Acute Coronary Syndrome
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
is sudden decreased blood flow to your heart. This causes a lack of oxygen to your heart and can lead to unstable angina or a heart attack. ACS is caused by narrowing of the blood vessels that carry blood and oxygen to the heart muscle. Unstable angina occurs when part of the artery is blocked, or a clot gets stuck and then breaks free. A heart attack occurs when the narrowed artery becomes totally blocked, usually by a blood clot or plaque.
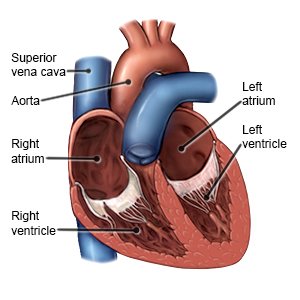 |
Common signs and symptoms of ACS:
- Chest pain or discomfort, including squeezing, crushing, pressure, tightness, or heaviness
- Pain or discomfort in your arms, shoulders, neck, back, or jaw
- Heartburn, nausea, or vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating, weakness, or fainting
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
Call your doctor if:
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines used to treat ACS:
- ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers keep your blood vessels open and help your heart pump strongly and regularly.
- Cholesterol medicine helps lower the amount of plaque buildup in your arteries.
- Blood pressure medicine helps decrease the strain on your heart.
- Pain medicine helps decrease your pain and slows your heart rate.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip does or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Antiplatelets , such as aspirin, help prevent blood clots. Take your antiplatelet medicine exactly as directed. These medicines make it more likely for you to bleed or bruise. If you are told to take aspirin, do not take acetaminophen or ibuprofen instead.
- Thrombolytics help break apart and dissolve clots.
- Nitroglycerin opens the arteries to your heart so the heart gets more oxygen. It is given as a pill, IV, or topical patch or paste.
Other ways ACS may be treated:
In addition to medicines, your healthcare provider may recommend a procedure or surgery. He or she can explain the benefits and risks of each treatment. The following are commonly used to treat ACS:
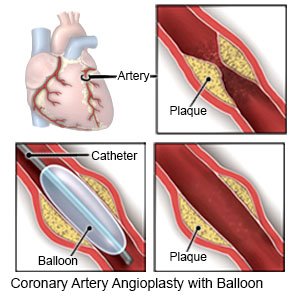
- An angioplasty is a procedure to open an artery blocked by plaque. A tube with a balloon on the end is threaded into the blocked artery. The balloon is filled with liquid, which presses the plaque against the artery wall. This opens the artery so blood can flow through it.
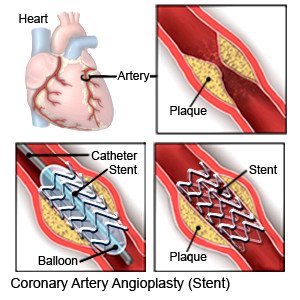
- Coronary intravascular stent placement is usually done during an angioplasty. A stent is a hollow tube made of wire mesh that is put into a coronary artery. The stent supports the artery and keeps it open so blood can flow through it.
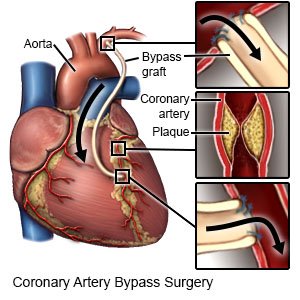
- Coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) is open-heart surgery. A graft is used from another artery in your body to replace the blocked artery.
- Cardiac rehab is a program that teaches you how to live a more heart-healthy lifestyle, including nutrition and exercise.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Manage or prevent ACS:
ACS cannot always be prevented. The following can help you manage ACS and may help prevent it if you have certain risk factors:
- Eat heart-healthy foods. Include fresh fruits and vegetables in your meal plan. Choose low-fat foods, such as skim or 1% fat milk, low-fat cheese and yogurt, fish, chicken (without skin), and lean meats. Eat two 4-ounce servings of fish high in omega-3 fats each week, such as salmon, fresh tuna, and herring.
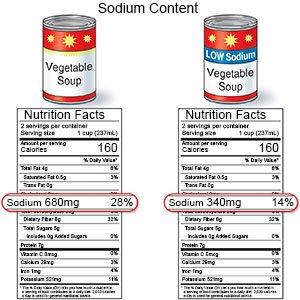
- Limit sodium (salt) as directed. Avoid foods that are high in sodium, such as canned foods, potato chips, salty snacks, and cold cuts. If you add salt when you cook, do not add more salt at the table.
- Ask about activity. Your healthcare provider will tell you which activities to limit or avoid. Ask when you can drive, return to work, and have sex. Ask about the best physical activity plan for you.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask him or her to help you create a safe weight loss plan, if needed.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause heart and lung damage. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. Your healthcare provider can tell you which vaccines you need, and when to get them. The following vaccines help prevent certain diseases that can put more stress on your heart:
- The influenza (flu) vaccine is given each year. Get a flu vaccine as soon as recommended, usually in September or October.
- The pneumonia vaccine is usually given every 5 years. Your healthcare provider may recommend the pneumonia vaccine if you are 65 or older.
- COVID-19 vaccines are given to adults as a shot. At least 1 dose of an updated vaccine is recommended for all adults. COVID-19 vaccines are updated throughout the year. Adults 65 or older need a second dose of updated vaccine at least 4 months after the first dose. Your healthcare provider can help you schedule all needed doses as updated vaccines become available.
 |
Follow up with your doctor or cardiologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Heart / High Blood Pressure Medications with Alcohol
- Understanding Opioid (Narcotic) Pain Medications
Treatment options
- Medications for Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Medications for Angina
- Medications for Heart Attack
- Medications for Ischemic Heart Disease
- Medications for Prinzmetal's Angina
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
