Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
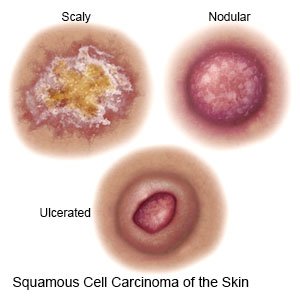
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a slow growing cancer that usually does not spread. Squamous cells are found in the skin, organs, respiratory tract, and digestive tract. SCC can develop in any of these areas, but it is most common in skin areas that get a lot of sun.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent an infection caused by bacteria.
- Pain medicine may be needed. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more pain medicine.
Tests:
Your healthcare provider may perform a biopsy (a small sample of skin is removed). The sample will be sent to a lab and checked for abnormal cells and cancer.
Treatment:
You may need more than one of the following:
- Cryosurgery is a procedure that uses a chemical, called liquid nitrogen, to freeze and kill a small area of tissue. The tissue dies and later falls off.
- Mohs surgery is used to remove only skin with cancer cells and as little healthy tissue as possible. Thin layers of the tumor are scraped off one at a time until all the cancer cells are removed.
- Surgery is used to remove the cancer.
- Electrodesiccation and curettage is used for skin SCC. The tumor is scraped and then heated with an electric probe to kill the cancer cells.
- Laser therapy uses a narrow beam of light to kill the cancer cells.
- Topical chemotherapy is given as a lotion or cream to put directly on skin cancer to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation uses x-rays or gamma rays to treat cancer. Radiation kills cancer cells and may stop the cancer from spreading. It may be used for hard-to-treat areas, such as the eyelids, tongue, or esophagus.
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor medicines may help your immune system kill the cancer or keep it from progressing as quickly.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
You may get an infection or bleed more than expected after surgery. If the cancer is not treated, it may spread to other parts of your body. When cancer spreads, it becomes more difficult to treat, and other serious medical problems can develop.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
