Angina
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
Angina is pain, pressure, or tightness that is usually felt in your chest. Chest pain may come on when you are stressed or do physical activities, such as walking or exercising. Angina is caused by decreased blood flow and oxygen to your heart. These are often caused by atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). Angina can be a warning sign that you may be at risk for a heart attack.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone call if:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You have chest pain that does not go away after you take medicine as directed.
- You lose feeling in your face, arms, or legs, or you suddenly feel weak.
Return to the emergency department if:
- Your angina is happening more often, lasting longer, or causing worse pain.
Call your doctor or cardiologist if:
- You are dizzy or nauseated after you take your medicine.
- You have shortness of breath at rest.
- You have new or worse swelling in your feet or ankles.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
Do not take certain medicines without asking your healthcare provider first. These include NSAIDs, herbal or vitamin supplements, or hormones (estrogen or progestin). You may need any of the following:
- Antiplatelets , such as aspirin, help prevent blood clots. Take your antiplatelet medicine exactly as directed. These medicines make it more likely for you to bleed or bruise. If you are told to take aspirin, do not take acetaminophen or ibuprofen instead.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip does or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Other medicines may be given to open the arteries to your heart, slow your heartbeat, or decrease your blood pressure or cholesterol.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Cardiac rehabilitation:
Your healthcare provider may recommend that you attend cardiac rehabilitation (rehab). This is a program run by specialists who will help you safely strengthen your heart and prevent more heart disease. The plan includes exercise, relaxation, stress management, and heart-healthy nutrition. Healthcare providers will also check to make sure any medicines you are taking are working. The plan may also include instructions for when you can drive, return to work, and do other normal daily activities.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Manage angina:
- Keep a record or a calendar with details about your symptoms. Every time you have pain or other symptoms, describe it, how long it lasts, and how severe it is. Also describe what you were doing when the symptom started, and what made it go away. Bring this with you every time you see your healthcare provider.
- Avoid activities that cause angina. Pay attention to your symptoms and find out what seems to make your angina worse.
- Manage health conditions that can cause angina. Healthcare providers can help you manage a chronic health condition such as diabetes. Ask your provider for more information.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. Your healthcare provider can tell you which vaccines you need, and when to get them. The following vaccines help prevent certain diseases that can put more stress on your heart:
- The influenza (flu) vaccine is given each year. Get a flu vaccine as soon as recommended, usually in September or October.
- The pneumonia vaccine is usually given every 5 years. Your healthcare provider may recommend the pneumonia vaccine if you are 65 or older.
- COVID-19 vaccines are given to adults as a shot. At least 1 dose of an updated vaccine is recommended for all adults. COVID-19 vaccines are updated throughout the year. Adults 65 or older need a second dose of updated vaccine at least 4 months after the first dose. Your healthcare provider can help you schedule all needed doses as updated vaccines become available.
Healthy living tips:
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause heart and lung damage. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Maintain a healthy weight. When you weigh more than is healthy for you, your heart must work harder. You are at higher risk for serious health problems if you are overweight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask him or her to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
- Ask about physical activity. Physical activity, such as exercise, can help strengthen your heart. Your healthcare provider can help you create a safe physical activity plan.

- Choose a variety of heart-healthy foods as often as possible. Include fresh, frozen, or canned fruits and vegetables. Also include low-fat dairy products, fish, chicken (without skin), and lean meats. Your healthcare provider or a dietitian can help you create meal plans.
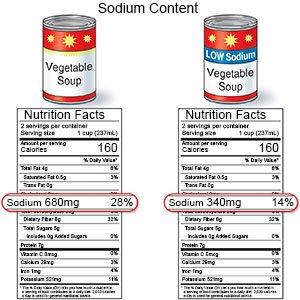
- Lower your sodium (salt) intake. Limit foods that are high in sodium, such as canned foods, salty snacks, and cold cuts. If you add salt when you cook food, do not add more at the table. Choose low-sodium canned foods as much as possible.
- Eat foods high in omega-3 fatty acids. Fish that are high in omega-3 fats include salmon, tuna, and herring. Other sources include broccoli, walnuts, and eggs.

 |
Follow up with your doctor or cardiologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Angina
- Heart / High Blood Pressure Medications with Alcohol
- Understanding Opioid (Narcotic) Pain Medications
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
