Endometriosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is endometriosis?
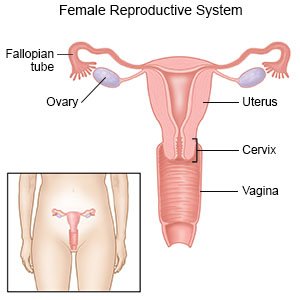
Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue that is normally only in your uterus grows outside of the uterus. Endometriosis causes tissue that should be shed during a monthly period to grow on your ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, or other organs. Organs and tissue may stick together and cause inflammation and pain.
 |
What increases my risk for endometriosis?
The cause of endometriosis may not be known. Any of the following may increase your risk:
- Monthly period that started early
- Older than 35 when you had your first child
- Menopause after age 55
- Born with a narrow cervix or vagina, or no opening of your cervix or vagina
- Family history of endometriosis
- A weak immune system
What are the signs and symptoms of endometriosis?
- Abdominal pain or nausea and vomiting before or during your period
- Painful periods
- Feeling full or bloated
- Dizziness or fatigue
- Heavy periods, or vaginal bleeding at times other than during your monthly period
- Infertility (being unable to get pregnant)
- Lower back pain or painful bowel movements during your monthly periods
- Pain during or after sex
- Pain when you urinate
How is endometriosis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask you questions about other medical conditions you may have. He or she may ask about your menstrual history, pregnancies, and if you have a family member with endometriosis. You may also have one or more of the following tests:
- A blood test can check for pregnancy, sexually transmitted infection, and anemia from blood loss.
- A pelvic exam may be needed to check the size and shape of your uterus, cervix, and ovaries. This may also help to find areas of endometriosis.
- A vaginal ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures of your uterus and ovaries on a monitor. An ultrasound may be done to show endometriosis.
- A CT or MRI may show the endometriosis. You may be given contrast liquid to help your abdomen show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- Laparoscopy is a procedure used to look inside your abdomen. A piece of tissue may be removed from your ovaries, fallopian tubes, bowels, or other organs. The tissues are sent to a lab for tests to see if endometriosis is present.
How is endometriosis treated?
- Medicines:
- Hormones may help shrink endometrial tissue and decrease pain and inflammation. You may be given birth control pills, androgen hormones, or medicine that makes your body produce less of certain hormones.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Surgery may be needed to determine if you have endometriosis. Endometrial tissue that is growing in the wrong places may be removed.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Apply heat on your abdomen for 20 to 30 minutes every 2 hours for as many days as directed. Heat helps decrease pain and muscle spasms.
- Exercise regularly to help reduce symptoms, such as pain. Ask about the best exercise plan for you.

Where can I find more information?
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
P.O. Box 70620
Washington , DC 20024-9998
Phone: 1- 202 - 638-5577
Phone: 1- 800 - 673-8444
Web Address: http://www.acog.org
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have severe pain that does not go away after you take pain medicine.
When should I contact my healthcare provider?
- Your symptoms return after treatment.
- You have heavy or unusual vaginal bleeding.
- You see blood in your urine or bowel movement.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Endometriosis
Treatment options
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
