Atrial Septal Defect Repair in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What do I need to know about an atrial septal defect (ASD) repair?
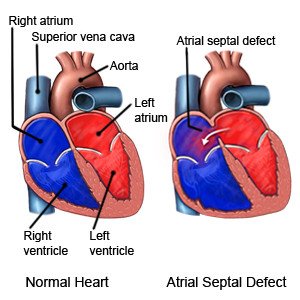
An ASD repair is surgery to close a hole in the septum (wall) between the upper chambers of your child's heart. The upper chambers are called the right atrium and the left atrium. An ASD repair is done through open heart surgery or a percutaneous (through the skin) procedure. The type of repair used depends on the size of the ASD and your child's age and symptoms.
 |
How can I help prepare my child for an ASD repair?
- Your child's provider will talk to you about how to prepare. Ask when and how to talk to your child about the surgery or procedure. If your child is old enough, talk to him or her and let him or her know what to expect. Explain that healthcare providers will make sure he or she is comfortable.
- Ask if there is information that explains anesthesia and the surgery to you and your child in more detail. Information given in a video or books may be available. Your child's provider may be able to take you and your child on a tour of the surgery or procedure room. Let your child pick a favorite blanket, stuffed animal, or toy to take with him or her to the hospital.
- Your child may need blood tests, a chest x-ray, an EKG, or an echocardiogram. The tests will help your child's provider plan for the repair. Your child may be able to donate his or her own blood. You, a family member, or a friend with the same blood type as your child may be able to donate blood for him or her.
- Your child's provider may tell you not to give your child anything to eat or drink after midnight before the procedure or surgery. The provider will tell you which medicines to give or not give your child. Your child will be given an antibiotic through his or her IV before the surgery or procedure. This will help prevent a bacterial infection. Tell the provider about any allergies your child has, including to antibiotics or anesthesia.
- Your child may need to take blood thinners if he or she having a procedure instead of surgery. Your child may start this medicine a few days before the procedure. Your child may instead be given a blood thinner through his or her IV on the day of the procedure. This will help prevent blood clots.
What will happen during a surgical ASD repair?
- Your child will be given general anesthesia to keep him or her asleep and free from pain during surgery. An IV may be placed in your child's wrist to monitor his or her blood pressure. A second IV may be placed in a large vein to monitor pressures in his or her heart. Your child's surgeon will make an incision in your child's chest. The surgeon will cut or spread your child's ribcage apart to reach his or her heart. Your child's heart may be connected to a bypass machine. This machine will pump blood to his or her body and keep blood out of his or her heart during surgery.
- Your child's surgeon will make an incision in your child's heart. The surgeon will close the ASD with stitches or a patch. The bypass machine will be stopped and blood will flow through your child's heart again. The incision in your child's heart will be closed with stitches. The surgeon may place a drain in your child's chest to remove air, blood, or fluid. The incision in your child's chest will be closed with stitches. A bandage will be placed over the incision.
What will happen during an ASD repair procedure?
- Your child may be given general anesthesia to keep him or her asleep and free from pain during the procedure. Your child may instead be given medicine to help him or her relax during the procedure. Your child will be awake with this medicine but should not feel pain during the procedure.
- Your child's provider will insert a catheter into a vein in your child's groin. The provider may use x-ray pictures to help guide the catheter to your child's heart. The provider will also use an echocardiogram to look at your child's heart during the procedure. The provider will insert a closure device into the ASD with the catheter. The provider will check to make sure the device is placed correctly and the ASD is closed. The provider will then remove the catheter and place a bandage over the incision.
What should I expect after an ASD repair?
- Healthcare providers will monitor your child's blood pressure, heartbeat, oxygen levels, and breathing. They will check your child's bandage for bleeding or swelling. Do not let your child get out of bed until healthcare providers say it is okay. Your child may need blood tests, chest x-rays, an EKG, or an echocardiogram before he or she leaves the hospital. These tests will make sure the ASD is closed and your child's heart is working correctly.
- Your child may need to stay in the hospital for a few days after surgery. Your child may spend the first 1 to 2 nights in the intensive care unit (ICU). He or she may have several drains and IVs, and be on a ventilator. A ventilator is a machine that gives your child oxygen and breathes for him or her. An endotracheal (ET) tube is put into his or her mouth or nose and attached to the ventilator. The ET tube may be removed when your child is awake and breathing well. Your child may need a blood transfusion to replace blood lost during surgery.
What can I do to help my child recover in the hospital?
- Do not give your child anything to eat until his or her healthcare provider says it is okay. He or she may be given ice chips at first. Then your child can have liquids such as water, broth, juice, and clear soft drinks. If his or her stomach does not get upset, he or she may be given soft foods, such as ice cream and applesauce. When your child can eat soft foods easily, he or she may slowly begin to eat solid foods.
- Help your child cough and deep breathe. This will decrease his or her risk for a lung infection. Have your child take deep breaths and cough 10 times each hour. Your child should hold a pillow tightly against his or her chest incision when he or she coughs. Tell your child to take a deep breath and hold it for as long as he or she can. Then tell him or her to let the air out and cough strongly.
- Help your child get out of bed when healthcare providers say it is okay. Help your child get out of bed to sit in a chair or take short walks. These activities will help prevent your child from getting a blood clot.
What are the risks of an ASD repair?
Your child may bleed more than expected or get an infection. Your child may get a blood clot in his or her leg, arm, heart, lungs, or brain. Fluid may build up around your child's heart or lungs and make it hard for him or her to breathe. Your child's heart muscle or valves may be damaged during surgery. Your child may have an irregular heartbeat or develop heart failure. The devices used to close the ASD may move out of place. Your child may need another surgery or procedure to fix this.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
