Breathing Techniques
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Why are breathing techniques important?
Breathing techniques help slow your breathing and lower anxiety. These techniques help you breathe in more oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Breathing techniques also help improve the function of your diaphragm and other muscles used for breathing. Practice breathing techniques at least 4 times per day. Practice them lying down, sitting, and walking.
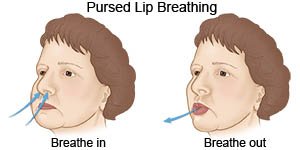
What is pursed-lip breathing?
Pursed-lip breathing is used to slow down your breathing rate. Breathe in through your nose for 2 seconds. Slowly breathe out through your mouth with your lips pursed for 4 seconds. Breathing out for 4 seconds helps get rid of carbon dioxide. You can also practice this breathing pattern while you bend, lift, climb stairs, or exercise. It slows down your breathing and helps move more air in and out of your lungs.
 |
- Pursed-lip breathing while walking: Inhale while taking 2 steps. Exhale through pursed lips while taking 4 steps. Stop and rest if you become short of breath.
- Pursed-lip breathing while climbing stairs: Inhale through your nose while standing still. Exhale through pursed lips while climbing 1 or 2 stairs. Repeat until you are at the top. Stop and rest if you become short of breath.
What is abdominal breathing?
Abdominal breathing is also called diaphragmatic breathing. This type of breathing helps control your breathing and strengthen your diaphragm. Your diaphragm is the main muscle you use when you breathe. You will be able to do this type of breathing during activities with practice.
- Lie on your back with pillows under your head and knees. If you cannot lie on your back, try sitting up in a chair.
- Put one hand on your abdomen and one on your upper chest.
- Breathe in slowly through your nose. Your abdomen should move out, and your chest should be as still as possible.
- Tighten, or pull, your stomach muscles in toward your back as you breathe out slowly through pursed lips. Your chest should continue to remain as still as possible.
What else can I do to breathe more easily?
- If prescribed, use oxygen as directed. You may need to use it when you do activities such as bathing, eating, and dressing.
- Sleep with your head elevated with many pillows or sleep in a recliner.
- Lean forward while sitting with your elbows on a table or on your knees.
- Relax by listening to soft music, getting a massage, or imagining a quiet place.
- Continue physical activity for strength and endurance. Learn how to plan your activities to conserve your energy.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
