Iron Deficiency Anemia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA)
means you have low red blood cell and hemoglobin levels. Hemoglobin is part of red blood cells and helps carry oxygen to your body. Iron helps make hemoglobin. IDA is caused by a lack of iron in the blood. Blood loss and not enough iron in the foods you eat are the most common causes of low iron.
Common symptoms include the following:
- Feeling weak, tired, or irritable
- Pale skin
- Headache, dizziness
- Shortness of breath with activity
- Fast or uneven heartbeat
- Sore or swollen tongue and mouth
- Nails that break easily
- An urge to eat ice, paint, starch, or dirt
Seek care immediately if:
- You have dark or bloody bowel movements.
- You vomit blood.
- You are too dizzy to stand up.
- You have trouble swallowing because of the pain in your mouth and throat.
Call your doctor or hematologist if:
- You have heartburn, constipation, or diarrhea.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You are dizzy or very tired.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment for IDA
may take 3 to 6 months. You may need medicines and supplements to increase the amount of iron in your blood. Ask your healthcare provider how much iron you should take each day. A blood transfusion may be needed if your anemia is severe. This will help replace the blood and iron you have lost.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
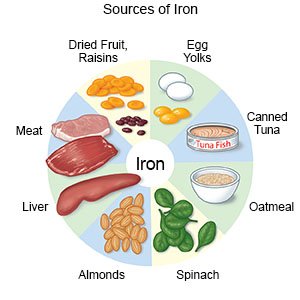
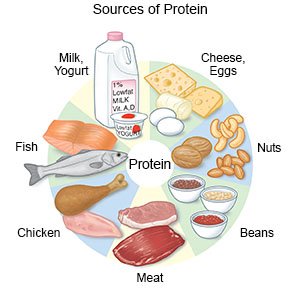
Eat foods rich in iron and protein:
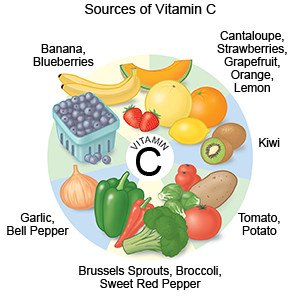
Nuts, meat, dark leafy green vegetables, and beans are high in iron and protein. Limit milk to 2 cups a day. The calcium in milk can interfere with how your body absorbs iron. Take the iron supplement with food or a drink that is high in vitamin C. This helps your body absorb the iron. You may need to meet with a dietitian to create the right food plan for you.
 |
 |
 |
Drink liquids as directed:
Iron supplements may cause constipation. Liquids help prevent constipation. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
Follow up with your doctor or hematologist as directed:
You may need to see a specialist to help find the cause of your IDA. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Iron Deficiency Anemia
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
