Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
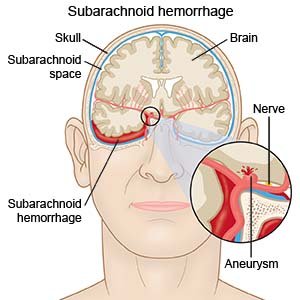
SAH is a type of hemorrhagic stroke that causes bleeding in the subarachnoid space. This space is under the protective tissues that cover the brain. SAH happens when a blood vessel bursts. SAH is a life-threatening condition that needs immediate medical care.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Have someone call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss

- You have a mild to moderate headache that lasts a few days.
- You have eye pain when you are in bright light, or you see double.
- You have a seizure, or someone sees you lose consciousness.
Call your doctor if:
- You have neck stiffness that does not go away.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antihypertensives help lower your blood pressure. This may help prevent another SAH. It is also used to prevent stroke, bleeding inside your brain, or heart or kidney damage caused by SAH.
- Anticonvulsants help prevent seizures.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip does or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Warning signs of a stroke:
The words BE FAST can help you remember and recognize warning signs of a stroke:
- B = Balance: Sudden loss of balance
- E = Eyes: Loss of vision in one or both eyes
- F = Face: Face droops on one side
- A = Arms: Arm drops when both arms are raised
- S = Speech: Speech is slurred or sounds different
- T = Time: Time to get help immediately
 |
What to expect after SAH:
- You may be referred to stroke rehabilitation (rehab). Rehab is a program run by specialists who will help you recover abilities you may have lost. Specialists include physical, occupational, and speech therapists. Physical therapists help you gain strength or keep your balance. Occupational therapists teach you new ways to do daily activities, such as getting dressed. Your therapy may include movements for everyday activities. An example is being able to raise yourself from a chair. A speech therapist helps you improve your ability to talk and swallow.
- Talk to your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your recovery process. You may not fully recover after SAH. You may not sleep well, think clearly, or be able to work as you did before. You may also be anxious, tired, or depressed. You may be worried about having another SAH. This may affect your relationships.
- Ask when it is safe to drive again. You may need someone to drive you until you have recovered.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Manage or prevent a SAH:
SAH is often caused by medical conditions that you cannot control. Healthcare providers will help you create goals for your recovery. The following lifestyle changes can help you reach your goals and lower your risk for a stroke:
- Manage health conditions. A condition such as diabetes can increase your risk for a stroke. Control your blood sugar level if you have hyperglycemia or diabetes. Take your prescribed medicines and check your blood sugar level as directed.
- Check your blood pressure as directed. High blood pressure can increase your risk for a stroke. Follow your healthcare provider's directions for controlling your blood pressure.

- Do not use nicotine products or illegal drugs. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause blood vessel damage and raise your risk for an aneurysm. A burst aneurysm is one of the main causes of SAH. Nicotine and illegal drugs both increase your risk for a stroke. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke or use drugs and need help to quit. E- cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Do not drink alcohol. Alcohol increases your risk for a stroke. Alcohol may also raise your blood pressure or thin your blood. Blood thinning can cause a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Eat at least 5 servings of fruits and vegetables each day. Choose foods that are low in fat, cholesterol, salt, and sugar. Eat foods that are high in potassium, such as potatoes and bananas. A dietitian can help you create healthy meal plans.

- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask him or her to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight. He or she can help you create small goals if you have a lot of weight to lose.
- Exercise as directed. Exercise can lower your blood pressure, cholesterol, weight, and blood sugar levels. Healthcare providers will help you create exercise goals. They can also help you make a plan to reach your goals. For example, you can break exercise into 10 minute periods, 3 times in a day. Find an exercise that you enjoy. This will make it easier for you to reach your exercise goals.

- Manage stress. Stress can raise your blood pressure. Find new ways to relax, such as deep breathing or listening to music.
What you need to know about depression after a stroke:
Talk to your healthcare provider if you have depression that continues or is getting worse. Your provider may be able to help treat your depression. Your provider can also recommend support groups for you to join. A support group is a place to talk with others who have had a stroke. It may also help to talk to friends and family members about how you are feeling. Tell your family and friends to let your healthcare provider know if they see signs of depression:
- Extreme sadness
- Avoiding social interaction with family or friends
- A lack of interest in things you once enjoyed
- Irritability
- Trouble sleeping
- Low energy levels
- A change in eating habits or sudden weight gain or loss
Follow up with your doctor or neurologist as directed:
You may need more tests to show if you need more treatment or surgery. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
For support and more information:
- American Stroke Association
Phone: 1- 888 - 478-7653
Web Address: http://www.stroke.org
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Treatment options
- Medications for Head Injury w/ Intracranial Hemorrhage and Loss of Consciousness
- Medications for Head Injury with Intracranial Hemorrhage
- Medications for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
