Inguinal Hernia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
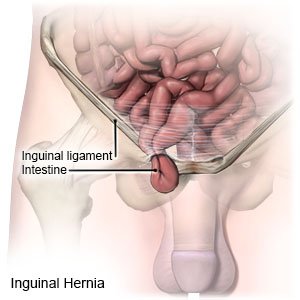
An inguinal hernia happens when organs or abdominal tissue push through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. The abdominal wall is made of fat and muscle. It holds the intestines in place. The hernia may contain fluid, tissue from the abdomen, or part of an organ (such as an intestine).
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Medicines:
- Antinausea medicine may be given to prevent or treat nausea.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
- Sedative medicine may be given to help you relax. You may need this medicine before your healthcare provider manually reduces your hernia.
- Antibiotics help prevent a bacterial infection. You may be given antibiotics before you have surgery to fix your hernia.
- IV fluids may be given to treat or prevent dehydration.
Tests:
- X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan pictures may show blockage in the intestines or lack of blood flow to organs. You may be given contrast liquid to help the organs show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- Blood and urine tests may be used to check your kidney function or find signs of infection.
Treatment:
- A nasogastric (NG) tube may be inserted to relieve nausea and vomiting. An NG tube is a thin tube that is inserted through your nose and into your stomach. The tube can remove fluid and air from your stomach.
- Manual reduction of the hernia may be needed. Manual reduction means your healthcare provider uses hands to put firm, steady pressure on your hernia. Your provider will continue until the hernia disappears inside the abdominal wall. You may need to wear a belt that holds the tissue in place.
- Surgery may be needed if the hernia stops blood flow to any of the organs. Surgery may also be needed if the hernia causes a hole in the intestines, or blocks the intestines.
RISKS:
Your hernia may become incarcerated or strangulated. Incarcerated means the hernia is trapped in an opening or pouch in the abdominal wall. The hernia cannot be pushed back inside the abdominal wall. Strangulated means that the hernia is trapped without blood or oxygen. The trapped tissue may die. If the intestines are trapped, food and fluid cannot move through. Pressure may build up in the intestines and a hole may form. This can become life-threatening. Surgery is done to fix these problems.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Inguinal Hernia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
