Zika Virus
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 29, 2024.
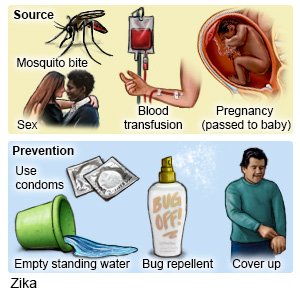
Zika virus is carried by mosquitos. The virus is spread to a human through the bite of an infected mosquito. Zika virus may be passed from a mother to her unborn baby. The virus may also be passed from one person to another through sex.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- You are pregnant and feel your baby move less or stop moving.
- You are pregnant and you have cramps or pain in your abdomen or back.
- You are pregnant and you have blood or clear fluid leaking from your vagina.
Call your doctor if:
- You have new symptoms.
- Your symptoms do not get better in 1 week, or they get worse.
- You want to get pregnant.
- You are pregnant or think you are pregnant.
- You are pregnant and have unprotected sex with a person who has been infected with, or exposed to, Zika virus.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage your symptoms:
- Drink plenty of liquids as directed. Liquids can prevent dehydration. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Rest as directed. Ask your healthcare provider when you can return to your normal activities.
Prevent Zika virus infection:
There is currently no vaccine to prevent Zika virus infection. Do not travel to areas where Zika virus is common. Ask your healthcare provider where it is safe to travel. Prevent mosquito bites to help decrease your risk for Zika virus infection:
- Apply insect repellent. Ask your healthcare provider which insect repellent is right for you. Follow directions on the insect repellent container. The following is a list of tips for insect repellent use:
- Do not apply insect repellent to skin under clothing.
- Apply sunscreen before you apply insect repellent.
- Wear insect repellent any time you plan to be outside. Wear insect repellent at all times if you travel or live in a high-risk area. Reapply insect repellent as directed.
- Apply insect repellent every day for 3 weeks after you travel to high-risk areas.
- Wear a long-sleeved shirt and pants. This will protect your skin from mosquito bites.
- Use screens and nets. Use a mosquito net around your bed. When you travel, choose a place to stay with screens on all windows and doors. Place screens over windows and doors in your home. Fix holes or tears in screens and nets, or buy new screens and nets.
- Keep doors and windows closed. If possible, use air conditioning to cool your home.
- Apply insect repellent to clothing and gear. This includes boots, pants, socks, and tents. Do this when you camp, hike, or work outside. You can also buy clothing and gear that comes with insect repellent already on it.
- Clean and empty containers of water once a week. Examples are animal bowls, buckets of water, gutters, flower vases, and bird baths. Mosquitoes lay eggs near water. Empty the water and scrub these containers with soap and water. Keep water containers covered with a tight-fitting lid, when possible.
- Use insect sprays inside and outside of your home. Use an insect spray that is safe to use inside of your home. Place a device that sprays mosquitoes outside of your home. Place it in a dark, cool, area. Ask your healthcare provider where to buy these items. Follow directions that come with these products.
 |
Prevent the spread of Zika virus through sex:
Zika virus may stay in your body for weeks to months after you are infected. You can spread Zika virus to your partner without knowing you are infected. Use protection for all types of sexual contact with a man or woman. Ask your healthcare provider how long you need to use protection. Protection may include a condom or barrier method. Use a new condom or latex barrier each time you have sex. This includes oral, vaginal, and anal sex. Make sure that the condom fits and is put on correctly. If you are allergic to latex, use a nonlatex product such as polyurethane.
What you need to know about Zika virus and pregnancy:
- Get tested for Zika virus before getting pregnant, if you live in or travel to where Zika is found.
- If you are a woman who has had Zika virus, wait at least 8 weeks before you try to get pregnant. This will decrease your baby's risk for Zika virus. If you have been exposed to Zika virus, you should also wait 8 weeks before you try to get pregnant . Risk for exposure includes travel to an area with Zika infection. It also includes unprotected sex with a man or a woman who has traveled to an area with Zika infection. Sex includes oral, vaginal, and anal sex.
- If you are a man who has had Zika virus you should wait at least 6 months before you try to get your female partner pregnant. If you have been exposed to Zika virus, you should also wait 6 months before you try to get your female partner pregnant. Risk for exposure includes travel to an area with Zika infection. It also includes unprotected sex with a man or a woman who has traveled to an area with Zika infection. Sex includes oral, vaginal, and anal sex.
- Couples who live in areas with Zika virus should talk to their healthcare provider before they try to get pregnant. Both partners should be tested for Zika virus before you try to get pregnant.
- Do not have sex with a man or a woman who is infected with Zika virus while you are pregnant. Do not have sex with a man or a woman who has been exposed to Zika virus while you are pregnant. These actions will help decrease your baby's risk for Zika infection.
- If you choose to have sex during pregnancy, use a condom or latex barrier every time you have sex. Use a new condom or latex barrier each time you have sex. This includes oral, vaginal, and anal sex. Make sure that the condom fits and is put on correctly. If you are allergic to latex, use a nonlatex product such as polyurethane.
For the most up-to-date information on Zika virus:
Knowledge about the Zika virus is changing quickly. Get the most up-to-date information at:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Information on Zika Virus
1600 Clifton Road
Atlanta , GA 30329
Phone: 1- 800 - 232-4636
Web Address: http://www.cdc.gov/zika/index.html
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Zika Virus
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
