Hemophilia in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Hemophilia is a disorder that causes your child to bleed more or longer than normal. Clotting factors such as platelets and fibrinogen help form clots to stop bleeding. The clotting factors in your child's blood may not work correctly, or his or her body may not make enough.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has a head injury or a seizure.
- Your child has bleeding from an injury to his or her throat, neck, or eyes.
- Your child has a bleeding episode that cannot be controlled.
- Your child has chest pain or trouble breathing.
Return to the emergency department if:
- Your child has many large bruises on his or her body, or swelling in his or her joints.
- Your child has joint pain that lasts longer than 3 days.
- Your child has severe hemophilia and has pain in the lower part of his or her stomach, groin, or lower back.
- Your child is vomiting blood or has blood in his or her bowel movement.
Call your child's doctor or hematologist if:
- Your child feels very tired and weak.
- Your child has chills or a fever.
- Your child has nausea, is vomiting, or has a severe headache.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Replacement therapy:
Certain blood components, called factor concentrates, may be given to your child. They replace the missing clotting factor in your child's blood. Replacement clotting factor is given so that your child's blood will be able to clot and to stop any bleeding. Clotting factor can come from human blood or be artificial. You may be taught how to give clotting factor to your child at home.
- Demand therapy is clotting factor given to stop a bleeding episode.
- Preventive therapy is given to prevent future bleeding episodes. This therapy is often used to prevent injury to your child's joints. Your child may be started on this therapy as early as 1 to 2 years of age, or after at least 1 joint bleeds. For severe hemophilia, these factor concentrates may be given regularly. If your child has hemophilia A, he or she may receive this treatment 3 times a week or every other day. If your child has hemophilia B, he or she may receive treatment 2 times a week.
Help your child manage hemophilia:
- Encourage your child to be physically active, as directed. Physical activity helps keep your child's muscles flexible and prevents muscle and joint damage. Always check with healthcare providers before your child starts any new physical activity. Physical or occupational therapists may need to help your child learn to be active safely or do daily activities more easily. Your child can play sports, but severe hemophilia may limit the type of sports he or she can play. Do not let your child play contact sports, such as football and basketball. Contact sports increase your child's risk for bruising and bleeding. Talk to your child's healthcare provider about the best sports and activities for your child.

- Keep your child's teeth and gums healthy. Ask your child's provider if certain therapies or medicines should be given to your child when his or her teeth get cleaned. The amount of his or her clotting factor may also need to be increased before he or she has dental procedures. Talk with your child's provider before your child has any dental work.
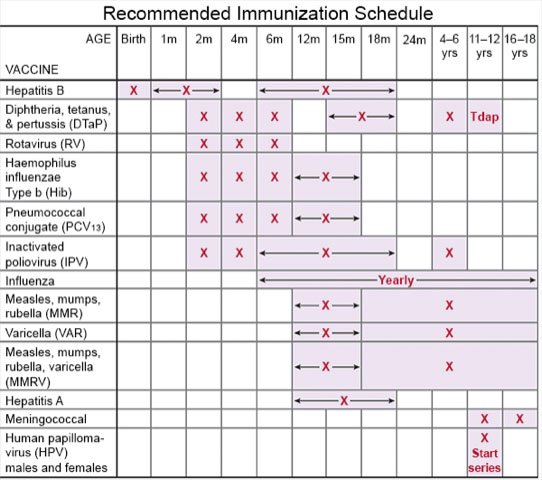
- Ask about vaccines your child may need. Examples include the hepatitis A and B, flu, and COVID-19 vaccines. Your child's provider can tell you if your child also needs other vaccines. The provider can help you schedule all needed vaccine doses.
- Help protect your child from injuries that can cause bleeding. Young children who are learning to walk can fall and hit hard items. You may need to pad hard items in your home during this period. Protect your child when he or she is riding in a car by always having him or her in a car seat, or use a seatbelt. Your child should always wear a helmet if he or she rides a bicycle or does other activities that may cause a head injury. Your child may also need to wear knee and elbow pads to protect joints from injury during activities.
- Learn more about hemophilia. The more you know about hemophilia, the better you will be able to help your child. Ask how you can learn more about the type of hemophilia your child has.
Manage bleeding episodes:
Use the following first aid steps as the first treatment for any bleeding episode. You and anyone else who cares for your child must know how to do first aid if your child starts bleeding. If these measures do not stop the bleeding, other treatments will be needed. The following may reduce bleeding and decrease pain:
- Prepare for bleeding episodes. Have the supplies ready that you may need to treat a bleeding episode. Have your child's provider help you prepare a written emergency plan for how to handle your child's bleeding episodes. The plan should cover care for your child at home and school, and what to do if he or she has to go to the hospital.
- Help your child rest. Have your child sit or lie quietly until the bleeding episode ends.
- Use pressure to help stop or slow skin bleeding. Place a clean cloth or towel over the area. Then apply pressure with your hands. Ask your child's provider how to clean open skin wounds.
- Manage bleeding from your child's nose or mouth. Have your child breathe through his or her mouth and lean forward. This will help stop blood from going down the back of your child's throat. Tell your child not to swallow the blood.
- Check for blood in your young child's urine. If you see blood in your child's urine or he or she has pelvic pain, have your child rest in bed for 2 days. Offer more liquids, such as water. Ask your child's provider how much liquid your child should drink each day.
- Manage joint bleeding. Apply ice to a painful or swollen joint. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you apply it to your child's joint. If the joint is on an arm or leg, prop it on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably. Have your child wait until the pain is gone before he or she uses the joint again. Call your child's provider if the pain is not gone within 3 days.
Have your child carry medical alert identification:
Your child can wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says he or she has hemophilia. Ask your provider where to get these items.
 |
Follow up with your child's doctor or hematologist as directed:
Your child may be referred to a hemophilia treatment center in your area. These are clinics that provide care to people with hemophilia and other bleeding disorders. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
For support and more information:
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute
Health Information Center
P.O. Box 30105
Bethesda , MD 20824-0105
Phone: 1- 301 - 592-8573
Web Address: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/infoctr/index.htm
- CDC National Center on Birth Defects & Developmental Disabilities, Blood Disorders
1600 Clifton Rd
Atlanta , GA 30333
Phone: 1- 800 - 232-4636
Web Address: http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/hbd/default.htm
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Hemophilia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
