Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is a posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury?
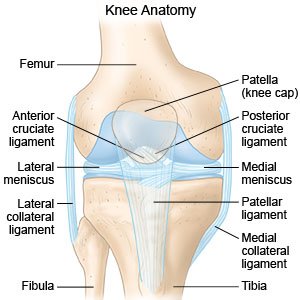
A PCL injury is a partial or complete tear of the ligament in the back of your knee. The PCL connects the tibia (shin bone) to the femur (thigh bone). The PCL stops the tibia from sliding too far backward or forward and keeps the knee stable.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of a PCL injury?
Unlike other ligament injuries, you will not hear a pop, snap, or tear when your PCL is injured. You may not have any signs or symptoms, or you may have any of the following:
- Sudden swelling or pain at the back of your knee
- Pain when you kneel
- Knee that gives way, causing a slight limp
- Pain when you run, or when you walk up or down steps
How is a PCL injury diagnosed?
Healthcare providers may test the function of your PCL by moving your knee, leg, or foot in different directions. They do this to look for changes in the position of the parts of your knee. This may show a PCL injury or injury to other knee ligaments. Both of your knees may be checked for any abnormal movement. You may need the following tests:
- An x-ray or MRI may be used to look for a PCL tear. You may be given contrast liquid to help the PCL show up better in pictures. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- Arthroscopy is a procedure used to look inside your knee for a PCL injury. A small incision is made in your knee and a scope is inserted. The scope is a long, bendable tube with a camera and light on the end.
How is a PCL injury treated?
You may only need physical therapy and supportive devices if your PCL injury is mild. You may need surgery if you have a PCL tear or damage to other knee ligaments. You may need any of the following:
- A support device such as a splint or knee brace helps limit movement and protects your knee. You may need to use crutches to help decrease your pain as you move around.
- Medicines:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Surgery may be needed. A PCL tear may be repaired by reattaching the torn ligament. You may need reconstruction if your PCL cannot be repaired. Your PCL can be replaced with tissue taken from another part of your body, or from a donor.
- Physical therapy may recommended. A physical therapist can teach you exercises to increase strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your toes are cold or numb.
- Your knee becomes more weak or unstable.
- Your pain has increased or returned, even after you take your pain medicine.
- Your swelling has increased or returned.
- Your symptoms are not getting better.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
