GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
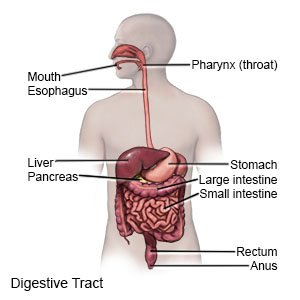
is reflux that occurs more than 2 times a week for a few weeks. Reflux means acid and food in your child's stomach back up into his or her esophagus. GERD can cause other health problems over time if it is not treated.
 |
Common causes of GERD:
GERD often happens because the lower muscle (sphincter) of your child's esophagus does not close properly. The sphincter normally opens to let food into the stomach. It then closes to keep food and stomach acid in the stomach. If the sphincter does not close properly, food and stomach acid may back up (reflux) into the esophagus. The following may also increase your child's risk for GERD:
- Neurological disorders such as cerebral palsy
- Asthma
- Premature birth
- Parents with GERD
- Obesity
- Hiatal hernia
- Certain foods such as spicy foods, chocolate, foods that contain caffeine, peppermint, and fried foods
- Exposure to secondhand smoke, or smoking cigarettes in adolescents
Common signs and symptoms of GERD:
- Heartburn (burning pain in his or her chest or below the breast bone), usually after meals
- Bitter or acid taste in the mouth
- Upper abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting
- Dry cough, hoarseness, or sore throat
- Trouble swallowing or pain with swallowing
- Gagging or choking while eating
- Poor feeding and growth
- Irritability or crying after eating
- Wheezing
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has severe chest pain.
- Your child suddenly stops breathing, begins choking, or his or her body becomes stiff or limp.
- Your child suddenly has trouble breathing or wheezes.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child has forceful vomiting.
- Your child's vomit is green or yellow, or has blood in it.
- Your child has severe stomach pain and swelling.
Call your child's doctor if:
- Your child becomes more irritable or fussy and does not want to eat.
- Your child becomes weak and urinates less than usual.
- Your child is losing weight.
- Your child has more trouble swallowing than before or feels new pain when he or she swallows.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Treatment:
The goal of treatment is to relieve your child's symptoms and prevent damage to his or her esophagus. Treatment is also done to promote healthy weight gain and growth. Your child may need any of the following:
- Medicines are used to decrease stomach acid. Medicine may also be used to help your child's lower esophageal sphincter and stomach contract (tighten) more.
- Surgery is done to wrap the upper part of the stomach around the esophageal sphincter. This will strengthen the sphincter and prevent reflux.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Help manage your child's symptoms:
- Keep a record of your child's symptoms. Write down your child's symptoms and what your child is doing when symptoms start. Bring the record to your visits with the healthcare provider. The diary may help your child's healthcare provider plan the best treatment for him or her.
- Remind your child not to eat large meals. The stomach produces more acid to help digest large meals. This can cause reflux. Have your child eat 6 small meals each day instead of 3 large meals. He or she should also eat slowly. Your child should not eat meals 2 to 3 hours before bedtime.
- Remind your child not to have foods or drinks that may increase heartburn. These include chocolate, peppermint, fried or fatty foods, drinks that contain caffeine, or carbonated drinks (soda). Other foods include spicy foods, onions, tomatoes, and tomato-based foods. He or she should also not have foods or drinks that can irritate the esophagus. Examples include citrus fruits and juices.
- Elevate the head of your child's bed. Place 6-inch blocks under the head of your child's bed frame to do this. This may decrease reflux while your child sleeps.
- Help your child maintain a healthy weight. Ask your child's provider what a healthy weight is for your child. Extra body weight can worsen GERD. Your child's provider can help you create a weight loss plan for your child, if needed.
- Help your child avoid pressure on his or her abdomen. Pressure pushes acid up into the esophagus. Have your child wear clothing that is loose around the waist. Remind him or her not to bend over. He or she should bend at the knees to pick something up.
- Keep your child away from cigarette smoke. Do not smoke or allow others to smoke around your child. If your adolescent smokes, encourage him or her to stop. Smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter and increases the risk for GERD. Ask your child's healthcare provider for information if your adolescent currently smokes and needs help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Have your adolescent talk to his or her healthcare provider before using these products.
Follow up with your child's doctor or gastroenterologist as directed:
Report any new or worsening symptoms your child has during your follow-up visits. Your child may need other tests if his or her symptoms do not improve. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about GERD
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Low Salicylate Diet
- Stomach / Heartburn Medications and Alcohol Interactions
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
