Type 2 Diabetes Management for Adolescents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
Type 2 diabetes management means you control your blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes complications. As you get older, you will be able to manage your own health. You may be away from home more often. You may spend more time with your friends or be involved in sports. Type 2 diabetes management will help you feel well and enjoy your daily activities. Your diabetes care team providers can show you how to fit diabetes care into your schedule. Your plan can change over time to fit your needs. Adults, such as your parents and care team providers, are available to help you as you become more active in your diabetes care.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Have someone call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You cannot be woken.
- You have signs of diabetic ketoacidosis:
- confusion, fatigue
- vomiting
- rapid heartbeat
- fruity smelling breath
- extreme thirst
- dry mouth and skin
Call your doctor or diabetes care team if:
- You have a sore or wound that will not heal.
- You have a change in the amount you urinate.
- Your blood sugar levels are higher than your target goals.
- You often have lower blood sugar levels than your target goals.
- Your skin is red, dry, warm, or swollen.
- You have trouble coping with diabetes, or you feel anxious or depressed.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Why you may still need diabetes education:
Your needs and wants change as you get older. Diabetes education will help you continue to manage your diabetes, make changes to your plan, and prevent complications. As you get older, you may be able to do diabetes education on your phone or computer. Diabetes education can help you continue learning about the following:
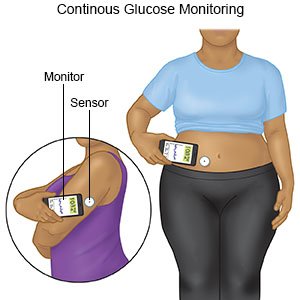
- When and how to check your blood sugar level: You will learn when to check your blood sugar level and what the level should be. You will learn what to do if your level is too high or too low. You may need to check a drop of your blood in a glucose test machine. Your diabetes care team provider may recommend a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). A CGM is a device that is worn at all times. The CGM checks your blood sugar level every 5 minutes. It sends results to an electronic device such as a smart phone. Write down the times of your checks and your levels. Take them to all follow-up appointments.
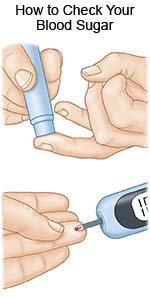
- How to take diabetes medicine or insulin: You may need diabetes medicine, insulin, or both to help control your blood sugar levels. Your diabetes care team provider will teach you how and when to take your diabetes medicine or insulin. Insulin may be given by injections, or in a pump or pen. You and your provider will decide on the best method for you:
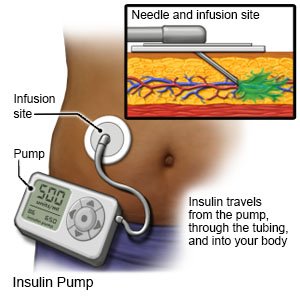
- An insulin pump is an implanted device gives you a constant amount of insulin through the day. The amount changes when the number of carbohydrates (carbs) are entered. A pump that is connected to a CGM is called an automated insulin delivery (AID) system.
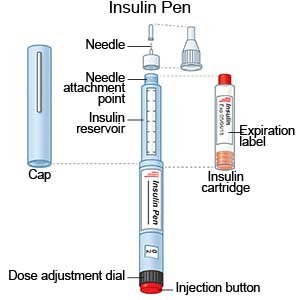
- An insulin pen is a device prefilled with the right amount of insulin.
- You and family members will be taught how to give insulin injections if this is the best method for you. You will also be taught how to dispose of used needles and syringes.
- You will learn how much insulin you need and the times to give insulin. You will be taught when not to give insulin. You will also be taught how to match the right amount of insulin with blood sugar levels, amount of activity, and amount of carbs.
- An insulin pump is an implanted device gives you a constant amount of insulin through the day. The amount changes when the number of carbohydrates (carbs) are entered. A pump that is connected to a CGM is called an automated insulin delivery (AID) system.
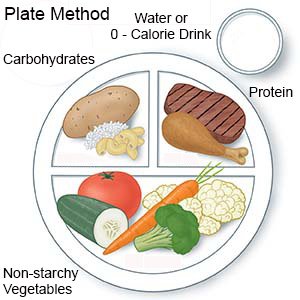
- Nutrition and diabetes: Healthy foods can give you energy to learn and be active. Healthy foods can also help you keep your blood sugar level in balance, and manage or lose weight safely. A dietitian can help you develop a meal plan that works for you and your schedule. Your dietitian can help you learn how to eat the right amount of carbs during your meals and snacks. Carbs can raise your blood sugar level if you eat too many at one time. Some foods that contain carbs include breads, cereals, French fries, chips, sweets, soda, and fruit juice.
- Physical activity and diabetes: You will learn why physical activity, such as exercise, is important. Your diabetes care team provider can help you create a plan to get at least 60 minutes of moderate to intense aerobic activity every day. Examples include brisk walking, dancing, running, or jumping rope. The plan will also include flexibility and resistance training, such as yoga and lifting weights, 3 days each week. You may need to have a snack before activity to prevent low blood sugar levels. Do not exercise if your blood sugar level is 350 mg/dL or higher. You may need to check your level before, during, and after exercise.


- Complications of diabetes: You will learn about complications, such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), neuropathy, and retinopathy. You will learn how to prevent and recognize some of these complications. You will also learn about conditions that may happen with diabetes, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
What you need to know about high blood sugar levels:
A high blood sugar level may not cause any symptoms. It may cause you to feel more thirsty or urinate more often than usual. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage your nerves, blood vessels, tissues, and organs.
- A lower dose of medicine or insulin, or a late dose, can raise your blood sugar level. Your medicine or insulin will not have enough time to lower your blood sugar level.
- Large meals or large amounts of carbs at one time can raise your blood sugar level. This is why you will need to know how many carbs to have in each meal and snack.
- Decreased physical activity can raise your blood sugar level. For example, your blood sugar level can increase if you stop playing a sport or getting regular physical activity. Do not sit for longer than 30 minutes at a time.
- Stress can raise your blood sugar level. Ask your parents or diabetes care team provider for help if you are having trouble managing stress.
- Illness can raise your blood sugar level. This can happen even if you eat less than usual while you are sick. Work with your provider and parents to develop a sick day plan. This is a plan that helps you manage your blood sugar levels while you are sick.
What you need to know about low blood sugar:
You can prevent symptoms of a low blood sugar level by preventing your blood sugar level from going too low. Symptoms may include feeling shaky, dizzy, irritable, or confused. Do the following to prevent or manage low blood sugar levels:
- Treat low blood sugar levels right away. Eat 15 grams of carbohydrate. This amount can be found in 4 ounces (½ cup) of fruit juice or 4 ounces of regular soft drink. Other examples are 2 tablespoons of raisins or 1 tube of glucose gel.
Check your blood sugar level again 10 to 15 minutes later. When it goes back to normal, eat a meal or snack to prevent another decrease in blood sugar. Left untreated, low blood sugar levels can lead to other serious conditions, such as seizures. It can become life-threatening.
- Your blood sugar level can get too low if you take diabetes medicine or insulin and do not eat enough food. It can also happen if you skip a meal or snack.
- Increased physical activity can cause a low blood sugar level. You may need to check your blood sugar level before activity. If the level is below 100 mg/dL, eat 15 grams of carbohydrate. If you will be active for more than 1 hour, check your level every 30 minutes. You may need to adjust your insulin before activity and have a carbohydrate snack during activity.
What you can do to manage your blood sugar levels:
- Know what your blood sugar levels should be. Before meals , your blood sugar should be between 90 and 130 mg/dL. At bedtime , it should be between 90 and 150 mg/dL.
- Check your blood sugar level as directed and as needed.
- Look at your schedule. Make a plan for how you will check your blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Check more often if you think your blood sugar is too high or too low. This will allow you to take care of any low or high blood sugar levels so they do not interfere with your activities.
- Rotate the sites where you do fingersticks. This will help make the checks less painful, and make fingerstick sites less noticeable.
- Write down your blood sugar levels so you can show them to your care team provider during your visits. Talk to your provider if you are having trouble keeping your blood sugar at the recommended levels.

- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your team what a healthy weight is for you. A healthy weight can help you control diabetes and prevent heart disease. Ask your team to help you create a weight loss plan, if needed. Weight loss can help make a difference in managing diabetes. Your team will help you set a weight-loss goal, such as 10 to 15 pounds, or 5% of your extra weight. Together you and your team can set manageable weight loss goals.
Other things you can do to manage type 2 diabetes:
- Wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says you have diabetes. Ask where to get these items.
- Be safe when you learn to drive. Check your blood sugar before you drive if you use insulin, and you think your blood sugar level is low. If your level is low, eat 15 grams of carbohydrate and wait for it to go back to normal. Keep snacks that contain carbohydrate in the car. If you feel like your blood sugar is low while you are driving, pull over and check your blood sugar level. Treat a low blood sugar level before you start driving again, if needed.
- Do not drink alcohol or use tobacco products, such as cigarettes. Alcohol affects your blood sugar level. You may not be aware of low blood sugar when you drink alcohol. Nicotine in tobacco products can damage blood vessels. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine. Ask your diabetes care team provider for information if you currently smoke and need help quitting.
- Have screenings for complications of diabetes and other conditions that happen with diabetes. You will need to be screened for kidney problems, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, blood vessel problems, eye problems, and eating disorders. Your feet may be checked for sores or other problems that can develop. Some screenings may begin right away and some may happen within the first 5 years of diagnosis. You will need to continue screenings through your lifetime. Keep your follow-up appointments with all providers.
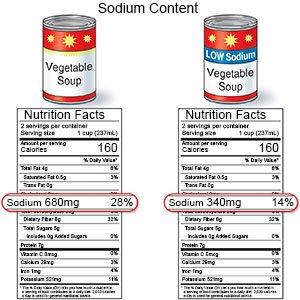
- Limit sodium (salt) as directed. Your dietitian may tell you to limit sodium to 2,300 milligrams (mg) each day. Your dietitian can help you create a meal plan that is low in sodium. If you use canned foods, choose low-sodium brands as often as possible. Do not add salt at the table if you add salt when you cook.
- Drink water throughout the day. Your dietitian may tell you to limit or not drink liquids that have artificial sweeteners. Water is the best liquid to drink.
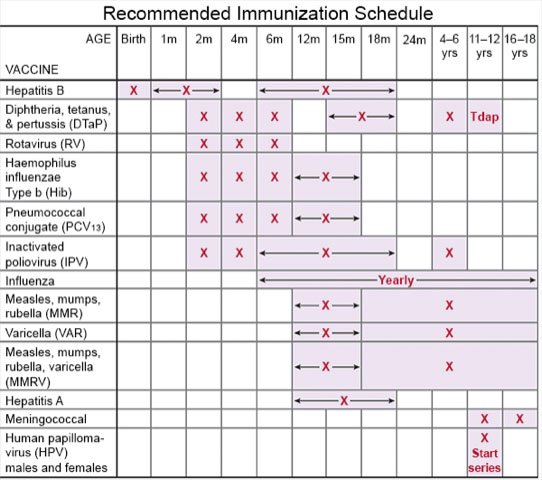
- Ask about vaccines you may need. You have a higher risk for serious illness if you get the flu, pneumonia, COVID-19, or hepatitis. Ask if you should get vaccines to prevent these or other diseases, and when to get the vaccines.
What you need to know about diabetes and pregnancy:
Talk to your care team provider about how to prevent an unplanned pregnancy. While you can have a safe pregnancy with diabetes, it is important to plan your pregnancy. Care team providers can help you have a healthy pregnancy and baby. Tell your care team provider immediately if you are pregnant or think you are pregnant.
Follow up with your doctor or care team provider as directed:
You may need to return to have your A1c checked every 3 months. An A1c test shows the average amount of sugar in your blood over the past 2 to 3 months. Your care team provider will tell you what your A1c level should be. You may need tests to check for a low vitamin B level if you take oral diabetes medicine for a long time. You may also need to return at least 1 time each year to have your feet checked. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Type 2 Diabetes Management for Adolescents
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
