Esophageal Varices
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
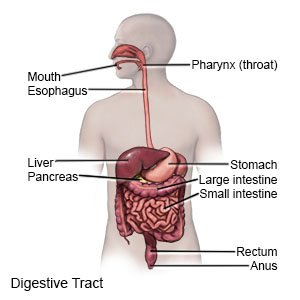
Esophageal varices
are swollen veins in the lower part of your esophagus. They are caused by increased pressure in the blood vessels of your liver. As the pressure builds in your liver, the pressure also builds in the veins in your esophagus.
 |
Common signs and symptoms:
- Weakness and fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Faster heartbeat or breathing than usual
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Cool, clammy skin
- Swollen abdomen and feet
Seek care immediately if:
- You have severe abdominal pain.
- You see blood in your vomit or bowel movements.
- You have chest pain or are short of breath.
- You have trouble thinking clearly.
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- You have a fever.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment:
The goal of treatment is to prevent the varices from breaking open and bleeding. You may be given medicines to decrease the pressure in your liver or to reduce stomach acid. You may need to have a shunt placed to relieve pressure. Bands may be placed around large varices to cause them to shrink. The bands may be used to prevent or stop bleeding. You may need surgery to remove the bleeding section of your esophagus if healthcare providers cannot stop the bleeding.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Prevent varices from bleeding:
- Do not drink alcohol. This will help prevent more damage to your esophagus and liver. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you need help to quit drinking.
- Eat healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Ask if you need to be on a special diet. You may need to eat foods that reduce stomach acid. Stomach acid can get into your esophagus and cause the varices to break open and bleed.

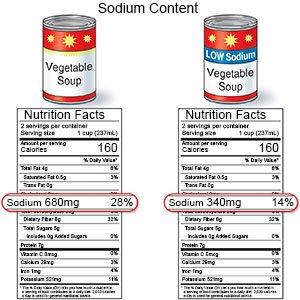
- Limit sodium (salt). You may need to decrease the amount of sodium you eat if you have swelling caused by fluid buildup. Fluid buildup can cause increased pressure in your veins. Sodium is found in table salt and salty foods such as canned foods, frozen foods, and potato chips.
- Drink liquids as directed. Too much liquid can increase the pressure in your veins. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
You may need to return for more treatment. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Esophageal Varices
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
