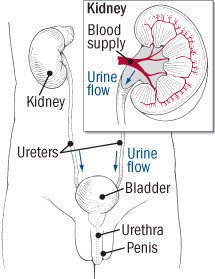
When a significant number of bacteria show up in the urine, this is called "bacteriuria." Finding bacteria in the urine can mean there is an infection somewhere in the urinary tract. The urinary tract is the system that includes:
- The kidneys, which make urine
- The ureters – thin tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder
- The bladder, where urine can be stored
- The urethra – the final pathway to move urine from the bladder to outside the body.
In asymptomatic bacteriuria, large numbers of bacteria are present in the urine. However, the person has no symptoms of a urinary tract infection (asymptomatic means without symptoms). It is not clear why the bacteria don't cause symptoms. It may be that asymptomatic bacteriuria is caused by weaker (less "virulent") bacteria. The condition does not always need to be treated.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is most common in:
- Elderly women
- People with diabetes
- People with bladder catheters.
Symptoms of asymptomatic bacteriuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria does not cause any symptoms.
Diagnosing asymptomatic bacteriuria
Your doctor will ask you to provide a clean-catch urine sample. You will be given a sterile container and instructions on how to clean the area around the urethra. Do not touch inside the container.
The urine sample will be sent to the laboratory where a urine culture is performed. The urine culture will determine if there are bacteria in your urine.
The diagnosis of asymptomatic bacteriuria requires:
- A urine culture that is positive for a large number of bacteria
- You do not have symptoms of a urinary tract infection.
Expected duration of asymptomatic bacteriuria
In some people, bacteria are present in the urine before symptoms of a urinary tract infection develop. If this occurs, your doctor will advise starting an antibiotic if symptoms arise. In other people, asymptomatic bacteriuria can continue indefinitely without causing obvious illness or discomfort.
Preventing asymptomatic bacteriuria
You may help prevent bacteriuria by drinking several glasses of water each day. This may discourage the growth of bacteria by flushing out your urinary tract, although this has not been proven. Drinking cranberry juice every day might also slow the growth of bacteria. But this also has not been definitively shown through medical studies.
To prevent the spread of intestinal bacteria from the rectum to the urinary tract, women should always wipe toilet tissue from front to back after having a bowel movement.
Treating asymptomatic bacteriuria
Antibiotic treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria is recommended for the following groups:
- Pregnant women
- People about to undergo surgery in any part of the urinary tract
- Men about to undergo prostate surgery.
When to call a professional
If you have asymptomatic bacteriuria, call your doctor if you
- Begin urinating more often than normal
- Develop an intense need to urinate
- Have pain during urination
- Develop pelvic pain, back pain, fevers or chills
- Your urine has blood in it, becomes discolored, cloudy or foul smelling.
Prognosis
For most people, asymptomatic bacteriuria does not cause any problems and treatment is not necessary. If you do develop a urinary tract infection, prompt treatment with antibiotics will almost always take care of it.
Additional info
National Kidney Foundation
https://www.kidney.org/
American Urological Association
https://www.urologyhealth.org/
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
