Insect Bite or Sting
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What do I need to know about an insect bite or sting?
Most insect bites and stings are not dangerous and go away without treatment. Common examples of insects that bite or sting are bees, ticks, mosquitoes, spiders, and ants. Insect bites or stings can lead to diseases such as malaria, West Nile virus, Lyme disease, or Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever.
What are the signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction to an insect bite or sting?
- Mild symptoms include a red bump, pain, swelling, and itching.
- Anaphylaxis symptoms include throat tightness, trouble breathing, tingling, dizziness, and wheezing. Anaphylaxis is a sudden, life-threatening reaction that needs immediate treatment.
How is an allergic reaction to an insect bite or sting treated?
Treatment depends on how severe your symptoms are and if you had anaphylaxis before. You may need any of the following:
- Antihistamines decrease mild symptoms such as itching and rash.
- Epinephrine is medicine used to treat severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis.
- A tetanus shot may be given. The shot is a vaccine that helps prevent a bacterial infection. Tetanus booster shots are usually given every 10 years.
What steps do I need to take for signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis?
- Immediately give 1 shot of epinephrine only into the outer thigh muscle.
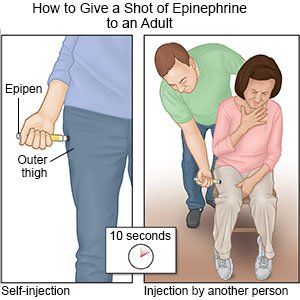
- Leave the shot in place as directed. Your healthcare provider may recommend you leave it in place for up to 10 seconds before you remove it. This helps make sure all of the epinephrine is delivered.
- Call 911 and go to the emergency department, even if the shot improved symptoms. Do not drive yourself. Bring the used epinephrine shot with you.
What should I do if an insect bites or stings me?
- Remove the stinger. Scrape the stinger out with your fingernail, edge of a credit card, or a knife blade. Do not squeeze the wound. Gently wash the area with soap and water.
- Remove the tick. Ticks must be removed as soon as possible so you do not get diseases passed through tick bites. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on tick bites and how to remove ticks.
What can I do to care for my bite or sting wound?
- Elevate (raise) the area above the level of your heart, if possible. Prop the area on pillows to keep it raised comfortably. Elevate the area for 10 to 20 minutes each hour or as directed by your healthcare provider.
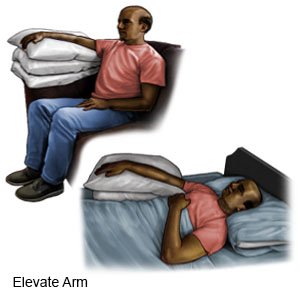
- Apply compresses. Soak a clean washcloth in cold water, wring it out, and put it on the bite or sting. Use the compress for 10 to 20 minutes each hour or as directed by your healthcare provider. After 24 to 48 hours, change to warm compresses.
- Apply a baking soda paste. Add water to baking soda to make a thick paste. Put the paste on the area for 5 minutes. Rinse gently to remove the paste.
What safety precautions do I need to take if I am at risk for anaphylaxis?
- Keep 2 shots of epinephrine with you at all times. You may need a second shot, because epinephrine only works for about 20 minutes and symptoms may return. Your healthcare provider can show you and family members how to give the shot. Check the expiration date every month and replace it before it expires.
- Create an action plan. Your healthcare provider can help you create a written plan that explains the allergy and an emergency plan to treat a reaction. The plan explains when to give a second epinephrine shot if symptoms return or do not improve after the first. Give copies of the action plan and emergency instructions to family members, work and school staff, and daycare providers. Show them how to give a shot of epinephrine.
- Carry medical alert identification. Wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says you have an insect allergy. Ask your healthcare provider where to get these items.
What can I do to prevent an insect bite or sting?
- Do not wear bright-colored or flower-print clothing when you plan to spend time outdoors. Do not use hairspray, perfumes, or aftershave.
- Do not leave food out.
- Empty any standing water. Wash containers with soap and water every 2 days.
- Put screens on all open windows and doors.
- Put insect repellent that contains DEET on skin that is showing when you go outside. Put insect repellent at the top of your boots, bottom of pant legs, and sleeve cuffs. Wear long sleeves, pants, and shoes.
- Use citronella candles outdoors to help keep mosquitoes away. Put a tick and flea collar on pets.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis,
such as trouble breathing, swelling in your mouth or throat, or wheezing. You may also have itching, a rash, hives, or feel like you are going to faint.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You are stung on your tongue or in your throat.
- A white area forms around the bite.
- You are sweating badly or have body pain.
- You think you were bitten or stung by a poisonous insect.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- The area becomes red, warm, tender, and swollen beyond the area of the bite or sting.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
