How to Tell If your Baby Is Getting Enough Breast Milk
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
You may worry that your baby is not getting enough breast milk. This may be because you do not know how much your baby drinks during a feeding. You may be concerned that you cannot produce enough milk if you have a small breast size. Breasts of any size can produce plenty of milk as long as your baby feeds regularly and often.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Contact your baby's healthcare provider if:
- Your baby is 4 or more days old and has fewer than 6 wet diapers each day.
- Your baby is 4 or more days old and has fewer than 3 bowel movements each day.
- Your baby is not gaining weight or looks like he or she is losing weight.
- Your breasts do not feel full, or you are not leaking breast milk within 5 days of giving birth.
- Your baby is feeding fewer than 8 times each day.
- Your baby is fussy or acts hungry after you breastfeed.
- You do not hear your baby swallowing while you are breastfeeding.
- You have nipple pain during breastfeeding or between feedings. Your nipples look red, dry, cracked, or they have scabs on them.
- Your baby becomes jaundiced (skin and whites of the eyes are turning yellow).
- You have any questions or concerns about breastfeeding.
How to help your baby latch on correctly:
Help your baby move his or her head to reach your breast. Hold the nape of his or her neck to help him or her latch onto your breast. Touch his or her top lip with your nipple and wait for him or her to open his or her mouth wide. Your baby's lower lip and chin should touch the areola (dark area around the nipple) first. Help him or her get as much of the areola in his or her mouth as possible. You should feel as if your baby will not separate from your breast easily. A correct latch helps your baby get the right amount of milk at each feeding. Allow your baby to breastfeed for as long as he or she is able.
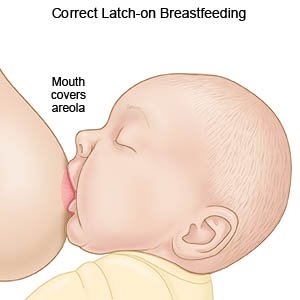 |
Signs your baby is latched on correctly:
- You can hear your baby swallow.
- Your baby is relaxed and takes slow, deep mouthfuls.
- Your breast or nipple does not hurt during breastfeeding.
- Your baby is able to suckle milk right away after he or she latches on.
- Your nipple is the same shape when your baby is done breastfeeding.
- Your breast is smooth, with no wrinkles or dimples where your baby is latched on.
How to know if your baby is getting enough breast milk:
You may want to keep a diary. Write down each time you breastfeed your baby and when you pump your breasts. Make a note of how much milk you pump out each time. You also can write down when your baby has wet or soiled diapers. A diary can help you and your healthcare provider know if your baby is getting enough milk. The following are signs that your baby is getting enough breast milk:
- Your baby is latched on to your breast correctly. You should have little or no discomfort in your nipple or breast. When your baby's chest is against your body, he or she should not have to turn his or her head to breastfeed. Your baby will seem calm after breastfeeding if he or she is latched on correctly and getting enough breast milk. He or she may fall asleep. His or her face, arms, and hands may look relaxed.
- Your baby has several wet or soiled diapers each day. When he or she is 4 days old, he or she should have 3 to 4 bowel movements each day. He or she should also have 6 to 8 wet diapers a day. His or her urine should be clear or pale yellow.
- Your baby is gaining weight. Your baby's healthcare provider will check his or her weight at each visit to see if he or she is gaining weight as he or she should. Your baby may lose weight in the first 3 days after birth. By 4 to 5 days old, your baby should start gaining weight.
- Your breasts feel different before and after breastfeeding. Your breasts should feel full before breastfeeding your baby and softer after. This means that your baby is emptying your breasts during breastfeeding.
- Your baby feeds 8 to 12 times each day. Your baby may let you know when he or she is ready to breastfeed. He or she may be wide awake and moving his or her arms and legs more. He or she may turn his or her head toward your breast and move his or her mouth more. He or she may put his or her hand up to his or her mouth and suck the fingers or fist. You may need to wake your baby to feed him or her.
Care for yourself while you are breastfeeding:
- Follow a healthy meal plan. A healthy meal plan provides the amount of calories and nutrients you need while you are breastfeeding. Your body needs extra calories and nutrients to keep you healthy and support milk production. A healthy meal plan includes a variety of foods from all the food groups. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on breastfeeding and your diet.
- Drink more liquids. You need about 8 to 12 cups of liquid each day to prevent dehydration and keep up your milk supply. Drink liquids throughout the day. Also drink a beverage each time you breastfeed. Choose liquids that do not contain caffeine. Examples are water, juice, and milk.
- Ask about medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider before you take any medicines. This includes all prescription and over-the-counter medicines. Some medicines may decrease the amount of breast milk you make. Other medicines may enter your breast milk and affect your baby.
For support and more information:
- American Academy of Pediatrics
345 Park Boulevard
Itasca , IL 60143
Phone: 1- 800 - 433-9016
Web Address: http://www.aap.org
- La Leche League International
957 North Plum Grove Road
Schaumburg , IL 60173
Phone: 1- 847 - 519-7730
Phone: 1- 800 - 525-3243
Web Address: http://www.lalecheleague.org
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
