Laceration
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
A laceration
is an injury to the skin and the soft tissue underneath it. Lacerations can happen anywhere on the body.
Common symptoms include the following:
- Injury or wound to skin and tissue of any shape size that looks like a cut, tear, or gash
- Edges of the wound may be close together or wide apart
- Pain, bleeding, bruising, or swelling
- Numbness around the wound
- Decreased movement in an area below the wound
Seek care immediately if:
- You have heavy bleeding or bleeding that does not stop after 10 minutes of holding firm, direct pressure over the wound.
- Your wound opens up.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- Your laceration is red, warm, or swollen.
- You have red streaks on your skin coming from your wound.
- You have white or yellow drainage from the wound that smells bad.
- You have pain that gets worse, even after treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment for a laceration
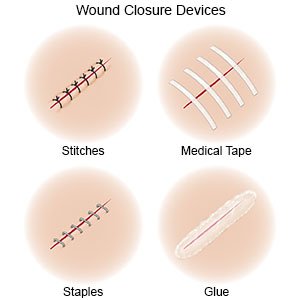
includes care to stop any bleeding. Your healthcare provider will stop the bleeding by applying pressure to the wound. He or she may need to check your wound for foreign objects and clean it to decrease the chance of infection. Your laceration may be closed with stitches, staples, tissue glue, or medical strips. Ask your healthcare provider if you need a tetanus shot.
 |
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent a bacterial infection.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for your wound as directed:
- Do not get your wound wet until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Do not soak your wound in water. Do not go swimming until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Carefully wash the wound with soap and water. Gently pat the area dry or allow it to air dry.
- Change your bandages when they get wet, dirty, or after washing. Apply new, clean bandages as directed. Do not apply elastic bandages or tape too tight. Do not put powders or lotions over your incision.
- Apply antibiotic ointment as directed. Your healthcare provider may give you antibiotic ointment to put over your wound if you have stitches. If you have strips of tape over your incision, let them dry up and fall off on their own. If they do not fall off within 14 days, gently remove them. If you have glue over your wound, do not remove or pick at it. If your glue comes off, do not replace it with glue that you have at home.
- Check your wound every day for signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, or pus.
Self-care:
- Apply ice on your wound for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
- Use a splint as directed. A splint will decrease movement and stress on your wound. It may help it heal faster. A splint may be used for lacerations over joints or areas of your body that bend. Ask your healthcare provider how to apply and remove a splint.
- Decrease scarring of your wound by applying ointments as directed. Do not apply ointments until your healthcare provider says it is okay. You may need to wait until your wound is healed. Ask which ointment to buy and how often to use it. After your wound is healed, use sunscreen over the area when you are out in the sun. You should do this for at least 6 months to 1 year after your injury.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You will need to return in 3 to 14 days to have stitches or staples removed. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Laceration
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
