SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)?
SARS is a respiratory illness caused by a virus. It is sometimes called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV). Coronavirus is the name of a group of viruses. The viruses are common and usually cause mild infections, such as a cold.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of SARS?
Signs and symptoms range from mild to severe. SARS may lead to severe, life-threatening problems. The virus damages the air sacs of the lungs. The lung tissues become inflamed and scarred. The damaged air sacs do not allow oxygen to get into your bloodstream, leading to respiratory failure. Respiratory failure means you cannot breathe well enough to get oxygen to the cells of your body. Your risk is higher if you have a weak immune system. A health condition such as diabetes or a lung disease also increases your risk. Any of the following may appear 4 to 10 days after you have been exposed to the SARS virus:
- Chills and a high fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher
- Headache, body aches and pains, and weakness
- Diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting
- Cough and shortness of breath (may appear 2 to 7 days after the start of the first symptoms)
How is SARS diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may diagnose SARS based on your signs and symptoms and recent travel history. He or she may also want to know if you had a possible exposure to someone infected with the SARS virus. You may also need one or more of the following tests:
- CT scan or x-ray pictures may show pneumonia. You may be given contrast liquid to help your lungs show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- Samples may be collected, such as mucus from your throat or nose. A sample of your urine or bowel movement may also be sent to a lab for tests. These may show which germ is causing your disease and help healthcare providers plan the best treatment for you.
How is SARS treated?
No medicine is available to treat SARS. Any of the following may be used to treat symptoms or pneumonia caused by SARS:
- Medicines may be given to relieve your fever, cough, or pain. Antivirals may also be given. You may also need medicines to help decrease swelling in your lungs and help you breathe easier.
- Extra oxygen may be given in the hospital if your oxygen level is low. A machine may be used to help you breathe if you cannot breathe well on your own.
What can I do to care for myself?
- Ask about inhalers and high-flow masks. A metered-dose inhaler may help open your airway so you can breathe easier. Do not use a nebulizer machine or humidifier that increases air moisture. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on using inhalers and masks correctly.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can make your symptoms worse. They can also cause infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. No vaccine is available for SARS. But any infection can affect your immune system and make you more vulnerable. Do the following to protect yourself:
- Get a flu vaccine as soon as recommended each year. The flu vaccine is available starting in September or October. Flu viruses change, so it is important to get a flu vaccine every year.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about your vaccine history. Tell him or her if you did not get certain vaccines as a child, or you did not get all recommended doses. Tell him or her if you do not know your vaccine history. He or she will tell you which vaccines you need, and when to get them.
How can I prevent the spread of the SARS virus?
The SARS virus is spread when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. Others can become infected by breathing in the virus or getting the virus in their eyes. Follow the directions below to prevent the spread of the SARS virus:
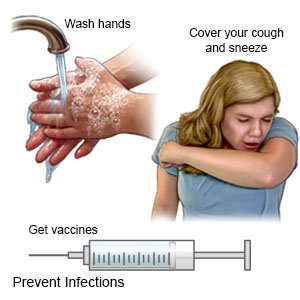
- Wash your hands often. Use soap and water every time you wash your hands. Rub your soapy hands together, lacing your fingers. Use the fingers of one hand to scrub under the nails of the other hand. Wash for at least 20 seconds. Rinse with warm, running water for several seconds. Then dry your hands. Use germ-killing gel if soap and water are not available. Do not touch your eyes or mouth without washing your hands first.

- Cover a sneeze or cough. Everyone should always cover a sneeze or cough. Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue. Throw the tissue away right after you use it. Use the bend of your arm if you do not have a tissue. Wash your hands after you sneeze or cough.
- Limit close contact with others. If you are sick, stay home or away from others until you are well. Stay in a different room from others in the house. Remind others to stay at least 3 feet (1 meter) away from you while you are sick. Do not share items with anyone. Items you use need to be washed before others use them. If you do not have SARS, it is still a good idea to be careful around others. Do not stand close to anyone who is sneezing or coughing.
- Do not go outside except for medical appointments. Call ahead to the healthcare provider's office. The provider will have to take safety steps to keep others in the office safe. Stay home from work, school, and other activities. Your provider will tell you when it is okay to be around others again.
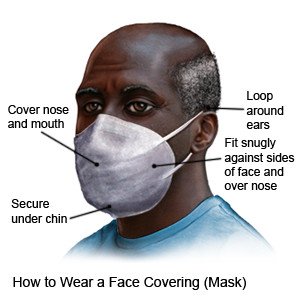
- Wear a medical mask if you have SARS or take care of someone who does. A medical mask can help prevent the virus from traveling through the air in droplets from your respiratory tract. Wash your hands after you take off your gloves and mask. Throw away the gloves after each use. Throw away your mask if it gets wet or comes in contact with body fluids.
- Clean surfaces often. Use bleach diluted with water or disinfecting wipes to clean counters, doorknobs, toilet seats, and other surfaces.
 |
Where can I find more information?
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
1600 Clifton Road
Atlanta , GA 30333
Phone: 1- 404 - 6393311
Phone: 1- 800 - 3113435
Web Address: http://www.cdc.gov
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have sudden shortness of breath.
- You have a fast heartbeat or chest pain.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You feel so dizzy that you have trouble standing up.
- Your lips and fingernails turn blue.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You are coughing up bloody sputum.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about SARS
Treatment options
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
