Deep Vein Thrombosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
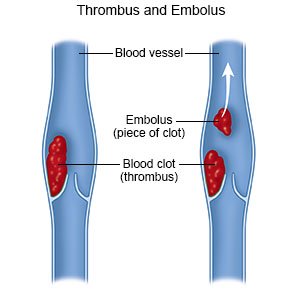
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein of the body. The DVT can break into smaller pieces and travel to your lungs and cause a blockage called a pulmonary embolism. A PE can become life-threatening. It is important to go to all follow-up appointments and to take blood thinners as directed. This is especially important if you were discharged home from the emergency department.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
Call your doctor or hematologist if:
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip does or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage a DVT:
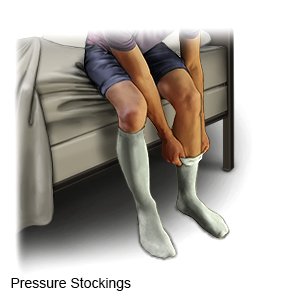
- Wear pressure stockings as directed. The stockings put pressure on your legs. This improves blood flow and helps prevent clots. Wear the stockings during the day. Do not wear them when you sleep.
- Elevate your legs above the level of your heart. Elevate your legs when you sit or lie down, as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop your legs on pillows or blankets to keep them elevated comfortably.

Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Prevent a DVT:
- Exercise regularly to help increase your blood flow. Walking is a good low-impact exercise. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you.

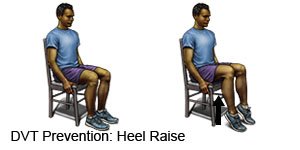
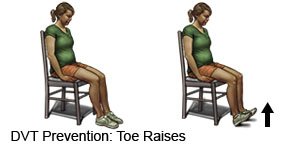
- Change your body position or move around often. Move and stretch in your seat several times each hour if you travel by car or work at a desk. In an airplane, get up and walk every hour. Move your legs by tightening and releasing your leg muscles while sitting. You can move your legs while sitting by raising and lowering your heels. Keep your toes on the floor while you do this. You can also raise and lower your toes while keeping your heels on the floor.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask him or her to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to manage your DVT. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Ask about birth control if you are a woman who takes the pill. A birth control pill increases the risk for PE in certain women. The risk is higher if you are also older than 35, smoke cigarettes, or have a blood clotting disorder. Talk to your healthcare provider about other ways to prevent pregnancy, such as a cervical cap or intrauterine device (IUD).
Follow up with your doctor or hematologist as directed:
You may need to come in regularly for scans to check for blood clots. Your blood may be checked to see how long it takes to clot. Your doctor or specialist will tell you if you need to have this test and how often to have it. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Deep Vein Thrombosis
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
