Low Back Strain
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is low back strain?
Low back strain is an injury to your lower back muscles or tendons. Tendons are strong tissues that connect muscles to bones. The lower back supports most of your body weight and helps you move, twist, and bend.
What causes low back strain?
Low back strain is usually caused by activities that increase stress on the lower back, such as exercise or injury. The following may increase your risk for low back strain:
- You have had low back strain before.
- You lift heavy objects with your back instead of your legs.
- You do not warm up before you exercise.
- You sit or stand for long periods of time.
- You are overweight.
What are the signs and symptoms of low back strain?
- Low back pain or muscle spasms
- Stiffness or limited movement
- Pain that goes down to the buttocks, groin, or legs
- Pain that is worse with activity
How is low back strain diagnosed?
An x-ray, CT scan, or MRI may be done to check for damage to your spine, muscles, or tendons. You may be given contrast liquid to help the tissues in your lower back show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is low back strain treated?
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Muscle relaxers help decrease pain and muscle spasms.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Surgery may be needed if your strain is severe.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Rest as directed. You may need to rest in bed for a period of time after your injury. Do not lift heavy objects.
- Apply ice on your back for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
- Apply heat on your lower back for 20 to 30 minutes every 2 hours for as many days as directed. Heat helps decrease pain and muscle spasms.
- Slowly start to increase your activity as the pain decreases, or as directed.
How can low back strain be prevented?
- Use correct body movements.
- Bend at the hips and knees when you pick up objects. Do not bend from the waist. Use your leg muscles as you lift the load. Do not use your back. Keep the object close to your chest as you lift it. Try not to twist or lift anything above your waist.

- Change your position often when you stand for long periods of time. Rest one foot on a small box or footrest, and then switch to the other foot often.
- Try not to sit for long periods of time. When you do, sit in a straight-backed chair with your feet flat on the floor.
- Never reach, pull, or push while you are sitting.
- Bend at the hips and knees when you pick up objects. Do not bend from the waist. Use your leg muscles as you lift the load. Do not use your back. Keep the object close to your chest as you lift it. Try not to twist or lift anything above your waist.
- Warm up before you exercise. Do exercises that strengthen your back muscles. Ask your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you.
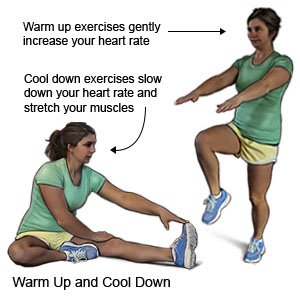
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider how much you should weigh. Ask him to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You hear or feel a pop in your lower back.
- You have increased swelling or pain in your lower back.
- You have trouble moving your legs.
- Your legs are numb.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- Your pain does not go away, even after treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Low Back Strain
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
