Near-Drowning Injuries
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Near-drowning injuries occur when a person has been unable to breathe after being under water. Liquid enters the lungs and prevents the person from getting enough oxygen. Alcohol or drug use while boating or swimming increase the risk of a near-drowning injury. Medical problems such as seizures, muscle cramps, or hypoglycemia while swimming may also increase risk.
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Activity:
At first, the person may need to rest in bed. The person may breathe easier if he or she rests with the head of the bed raised. The person may also breathe easier if he or she rests his or her head on 3 or 4 pillows. If the person has trouble breathing, call his or her healthcare provider right away. When the person's breathing has improved, he or she may get out of bed.
Neurologic signs:
Healthcare providers will check the person's eyes, memory, and how easily he or she wakes up. The person's hand grasp and balance may also be tested. This helps healthcare providers know how the person's brain is working. The person may need to have his or her neurologic signs checked often.
Vital signs:
The person's blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate, and temperature will be checked regularly by healthcare providers. They will also ask about the person's pain. These vital signs give healthcare providers information about the person's current health.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics may be given to help treat or prevent a lung infection.
- Glucose may be given to raise blood sugar.
Tests:
- Arterial blood gases (ABG) show oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Blood is taken from a vein in the wrist, arm, or groin.
- A pulse oximeter measures the amount of oxygen in the person's blood. A cord with a clip or sticky strip is placed on his or her foot, toe, hand, finger, or earlobe. The other end of the cord is hooked to a machine. Never turn the pulse oximeter or alarm off. An alarm will sound if the person's oxygen level is low or cannot be read.
- Blood and urine tests can get information about the person's overall health.
- An EEG , or electroencephalogram, shows the electrical activity of the brain. Small pads or metal discs are put on the head. Each has a wire that is hooked to a machine. This machine prints a paper tracing of brain wave activity from different parts of the brain.
- A chest x-ray may show lung problems, such as pneumonia, collapsed lungs, or ARDS.
- A CT scan may show brain edema. The person may be given contrast liquid before the scan. Tell the healthcare provider if the person has ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
Treatment:
- Oxygen may be given if the person's blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. The person may get oxygen through a mask placed over his or her nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in the nostrils. Ask before you take off the mask or oxygen tubing.
- A ventilator is a machine that provides oxygen and breathes for the person when he or she cannot breathe well on his or her own. An endotracheal (ET) tube is put into the person's mouth or nose and attached to the ventilator. He or she may need a trach if an ET tube cannot be placed. A trach is a tube put through an incision and into the windpipe.
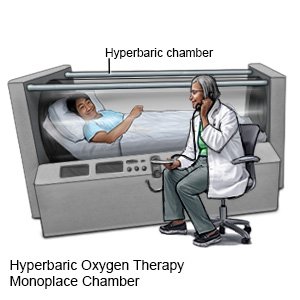
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used to get more oxygen into the body. The oxygen is given under pressure to get it into the tissues and blood. The person may need to have this therapy more than 1 time.
RISKS:
Endotracheal intubation and other procedures may cause bleeding and infection. Without treatment, near-drowning injuries may lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonia, brain edema, and kidney failure. Near-drowning injuries can also lead to seizures. These problems may become life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Near-Drowning Injuries
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
