Hydrocele in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is a hydrocele?
A hydrocele is a collection of fluid inside your child's scrotum. The scrotum is a sac that holds the testicles. Hydroceles can occur in one or both sides of the scrotum and usually grow slowly. They are common in newborns but can also occur in children and adolescents.
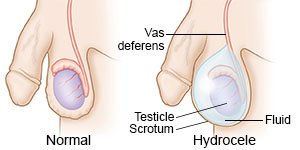 |
What are the different types of hydrocele?
- A simple hydrocele can form at any age. This kind of hydrocele does not change in size.
- A communicating hydrocele is more common in infants and children. This kind of hydrocele changes in size when your child moves. Size changes are caused by fluid flowing through a tube from the abdomen into the scrotum. This occurs when the tube does not close as it should. The hydrocele may grow larger when your child is active and may shrink when your child is at rest. A hydrocele may occur with a hernia. A hernia is when part of the intestine goes through a hole in the lining of the abdomen or groin.
What causes a hydrocele?
The cause of a hydrocele is not always known. A hydrocele may be congenital or acquired. Congenital means it is present at birth. Acquired means the hydrocele is caused by a medical condition, infection, or injury to the scrotum.
What are the signs and symptoms of a hydrocele?
A painless, swollen scrotum is the most common sign of a hydrocele. Your child's scrotum may feel sore and heavy from the swelling.
How is a hydrocele diagnosed?
Your child's healthcare provider will examine your child's scrotum. The provider may apply gentle pressure to the scrotum to check if the hydrocele gets smaller. These or other tests may also be needed:
- Transillumination is when the provider shines a bright light on your child's scrotum. This helps the provider see the fluid inside your child's scrotum. Transillumination can help identify other problems, such as a hernia.
- An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures of your child's scrotum on a monitor. An ultrasound can help show the hydrocele and any other problems in your child's scrotum.
How is a hydrocele treated?
Hydroceles usually go away without treatment. Your child's hydrocele will usually go away by the time he is 2 years old. The hydrocele will need to be removed if it does not go away or gets very large. Surgery may be needed to remove the hydrocele or close the tube between the abdomen and scrotum. Surgery may also be needed if your child has a hernia.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child has severe pain or swelling in his scrotum.
When should I call my child's doctor?
- Your child's hydrocele gets bigger or does not go away.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
